Climate of Adelaide
Encyclopedia
Adelaide has a hot Mediterranean climate
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
(Köppen climate classification
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
Csa), which generally means mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Of all the Australian capital cities, Adelaide is the driest. Rainfall is unreliable, light and infrequent throughout summer. The average in January and February is around 20 millimetres (0.8 inches) but completely rainless months are by no means uncommon and in 1893 sixty-nine days passed without measurable rainfall. In contrast, the winter has fairly reliable rainfall with June being the wettest month of the year, averaging around 80 mm.
In the summer, maximum average is 29 °C (84.2 °F) but there is considerable variation and Adelaide can usually expect around 3 days a year when the daytime temperature is 40 °C or above. In January 1939, the temperature reached 46.1 °C (115 °F) twice. From 3 March 2008, Adelaide recorded 15 consecutive days of temperatures over 35 °C, again a record for an Australian capital. In winter from June to August, maximum average is 15–16 °C (59–60.8 F) and minimum is usually around 8 °C (46.4 °F). Frost
Frost
Frost is the solid deposition of water vapor from saturated air. It is formed when solid surfaces are cooled to below the dew point of the adjacent air as well as below the freezing point of water. Frost crystals' size differ depending on time and water vapour available. Frost is also usually...
s are common in the valleys of the Adelaide Hills
Adelaide Hills
The Adelaide Hills are part of the Mount Lofty Ranges, east of the city of Adelaide in the state of South Australia. It is unofficially centred on the largest town in the area, Mount Barker, which has a population of around 29,000 and is also one of Australia's fastest growing towns.- History :The...
, but rare elsewhere, with the most notable occurrences having occurred in July 1908 and July 1982. There is usually no appreciable snow
Snow
Snow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
fall in Adelaide, except on rare occasions at Mount Lofty
Mount Lofty
Mount Lofty is the highest point in the Mount Lofty Ranges. It is located about 15km east of the centre of the city of Adelaide in South Australia and gives unrivalled panoramic views of the city and the Adelaide plains and foothills. It was first climbed by a European when explorer Collet Barker...
and in some places in the Adelaide Hills
Adelaide Hills
The Adelaide Hills are part of the Mount Lofty Ranges, east of the city of Adelaide in the state of South Australia. It is unofficially centred on the largest town in the area, Mount Barker, which has a population of around 29,000 and is also one of Australia's fastest growing towns.- History :The...
.
Recorded extremes:
- Hottest temperature – 12 January 1939, 46.1 °C (115 °F)
- Coldest temperature – 8 June 1982, -0.4 °C
- Wettest month – June 1916, 217.9 mm (8.6 in)
- Hottest Minimum- 33.9°C, 28- 29 January 2009
(Records from West Tce weather station 1839-1977 & Kent Town weather station 1977-present)
2008 Heatwave (2- 17 March 2008)
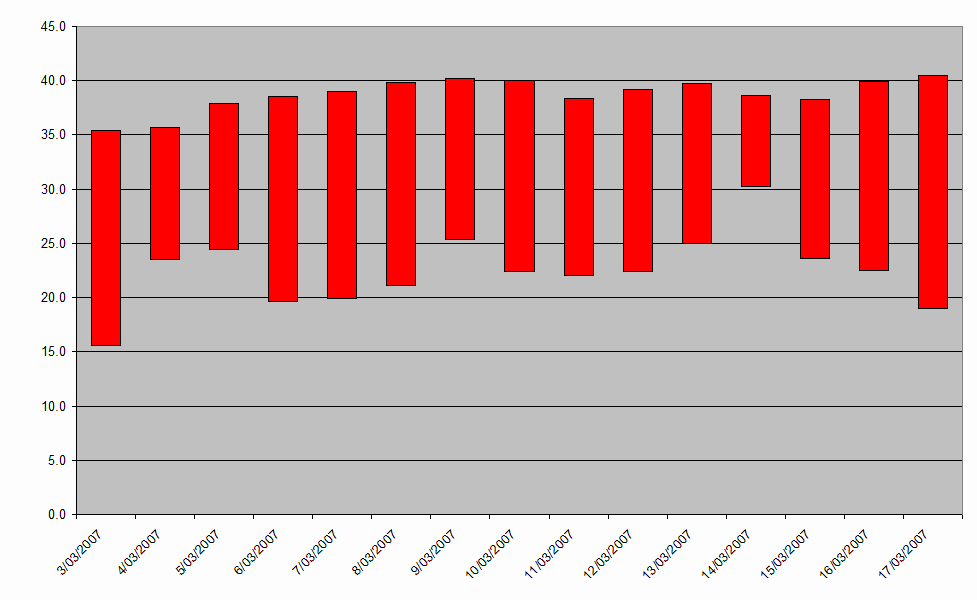
2009 Heatwave (26 January 2009- 3 February)
On 25 January 2009, the city was affected by the 2009 Southern Australia heat wave, due to a virtually stand-still high pressure system that dragged northerly air streams towards the city. The heatwave broke numerous records and has affected all of south-eastern Australia, including MelbourneMelbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
