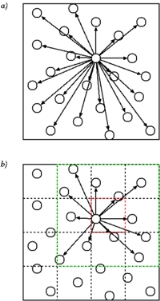
Cell lists
Encyclopedia
Cell lists are a tool for finding all atom pairs within a given cut-off distance of each other in Molecular dynamics
simulations. These pairs are needed to compute the short-range non-bonded interactions in a system, such as Van der Waals force
s or the short-range part of the electrostatic interaction when using Ewald summation
.
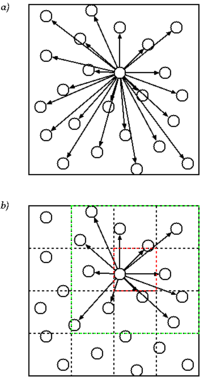 Cell lists work by subdividing the simulation domain into cells with an edge length greater than or equal to the cut-off radius of the interaction to be computed. The particles are sorted into these cells and the interactions are computed between particles in the same or neighbouring cells.
Cell lists work by subdividing the simulation domain into cells with an edge length greater than or equal to the cut-off radius of the interaction to be computed. The particles are sorted into these cells and the interactions are computed between particles in the same or neighbouring cells.
In its most basic form, the non-bonded interactions for a cut-off distance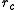 are computed as follows:
are computed as follows:
Since the cell length is at least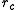 in all dimensions, no particles within
in all dimensions, no particles within 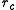 of each other can be missed.
of each other can be missed.
Given a simulation with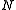 particles with a homogeneous particle density, the number of cells
particles with a homogeneous particle density, the number of cells 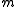 is proportional to
is proportional to 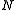 and the cut-off radius (i.e. if
and the cut-off radius (i.e. if 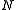 increases, so does the number of cells). The average number of particles per cell
increases, so does the number of cells). The average number of particles per cell 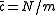 therefore does not depend on the total number of particles. The cost of interacting two cells is in
therefore does not depend on the total number of particles. The cost of interacting two cells is in 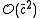 . The number of cell pairs is proportional to the number of cells which is again proportional to the number of particles
. The number of cell pairs is proportional to the number of cells which is again proportional to the number of particles 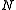 . The total cost of finding all pairwise distances within a given cut-off is in
. The total cost of finding all pairwise distances within a given cut-off is in 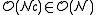 , which is significantly better than computing the
, which is significantly better than computing the 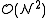 pairwise distances naively.
pairwise distances naively.
are used to avoid imposing artificial boundary conditions. Using cell lists, these boundaries can be implemented in two ways
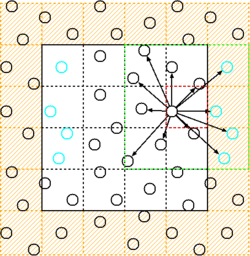 In the ghost cells approach, the simulation box is wrapped in an additional layer of cells. These cells contain periodically wrapped copies of the corresponding simulation cells inside the domain.
In the ghost cells approach, the simulation box is wrapped in an additional layer of cells. These cells contain periodically wrapped copies of the corresponding simulation cells inside the domain.
Although the data—and usually also the computational cost—is doubled for interactions over the periodic boundary, this approach has the advantage of being straightforward to implement and very easy to parallelize, since cells will only interact with their geographical neighbours.
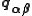 . This vector, which can be stored or computed for every cell pair
. This vector, which can be stored or computed for every cell pair 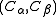 contains the correction which needs to be applied to "wrap" one cell around the domain to neighbour the other. The pairwise distance between two particles
contains the correction which needs to be applied to "wrap" one cell around the domain to neighbour the other. The pairwise distance between two particles 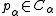 and
and 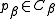 is then computed as
is then computed as
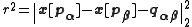 .
.
This approach, although more efficient than using ghost cells, is less straightforward to implement (the cell pairs need to be identified over the periodic boundaries and the vector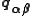 needs to be computed/stored).
needs to be computed/stored).
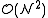 to
to 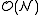 , the cell list algorithm listed above still has some inefficiencies.
, the cell list algorithm listed above still has some inefficiencies.
