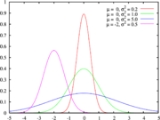
Mixture model
Overview
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, a mixture model is a probabilistic model for representing the presence of sub-populations within an overall population, without requiring that an observed data-set should identify the sub-population to which an individual observation belongs. Formally a mixture model corresponds to the mixture distribution that represents the probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of observations in the overall population. However, while problems associated with "mixture distributions" relate to deriving the properties of the overall population from those of the sub-populations, "mixture models" are used to make statistical inference
Statistical inference
In statistics, statistical inference is the process of drawing conclusions from data that are subject to random variation, for example, observational errors or sampling variation...
s about the properties of the sub-populations given only observations on the pooled population, without sub-population-identity information.
Some ways of implementing mixture models involve steps that do attribute postulated sub-population-identities to individual observations (or weights towards such sub-populations), in which case these can be regarded as a types of unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning
In machine learning, unsupervised learning refers to the problem of trying to find hidden structure in unlabeled data. Since the examples given to the learner are unlabeled, there is no error or reward signal to evaluate a potential solution...
or clustering procedures.