, another southern Australian city, cancelling outdoor games during the 2009 Australian Open
2009 Australian Open
The 2009 Australian Open was a tennis tournament played on outdoor hard courts. It was the 97th edition of the Australian Open, and the first Grand Slam event of the year. It took place at the Melbourne Park in Melbourne, Australia, from 19 January through 1 February 2009. The 2009 men's...
.
The heatwave commenced on Australia Day 2009 with temperatures above 35 degrees Celsius. From 27 January onward the temperature has soared above 40 degrees for 3 consecutive days with another 3 days planned and no temperatures below 40 until at least 2 February where the temperature is expected to reach 39 degrees Celsius. This would be the longest straight run of 40 degrees Celsius plus temperatures in Australian history.
On 28 January, the third day into the heatwave, the temperature soared to 45.7 degrees Celsius, making it the 3rd hottest day on record in Adelaide. On that same night, the temperature only dipped to 33.9 degrees Celsius making it the highest minimum temperature on South Australian record.
November 2009 Heatwave
The November 2009 heat wave was a heat waveHeat wave
A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity. There is no universal definition of a heat wave; the term is relative to the usual weather in the area...
that occurred in the Australian states of South Australia
South Australia
South Australia is a state of Australia in the southern central part of the country. It covers some of the most arid parts of the continent; with a total land area of , it is the fourth largest of Australia's six states and two territories.South Australia shares borders with all of the mainland...
, Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
and southern New South Wales
New South Wales
New South Wales is a state of :Australia, located in the east of the country. It is bordered by Queensland, Victoria and South Australia to the north, south and west respectively. To the east, the state is bordered by the Tasman Sea, which forms part of the Pacific Ocean. New South Wales...
. Daily maximum temperatures during the heat wave were roughly 10 °C (18 °F) above average in many locations. Capital cities Adelaide
Adelaide
Adelaide is the capital city of South Australia and the fifth-largest city in Australia. Adelaide has an estimated population of more than 1.2 million...
and Melbourne
Melbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
recorded temperatures over 35 °C (95 °F), and some regional towns recorded temperatures above 40 °C (104 °F). Above average temperatures in the region began in late October and persisted until mid-November 2009.
- 10 Consecutive days over 30 °C (86 °F)
- 8 Consecutive days over 35 °C (95 °F) – New record set on 12 November 2009 and broken again on 13 November after breaking the previous 4 consecutive days over 35 °C (95 °F) record which was set in 1894.
- 6 Consecutive days over 38 °C (100.4 °F) – New record set after breaking the previous 3 consecutive days over 38 °C (100.4 °F) record which was set in 1888, 1922 and 1984.
- Highest November temperature ever recorded – 43 °C (109.4 °F) 19 November 2009 at 4:32pm ACDT. Previous record was 42 °C (107.6 °F) recorded on 13 November 1993.

