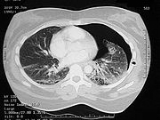
Chest trauma
Encyclopedia
Chest trauma is a serious injury
of the chest
. Thoracic trauma is a common cause of significant disability and mortality, the leading cause of death from physical trauma
after head and spinal cord injury. Blunt thoracic injuries are the primary or a contributing cause of about a quarter of all trauma-related deaths. The mortality rate
is about 10%. Chest injuries were first described in detail in around 1600 BC in the ancient Egyptian Edwin Smith Papyrus
.
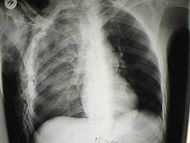 Chest trauma can be classified as blunt
Chest trauma can be classified as blunt
or penetrating
. Blunt and penetrating injuries have different pathophysiologies
and clinical courses.
Specific types of chest trauma include:
and mechanical ventilation
and chest tube
insertion. Diagnosis of blunt injuries may be more difficult and require additional investigations such as CT scanning. Penetrating injuries often require surgery
, and complex investigations are usually not needed to come to a diagnosis. Patients with penetrating trauma may deteriorate rapidly, but may also recover much faster than patients with blunt injury.
Injury
-By cause:*Traumatic injury, a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident*Other injuries from external physical causes, such as radiation injury, burn injury or frostbite*Injury from infection...
of the chest
Chest
The chest is a part of the anatomy of humans and various other animals. It is sometimes referred to as the thorax or the bosom.-Chest anatomy - Humans and other hominids:...
. Thoracic trauma is a common cause of significant disability and mortality, the leading cause of death from physical trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
after head and spinal cord injury. Blunt thoracic injuries are the primary or a contributing cause of about a quarter of all trauma-related deaths. The mortality rate
Mortality rate
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
is about 10%. Chest injuries were first described in detail in around 1600 BC in the ancient Egyptian Edwin Smith Papyrus
Edwin Smith papyrus
The Edwin Smith Papyrus is an Ancient Egyptian medical text and the oldest known surgical treatise on trauma. It dates to Dynasties 16-17 of the Second Intermediate Period in Ancient Egypt, ca. 1500 BCE. The Edwin Smith papyrus is unique among the four principal medical papyri in existencethat...
.
Classification

Blunt trauma
In medical terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma...
or penetrating
Penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
. Blunt and penetrating injuries have different pathophysiologies
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology is the study of the changes of normal mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions, either caused by a disease, or resulting from an abnormal syndrome...
and clinical courses.
Specific types of chest trauma include:
- Injuries to the chest wall
- Chest wall contusions or hematomaHematomaA hematoma, or haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise...
s. - Rib fractureRib fractureA rib fracture is a break or fracture in one or more of the bones making up the rib cage.The first rib is rarely fractured because of its protected position behind the clavicle . However, if it is broken serious damage can occur to the brachial plexus of nerves and the subclavian vessels...
s - Flail chestFlail chestA flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks under extreme stress and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. It occurs when multiple adjacent ribs are broken in multiple places, separating a segment, so a part of the chest wall...
- Sternal fractureSternal fractureA sternal fracture is a fracture of the sternum , located in the center of the chest. The injury, which occurs in 5–8% of people who experience significant blunt chest trauma, may occur in vehicle accidents, when the still-moving chest strikes a steering wheel or dashboard or is injured by a...
s - FractureFractureA fracture is the separation of an object or material into two, or more, pieces under the action of stress.The word fracture is often applied to bones of living creatures , or to crystals or crystalline materials, such as gemstones or metal...
s of the shoulder girdle
- Chest wall contusions or hematoma
- Pulmonary injury (injury to the lung) and injuries involving the pleural space
- Pulmonary contusionPulmonary contusionA pulmonary contusion is a contusion of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels...
- Pulmonary lacerationPulmonary lacerationA pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut. An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung, while pulmonary contusion does not...
- PneumothoraxPneumothoraxPneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity of the chest between the lung and the chest wall. It may occur spontaneously in people without chronic lung conditions as well as in those with lung disease , and many pneumothoraces occur after physical trauma to the chest, blast...
- HemothoraxHemothoraxA hemothorax is a condition that results from blood accumulating in the pleural cavity.-Cause and presentation:Its cause is usually traumatic, from a blunt or penetrating injury to the thorax, resulting in a rupture of the serous membrane either lining the thorax or covering the lungs...
- HemopneumothoraxHemopneumothoraxHemopneumothorax, or haemopneumothorax, is a medical term describing the combination of two conditions: pneumothorax, or air in the chest cavity, and hemothorax , or blood in the chest cavity....
- Pulmonary contusion
- Injury to the airways
- Tracheobronchial tear
- Cardiac injury
- Pericardial tamponade
- Myocardial contusion
- Blood vessel injuries
- Traumatic aortic ruptureTraumatic aortic ruptureTraumatic aortic rupture, also called traumatic aortic disruption or transection, is a condition in which the aorta, the largest artery in the body, is torn or ruptured as the result of trauma. The condition is frequently fatal due to the profuse bleeding that results from the rupture...
, thoracic aorta injuryThoracic aorta injuryInjury of the thoracic aorta refers to any injury which affects the portion of the aorta which lies within the chest cavity. Injuries of the thoracic aorta are usually the result of physical trauma; however, they can also be the result of a pathological process...
, aortic dissectionAortic dissectionAortic dissection occurs when a tear in the inner wall of the aorta causes blood to flow between the layers of the wall of the aorta and force the layers apart. The dissection typically extends anterograde, but can extend retrograde from the site of the intimal tear. Aortic dissection is a medical...
- Traumatic aortic rupture
- And injuries to other structures within the torso
- Esophageal injury (Boerhaave syndromeBoerhaave syndromeEsophageal rupture is rupture of the esophageal wall due to vomiting. 56% of esophageal perforations are iatrogenic, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal surgery...
) - Diaphragm injury
- Esophageal injury (Boerhaave syndrome
Diagnosis
Most blunt injuries are managed with relatively simple interventions like tracheal intubationTracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs...
and mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation
In medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
and chest tube
Chest tube
A chest tube is a flexible plastic tube that is inserted through the side of the chest into the pleural space. It is used to remove air or fluid , or pus from the intrathoracic space...
insertion. Diagnosis of blunt injuries may be more difficult and require additional investigations such as CT scanning. Penetrating injuries often require surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, and complex investigations are usually not needed to come to a diagnosis. Patients with penetrating trauma may deteriorate rapidly, but may also recover much faster than patients with blunt injury.

