
Pulmonary laceration
Encyclopedia
A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung
tissue is torn or cut. An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion
, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung, while pulmonary contusion does not. Pulmonary laceration is commonly caused by penetrating trauma
but may also result from forces involved in blunt trauma
such as shear stress
. A cavity filled with blood, air, or both can form. The injury is diagnosed when collections of air or fluid are found on a CT scan of the chest. Surgery may be required to stitch the laceration, to drain blood, or even to remove injured parts of the lung. The injury commonly heals quickly with few problems if it is given proper treatment; however it may be associated with scarring of the lung or other complications.
but may also be caused by blunt trauma
; broken ribs
may perforate the lung, or the tissue may be torn due to shearing force
s that result from different rates of acceleration or deceleration of different tissues of the lung. Violent compression of the chest can cause lacerations by rupturing or shearing the lung tissue. Pulmonary laceration may result from blunt and penetrating forces that occur in the same injury and may be associated with pulmonary contusion. Lacerations of the lung tissue can also occur by compression of the alveoli against the ribs or spine. As with contusions, pulmonary lacerations usually occur near solid structures in the chest such as ribs. Pulmonary laceration is suspected when rib fractures are present.
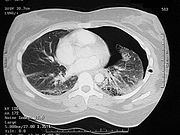 A pulmonary laceration can cause air to leak out of the lacerated lung and into the pleural space
A pulmonary laceration can cause air to leak out of the lacerated lung and into the pleural space
, if the laceration goes through to it. Pulmonary laceration invariably results in pneumothorax
(due to torn airway
s), hemothorax
(due to torn blood vessel
s), or a hemopneumothorax
(with both blood and air in the chest cavity). Unlike hemothoraces that occur due to pulmonary contusion, those due to lung laceration may be large and long lasting. However, the lungs do not usually bleed very much because the blood vessels involved are small and the pressure within them is low. Therefore, pneumothorax is usually more of a problem than hemothorax. A pneumothorax may form or be turned into a tension pneumothorax by mechanical ventilation
, which may force air out of the tear in the lung.
The laceration may also close up by itself, which can cause it to trap blood and potentially form a cyst
or hematoma
. Because the lung is elastic, the tear forms a round cyst called a traumatic air cyst that may be filled with air, blood, or both and that usually shrinks over a period of weeks or months. Lacerations that are filled with air are called pneumatocele
s, and those that are filled with blood are called pulmonary hematoma
s. In some cases, both pneumatoceles and hematomas exist in the same injured lung. A pneumatocele can become enlarged, for example when the patient is mechanically ventilated or has acute respiratory distress syndrome
, in which case it may not go away for months. Pulmonary hematomas take longer to heal than simple pneumatoceles and commonly leave the lungs scarred.
Over time, the walls of lung lacerations tend to grow thicker due to edema and bleeding at the edges.
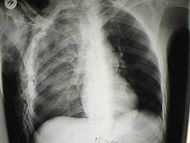 Pulmonary laceration may not be visible using chest X-ray
Pulmonary laceration may not be visible using chest X-ray
because an associated pulmonary contusion
or hemorrhage may mask it. As the lung contusion clears (usually within two to four days), lacerations begin to become visible on chest X-ray. CT scanning is more sensitive and better at detecting pulmonary laceration than X-ray
s are, and often reveals multiple lacerations in cases where chest X-ray showed only a contusion. Before CT scanning was widely available, pulmonary laceration was considered unusual because it was not common to find with X-ray alone. On a CT scan, pulmonary lacerations show up in a contused area of the lung, typically appearing as cavities filled with air or fluid that usually have a round or ovoid shape due to the lung's elasticity.
Hematomas appear on chest radiographs as smooth masses that are round or ovoid in shape. Like lacerations, hematomas may initially be hidden on X-ray by lung contusions, but they become more apparent as the contusion begins to heal. Pneumatoceles have a similar shape to that of hematomas but have thin, smooth walls. Lacerations may be filled completely with blood, completely with air, or partially with both. Lacerations filled with both blood and air display a distinctive air-fluid level. A single laceration may occur by itself, or many may be present, creating an appearance like Swiss cheese in the radiography of the lung.
