
Cluster-weighted modeling
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, cluster-weighted modeling (CWM) is an algorithm-based approach to non-linear prediction of outputs (dependent variables
) from inputs (independent variables
) based on density estimation
using a set of models (clusters) that are each notionally appropriate in a sub-region of the input space. The overall approach works in jointly input-output space and an initial version was proposed by Neil Gershenfeld
.
providing an indication of uncertainty.
The important step of the modeling is that p(y|x) is assumed to take the following form, as a mixture model
:
where n is the number of clusters and {wj} are weights that sum to one. The functions pj(y,x) are joint probability density functions that relate to each of the n clusters. These functions are modeled using a decomposition into a conditional and a marginal density
: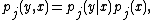
where:
In the same way as for regression analysis
, it will be important to consider preliminary data transformation
s as part of the overall modeling strategy if the core components of the model are to be simple regression models for the cluster-wise condition densities, and normal distributions for the cluster-weighting densities pj(x).
The original form proposed by Gershenfeld describes two innovations:
CWM can be used to classify media in printer applications, using at least two parameters to generate an output that has a joint dependency on the input parameters.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, cluster-weighted modeling (CWM) is an algorithm-based approach to non-linear prediction of outputs (dependent variables
Dependent and independent variables
The terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
) from inputs (independent variables
Dependent and independent variables
The terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
) based on density estimation
Density estimation
In probability and statistics,density estimation is the construction of an estimate, based on observed data, of an unobservable underlying probability density function...
using a set of models (clusters) that are each notionally appropriate in a sub-region of the input space. The overall approach works in jointly input-output space and an initial version was proposed by Neil Gershenfeld
Neil Gershenfeld
Neil Gershenfeld is a professor at MIT and the head of MIT's Center for Bits and Atoms, a sister lab spun out of the popular MIT Media Lab. His research interests are mainly in interdisciplinary studies involving physics and computer science, in such fields as quantum computing, nanotechnology,...
.
Basic form of model
The procedure for cluster-weighted modeling of an input-output problem can be outlined as follows. In order to construct predicted values for an output variable y from an input variable x, the modeling and calibration procedure arrives at a joint probability density function, p(y,x). Here the "variables" might be uni-variate, multivariate or time-series. For convenience, any model parameters are not indicated in the notation here and several different treatments of these are possible, including setting them to fixed values as a step in the calibration or treating them using a Bayesian analysis. The required predicted values are obtained by constructing the conditional probability density p(y|x) from which the prediction using the conditional expected value can be obtained, with the conditional varianceConditional variance
In probability theory and statistics, a conditional variance is the variance of a conditional probability distribution. Particularly in econometrics, the conditional variance is also known as the scedastic function or skedastic function...
providing an indication of uncertainty.
The important step of the modeling is that p(y|x) is assumed to take the following form, as a mixture model
Mixture model
In statistics, a mixture model is a probabilistic model for representing the presence of sub-populations within an overall population, without requiring that an observed data-set should identify the sub-population to which an individual observation belongs...
:

where n is the number of clusters and {wj} are weights that sum to one. The functions pj(y,x) are joint probability density functions that relate to each of the n clusters. These functions are modeled using a decomposition into a conditional and a marginal density
Marginal distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the marginal distribution of a subset of a collection of random variables is the probability distribution of the variables contained in the subset. The term marginal variable is used to refer to those variables in the subset of variables being retained...
:
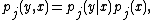
where:
- pj(y|x) is a model for predicting y given x, and given that the input-output pair should be associated with cluster j on the basis of the value of x. This model might be a regression modelRegression analysisIn statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
in the simplest cases.
- pj(x) is formally a density for values of x, given that the input-output pair should be associated with cluster j. The relative sizes of these functions between the clusters determines whether a particular value of x is associated with any given cluster-center. This density might be a Gaussian function centered at a parameter representing the cluster-center.
In the same way as for regression analysis
Regression analysis
In statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
, it will be important to consider preliminary data transformation
Data transformation
In metadata and data warehouse, a data transformation converts data from a source data format into destination data.Data transformation can be divided into two steps:...
s as part of the overall modeling strategy if the core components of the model are to be simple regression models for the cluster-wise condition densities, and normal distributions for the cluster-weighting densities pj(x).
General versions
The basic CWM algorithm gives a single output cluster for each input cluster. However, CWM can be extended to multiple clusters which are still associated with the same input cluster. Each cluster in CWM is localized to a Gaussian input region, and this contains its own trainable local model. It is recognized as a versatile inference algorithm which provides simplicity, generality, and flexibility; even when a feedforward layered network might be preferred, it is sometimes used as a "second opinion" on the nature of the training problem.The original form proposed by Gershenfeld describes two innovations:
- Enabling CWM to work with continuous streams of data
- Addressing the problem of local minima encountered by the CWM parameter adjustment process
CWM can be used to classify media in printer applications, using at least two parameters to generate an output that has a joint dependency on the input parameters.

