
Cochran-Armitage test for trend
Encyclopedia
The Cochran-Armitage test for trend, named for William Cochran
and Peter Armitage
, is used in categorical data
analysis when the aim is to assess for the presence of an association
between a variable with two categories and a variable with k categories. It modifies the chi-squared test to incorporate a suspected ordering in the effects of the k categories of the second variable. For example, doses of a treatment can be ordered as 'low', 'medium', and 'high', and we may suspect that the treatment benefit cannot become smaller as the dose increases. The trend test is often used as a genotype
-based test for case-control genetic
association studies
.
. For example, if k = 3 we have
This table can be completed with the marginal totals of the two variables
where R1 = N11 + N12 + N13, and
C1 = N11 + N21, etc.
The trend test statistic
is
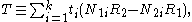
where the ti are weights, and the difference N1iR2 −N2iR1 can be seen as the difference between N1i and N2i after reweighting the rows to have the same total.
The hypothesis of no association (the null hypothesis
) can be expressed as:
 .
.
Assuming this holds, then, using iterated expectation,

The variance can be computed by decomposition, yielding
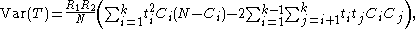
and as a large sample approximation,
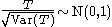 .
.
The weights ti can be chosen such that the trend test becomes locally most powerful
for detecting particular types of associations. For example, if k = 3 and we suspect that B = 1 and B = 2 have similar frequencies (within each row), but that B = 3 has a different frequency, then the weights t = (1,1,0) should be used. If we suspect a linear trend in the frequencies, then the weights t = (0,1,2) should be used. These weights are also often used when the frequencies are suspected to change monotonically with B, even if the trend is not necessarily linear.
than the chi-squared test when the suspected trend is correct, but the ability to detect unsuspected trends is sacrificed. This is an example of a general technique of directing hypothesis tests toward narrow alternatives. The trend test exploits the suspected effect direction to increase power, but this does not affect the sampling distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis
. Thus, the suspected trend in effects is not an assumption that must hold in order for the test results to be meaningful.
s at some locus
, and we refer to these as aa, Aa and AA. The distribution of genotype counts can be put in a 2 × 3 contingency table. For example, consider the following data, in which the genotype frequencies vary linearly in the cases and are constant in the controls:
In genetics applications, the weights are selected according to the suspected mode of inheritance
. For example, in order to test whether allele
a is dominant over allele A, the choice t = (1, 1, 0) is locally optimal. To test whether allele a is recessive to allele A, the optimal choice is t = (0, 0, 1). To test whether alleles a and A are codominant, the choice t = (0, 1, 2) is locally optimal. For complex diseases, the underlying genetic model is often unknown. In genome-wide association studies
, the additive (or codominant) version of the test is often used.
In the numerical example, the standardized test statistics for various weight vectors are
and the Pearson chi-squared test gives a standardized test statistic of 2. Thus, we obtain a stronger significance level if the weights corresponding to additive (codominant) inheritance are used. Note that for the significance level to give a p-value
with the usual probabilistic interpretation, the weights must be specified before examining the data, and only one set of weights may be used.
William Gemmell Cochran
William Gemmell Cochran was a prominent statistician; he was born in Scotland but spent most of his life in the United States....
and Peter Armitage
Peter Armitage
Peter Armitage is a statistician specialising in medical statistics.Peter Armitage attended Huddersfield College and went on to read mathematics at Trinity College, Cambridge. Armitage belonged to the generation of mathematicians who came to maturity in the Second World War...
, is used in categorical data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
analysis when the aim is to assess for the presence of an association
Association (statistics)
In statistics, an association is any relationship between two measured quantities that renders them statistically dependent. The term "association" refers broadly to any such relationship, whereas the narrower term "correlation" refers to a linear relationship between two quantities.There are many...
between a variable with two categories and a variable with k categories. It modifies the chi-squared test to incorporate a suspected ordering in the effects of the k categories of the second variable. For example, doses of a treatment can be ordered as 'low', 'medium', and 'high', and we may suspect that the treatment benefit cannot become smaller as the dose increases. The trend test is often used as a genotype
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
-based test for case-control genetic
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
association studies
Genetic association
Genetic association is the occurrence, more often than can be readily explained by chance, of two or more traits in a population of individuals, of which at least one trait is known to be genetic....
.
Introduction
The trend test is applied when the data take the form of a 2 × k contingency tableContingency table
In statistics, a contingency table is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the frequency distribution of the variables...