Pulmonary laceration is usually accompanied by hemoptysis
(coughing up blood or of blood-stained sputum).
Thoracoscopy
may be used in both diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary laceration.
A healing laceration may resemble a pulmonary nodule on radiographs, but unlike pulmonary nodules, lacerations decrease in size over time on radiographs.
can be used to remove blood and air from the chest cavity. About 5% of cases require surgery, called thoracotomy
. Thoracotomy is especially likely to be needed if a lung fails to re-expand; if pneumothorax, bleeding, or coughing up blood persist; or in order to remove clotted blood from a hemothorax. Surgical treatment includes suturing, stapling, oversewing, and wedging out of the laceration. Occasionally, surgeons must perform a lobectomy
, in which a lobe of the lung is removed, or a pneumonectomy
, in which an entire lung is removed.
red. Small pulmonary lacerations frequently heal by themselves if material is removed from the pleural space, but surgery may be required for larger lacerations that do not heal properly or that bleed.
(a fistula
between the pleural space and the bronchial tree). A bronchopleural fistula results when there is a communication between the laceration, a bronchiole, and the pleura; it can cause air to leak into the pleural space despite the placement of a chest tube. The laceration can also enlarge, as may occur when the injury creates a valve that allows air to enter the laceration, progressively expanding it. One complication, air embolism
, in which air enters the bloodstream, is potentially fatal, especially when it occurs on the left side of the heart. Air can enter the circulatory system through a damaged vein
in the injured chest and can travel to any organ; it is especially deadly in the heart or brain. Positive pressure ventilation can cause pulmonary embolism by forcing air out of injured lungs and into blood vessels.
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
tissue is torn or cut. An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion
Pulmonary contusion
A pulmonary contusion is a contusion of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels...
, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung, while pulmonary contusion does not. Pulmonary laceration is commonly caused by penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
but may also result from forces involved in blunt trauma
Blunt trauma
In medical terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma...
such as shear stress
Shear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
. A cavity filled with blood, air, or both can form. The injury is diagnosed when collections of air or fluid are found on a CT scan of the chest. Surgery may be required to stitch the laceration, to drain blood, or even to remove injured parts of the lung. The injury commonly heals quickly with few problems if it is given proper treatment; however it may be associated with scarring of the lung or other complications.
Causes
Pulmonary laceration is a common result of penetrating traumaPenetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
but may also be caused by blunt trauma
Blunt trauma
In medical terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma...
; broken ribs
Rib fracture
A rib fracture is a break or fracture in one or more of the bones making up the rib cage.The first rib is rarely fractured because of its protected position behind the clavicle . However, if it is broken serious damage can occur to the brachial plexus of nerves and the subclavian vessels...
may perforate the lung, or the tissue may be torn due to shearing force
Shear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
s that result from different rates of acceleration or deceleration of different tissues of the lung. Violent compression of the chest can cause lacerations by rupturing or shearing the lung tissue. Pulmonary laceration may result from blunt and penetrating forces that occur in the same injury and may be associated with pulmonary contusion. Lacerations of the lung tissue can also occur by compression of the alveoli against the ribs or spine. As with contusions, pulmonary lacerations usually occur near solid structures in the chest such as ribs. Pulmonary laceration is suspected when rib fractures are present.
Classification
In 1988, a group led by R.B. Wagner divided pulmonary lacerations into four types based on the manner in which the person was injured and indications found on a CT scan. In type 1 lacerations, which occur in the mid lung area, the air-filled lung bursts as a result of sudden compression of the chest. Also called compression-rupture lacerations, type 1 are the most common type and usually occur in a central location of the lung. They tend to be large, ranging in size from 2–8 cm. The shearing stress in type 2 results when the lower chest is suddenly compressed and the lower lung is suddenly moved across the vertebral bodies. Type 2, also called compression-shear, tends to occur near the spine and have an elongated shape. Type 2 lacerations usually occur in younger people with more flexible chests. Type 3, which are caused by punctures from fractured ribs, occur in the area near the chest wall underlying the broken rib. Also called rib penetration lacerations, type 3 lacerations tend to be small and accompanied by pneumothorax. Commonly, more than one type 3 laceration will occur. Type 4, also called adhesion tears, occur in cases where a pleuropulmonary adhesion had formed prior to the injury, in which the chest wall is suddenly fractured or pushed inwards. They occur in the subpleural area and result from shearing forces at sites of transpleural adhesion.Pathophysiology

Pleural cavity
In human anatomy, the pleural cavity is the potential space between the two pleura of the lungs. The pleura is a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered, membrane structure. The thin space between the two pleural layers is known as the pleural cavity; it normally...
, if the laceration goes through to it. Pulmonary laceration invariably results in pneumothorax
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity of the chest between the lung and the chest wall. It may occur spontaneously in people without chronic lung conditions as well as in those with lung disease , and many pneumothoraces occur after physical trauma to the chest, blast...
(due to torn airway
Airway
The pulmonary airway comprises those parts of the respiratory system through which air flows, conceptually beginning at the nose and mouth, and terminating in the alveoli...
s), hemothorax
Hemothorax
A hemothorax is a condition that results from blood accumulating in the pleural cavity.-Cause and presentation:Its cause is usually traumatic, from a blunt or penetrating injury to the thorax, resulting in a rupture of the serous membrane either lining the thorax or covering the lungs...
(due to torn blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s), or a hemopneumothorax
Hemopneumothorax
Hemopneumothorax, or haemopneumothorax, is a medical term describing the combination of two conditions: pneumothorax, or air in the chest cavity, and hemothorax , or blood in the chest cavity....
(with both blood and air in the chest cavity). Unlike hemothoraces that occur due to pulmonary contusion, those due to lung laceration may be large and long lasting. However, the lungs do not usually bleed very much because the blood vessels involved are small and the pressure within them is low. Therefore, pneumothorax is usually more of a problem than hemothorax. A pneumothorax may form or be turned into a tension pneumothorax by mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation
In medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
, which may force air out of the tear in the lung.
The laceration may also close up by itself, which can cause it to trap blood and potentially form a cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
or hematoma
Hematoma
A hematoma, or haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise...
. Because the lung is elastic, the tear forms a round cyst called a traumatic air cyst that may be filled with air, blood, or both and that usually shrinks over a period of weeks or months. Lacerations that are filled with air are called pneumatocele
Pneumatocele
A pneumatocele, or pneumatocyst is a cavity in the lungs filled with air that may result from pulmonary trauma. A pneumatocele results when a lung laceration, a cut or tear in the lung tissue, fills with air. A rupture of a small airway creates the air-filled cavity. Pulmonary lacerations that...
s, and those that are filled with blood are called pulmonary hematoma
Pulmonary hematoma
A pulmonary hematoma is a collection of blood within the tissue of the lung. It may result when a pulmonary laceration fills with blood. A lung laceration filled with air is called a pneumatocele. In some cases, both pneumatoceles and hematomas exist in the same injured lung. Pulmonary...
s. In some cases, both pneumatoceles and hematomas exist in the same injured lung. A pneumatocele can become enlarged, for example when the patient is mechanically ventilated or has acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome , also known as respiratory distress syndrome or adult respiratory distress syndrome is a serious reaction to various forms of injuries to the lung....
, in which case it may not go away for months. Pulmonary hematomas take longer to heal than simple pneumatoceles and commonly leave the lungs scarred.
Over time, the walls of lung lacerations tend to grow thicker due to edema and bleeding at the edges.
Diagnosis

Chest X-ray
In medicine, a chest radiograph, commonly called a chest X-ray , is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures...
because an associated pulmonary contusion
Pulmonary contusion
A pulmonary contusion is a contusion of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels...
or hemorrhage may mask it. As the lung contusion clears (usually within two to four days), lacerations begin to become visible on chest X-ray. CT scanning is more sensitive and better at detecting pulmonary laceration than X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s are, and often reveals multiple lacerations in cases where chest X-ray showed only a contusion. Before CT scanning was widely available, pulmonary laceration was considered unusual because it was not common to find with X-ray alone. On a CT scan, pulmonary lacerations show up in a contused area of the lung, typically appearing as cavities filled with air or fluid that usually have a round or ovoid shape due to the lung's elasticity.