. For example, if k = 3 we have
| B=1 | B=2 | B=3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A=1 | N11 | N12 | N13 |
| A=2 | N21 | N22 | N23 |
This table can be completed with the marginal totals of the two variables
| B=1 | B=2 | B=3 | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A=1 | N11 | N12 | N13 | R1 |
| A=2 | N21 | N22 | N23 | R2 |
| Sum | C1 | C2 | C3 | N |
where R1 = N11 + N12 + N13, and
C1 = N11 + N21, etc.
The trend test statistic
Test statistic
In statistical hypothesis testing, a hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, which is a function of the sample; it is considered as a numerical summary of a set of data that...
is
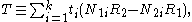
where the ti are weights, and the difference N1iR2 −N2iR1 can be seen as the difference between N1i and N2i after reweighting the rows to have the same total.
The hypothesis of no association (the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
) can be expressed as:
 .
.Assuming this holds, then, using iterated expectation,

The variance can be computed by decomposition, yielding
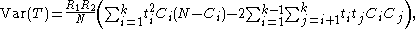
and as a large sample approximation,
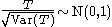 .
.The weights ti can be chosen such that the trend test becomes locally most powerful
Statistical power
The power of a statistical test is the probability that the test will reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually false . The power is in general a function of the possible distributions, often determined by a parameter, under the alternative hypothesis...
for detecting particular types of associations. For example, if k = 3 and we suspect that B = 1 and B = 2 have similar frequencies (within each row), but that B = 3 has a different frequency, then the weights t = (1,1,0) should be used. If we suspect a linear trend in the frequencies, then the weights t = (0,1,2) should be used. These weights are also often used when the frequencies are suspected to change monotonically with B, even if the trend is not necessarily linear.
Interpretation and role
The trend test will have higher powerStatistical power
The power of a statistical test is the probability that the test will reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually false . The power is in general a function of the possible distributions, often determined by a parameter, under the alternative hypothesis...
than the chi-squared test when the suspected trend is correct, but the ability to detect unsuspected trends is sacrificed. This is an example of a general technique of directing hypothesis tests toward narrow alternatives. The trend test exploits the suspected effect direction to increase power, but this does not affect the sampling distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
. Thus, the suspected trend in effects is not an assumption that must hold in order for the test results to be meaningful.
Application to genetics
Suppose that there are three possible genotypeGenotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
s at some locus
Locus (genetics)
In the fields of genetics and genetic computation, a locus is the specific location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome. A variant of the DNA sequence at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a genetic map...
, and we refer to these as aa, Aa and AA. The distribution of genotype counts can be put in a 2 × 3 contingency table. For example, consider the following data, in which the genotype frequencies vary linearly in the cases and are constant in the controls:
| Genotype aa | Genotype Aa | Genotype AA | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | 20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
| Cases | 10 | 20 | 30 | 60 |
| Sum | 30 | 40 | 50 | 120 |
In genetics applications, the weights are selected according to the suspected mode of inheritance
Heredity
Heredity is the passing of traits to offspring . This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes predisposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. Through heredity, variations exhibited by individuals can accumulate and cause some species to evolve...
. For example, in order to test whether allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
a is dominant over allele A, the choice t = (1, 1, 0) is locally optimal. To test whether allele a is recessive to allele A, the optimal choice is t = (0, 0, 1). To test whether alleles a and A are codominant, the choice t = (0, 1, 2) is locally optimal. For complex diseases, the underlying genetic model is often unknown. In genome-wide association studies
Genome-wide association study
In genetic epidemiology, a genome-wide association study , also known as whole genome association study , is an examination of many common genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait...
, the additive (or codominant) version of the test is often used.
In the numerical example, the standardized test statistics for various weight vectors are
| Weights | Standardized test statistic |
|---|---|
| 1,1,0 | 1.85 |
| 0,1,1 | -2.1 |
| 0,1,2 | -2.3 |
and the Pearson chi-squared test gives a standardized test statistic of 2. Thus, we obtain a stronger significance level if the weights corresponding to additive (codominant) inheritance are used. Note that for the significance level to give a p-value
P-value
In statistical significance testing, the p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one that was actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. One often "rejects the null hypothesis" when the p-value is less than the significance level α ,...
with the usual probabilistic interpretation, the weights must be specified before examining the data, and only one set of weights may be used.