Hematomas appear on chest radiographs as smooth masses that are round or ovoid in shape. Like lacerations, hematomas may initially be hidden on X-ray by lung contusions, but they become more apparent as the contusion begins to heal. Pneumatoceles have a similar shape to that of hematomas but have thin, smooth walls. Lacerations may be filled completely with blood, completely with air, or partially with both. Lacerations filled with both blood and air display a distinctive air-fluid level. A single laceration may occur by itself, or many may be present, creating an appearance like Swiss cheese in the radiography of the lung.
Pulmonary laceration is usually accompanied by hemoptysis
Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the expectoration of blood or of blood-stained sputum from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the expectoration (coughing up) of blood or of blood-stained sputum from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs Hemoptysis or haemoptysis ...
(coughing up blood or of blood-stained sputum).
Thoracoscopy
Thoracoscopy
Thoracoscopy is a medical procedure involving internal examination, biopsy, and/or resection of disease or masses within the pleural cavity and thoracic cavity...
may be used in both diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary laceration.
A healing laceration may resemble a pulmonary nodule on radiographs, but unlike pulmonary nodules, lacerations decrease in size over time on radiographs.
Treatment
As with other chest injuries such as pulmonary contusion, hemothorax, and pneumothorax, pulmonary laceration can often be treated with just supplemental oxygen, ventilation, and drainage of fluids from the chest cavity. A thoracostomy tubeChest tube
A chest tube is a flexible plastic tube that is inserted through the side of the chest into the pleural space. It is used to remove air or fluid , or pus from the intrathoracic space...
can be used to remove blood and air from the chest cavity. About 5% of cases require surgery, called thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
. Thoracotomy is especially likely to be needed if a lung fails to re-expand; if pneumothorax, bleeding, or coughing up blood persist; or in order to remove clotted blood from a hemothorax. Surgical treatment includes suturing, stapling, oversewing, and wedging out of the laceration. Occasionally, surgeons must perform a lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
, in which a lobe of the lung is removed, or a pneumonectomy
Pneumonectomy
A pneumonectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a lung. Removal of just one lobe of the lung is specifically referred to as a lobectomy, and that of a segment of the lung as a wedge resection .-Indications:...
, in which an entire lung is removed.
Prognosis
Full recovery is common with proper treatment. Pulmonary laceration usually heals quickly after a chest tube is inserted and is usually not associated with major long-term problems. Pulmonary lacerations usually heal within three to five weeks, and lacerations filled with air will commonly heal within one to three weeks but on occasion take longer. However, the injury often takes weeks or months to heal, and the lung may be scarScar
Scars are areas of fibrous tissue that replace normal skin after injury. A scar results from the biological process of wound repair in the skin and other tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound results in...
red. Small pulmonary lacerations frequently heal by themselves if material is removed from the pleural space, but surgery may be required for larger lacerations that do not heal properly or that bleed.
Complications
Complications are not common but include infection, pulmonary abscess, and bronchopleural fistulaBronchopleural fistula
A bronchopleural fistula is a fistula between the pleural space and the lung. It sometimes develops following pneumonectomy or an infection.-External links:* http://www.cuhk.edu.hk/med/ans/Trainee%20Manual/Respiratory%20Problems/BRONCHOPLEURAL.pdf...
(a fistula
Fistula
In medicine, a fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two epithelium-lined organs or vessels that normally do not connect. It is generally a disease condition, but a fistula may be surgically created for therapeutic reasons.-Locations:Fistulas can develop in various parts of the...
between the pleural space and the bronchial tree). A bronchopleural fistula results when there is a communication between the laceration, a bronchiole, and the pleura; it can cause air to leak into the pleural space despite the placement of a chest tube. The laceration can also enlarge, as may occur when the injury creates a valve that allows air to enter the laceration, progressively expanding it. One complication, air embolism
Air embolism
An air embolism, or more generally gas embolism, is a pathological condition caused by gas bubbles in a vascular system. The most common context is a human body, in which case it refers to gas bubbles in the bloodstream...
, in which air enters the bloodstream, is potentially fatal, especially when it occurs on the left side of the heart. Air can enter the circulatory system through a damaged vein
Vein
In the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
in the injured chest and can travel to any organ; it is especially deadly in the heart or brain. Positive pressure ventilation can cause pulmonary embolism by forcing air out of injured lungs and into blood vessels.