Consider a computational cell with edge length equal to the cut-off radius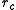 . The pairwise distance between all particles in the cell and in one of the neighbouring cells is computed. The cell has 26 neighbours: 6 sharing a common face, 12 sharing a common edge and 8 sharing a common corner. Of all the pairwise distances computed, only about 16% percent will actually be less than or equal to
. The pairwise distance between all particles in the cell and in one of the neighbouring cells is computed. The cell has 26 neighbours: 6 sharing a common face, 12 sharing a common edge and 8 sharing a common corner. Of all the pairwise distances computed, only about 16% percent will actually be less than or equal to 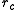 . In other words, 84% of all pairwise distance computations are spurious.
. In other words, 84% of all pairwise distance computations are spurious.
One way of overcoming this inefficiency is to partition the domain into cells of edge length smaller than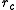 . The pairwise interactions are then not just computed between neighboring cells, but between all cells within
. The pairwise interactions are then not just computed between neighboring cells, but between all cells within 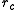 of each other (first suggested in and implemented and analysed in , and ). This approach can be
of each other (first suggested in and implemented and analysed in , and ). This approach can be
taken to the limit wherein each cell holds at most one single particle, therefore reducing the number of spurious pairwise distance evaluations to zero. This gain in efficiency, however, is quickly offset by the number of cells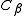 that need to be inspected for every interaction with a cell
that need to be inspected for every interaction with a cell 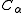 , which, for example in 3d, grows cubically with the inverse of the cell edge length. Setting the edge length to
, which, for example in 3d, grows cubically with the inverse of the cell edge length. Setting the edge length to 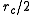 , however, already reduces the number of spurious distance evaluations to 63%.
, however, already reduces the number of spurious distance evaluations to 63%.
Another approach is outlined and tested in , in which the particles are first sorted along the axis connecting the cell centers. This approach generates only about 40% spurious pairwise distance computations, yet carries an additional cost due to sorting the particles.
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
simulations. These pairs are needed to compute the short-range non-bonded interactions in a system, such as Van der Waals force
Van der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
s or the short-range part of the electrostatic interaction when using Ewald summation
Ewald summation
Ewald summation, named after Paul Peter Ewald, is a method for computing the interaction energies of periodic systems , particularly electrostatic energies. Ewald summation is a special case of the Poisson summation formula, replacing the summation of interaction energies in real space with an...
.
Algorithm

In its most basic form, the non-bonded interactions for a cut-off distance
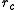 are computed as follows:
are computed as follows:- for all neighbouring cell pairs
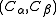 do
do
- for all
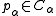 do
do
- for all
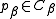 do
do
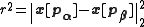
- if
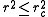 then
then
- Compute the interaction between
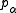 and
and 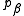 .
.
- Compute the interaction between
- end if
- end for
- for all
- end for
- for all
- end for
Since the cell length is at least
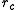 in all dimensions, no particles within
in all dimensions, no particles within 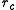 of each other can be missed.
of each other can be missed.Given a simulation with
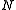 particles with a homogeneous particle density, the number of cells
particles with a homogeneous particle density, the number of cells 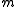 is proportional to
is proportional to 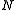 and the cut-off radius (i.e. if
and the cut-off radius (i.e. if 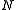 increases, so does the number of cells). The average number of particles per cell
increases, so does the number of cells). The average number of particles per cell 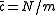 therefore does not depend on the total number of particles. The cost of interacting two cells is in
therefore does not depend on the total number of particles. The cost of interacting two cells is in 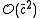 . The number of cell pairs is proportional to the number of cells which is again proportional to the number of particles
. The number of cell pairs is proportional to the number of cells which is again proportional to the number of particles 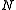 . The total cost of finding all pairwise distances within a given cut-off is in
. The total cost of finding all pairwise distances within a given cut-off is in 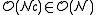 , which is significantly better than computing the
, which is significantly better than computing the 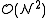 pairwise distances naively.
pairwise distances naively.Periodic Boundary Conditions
In most simulations, Periodic boundary conditionsPeriodic boundary conditions
In mathematical models and computer simulations, periodic boundary conditions are a set of boundary conditions that are often used to simulate a large system by modelling a small part that is far from its edge...
are used to avoid imposing artificial boundary conditions. Using cell lists, these boundaries can be implemented in two ways
Ghost Cells

Although the data—and usually also the computational cost—is doubled for interactions over the periodic boundary, this approach has the advantage of being straightforward to implement and very easy to parallelize, since cells will only interact with their geographical neighbours.
Periodic Wrapping
Instead of creating ghost cells, cell pairs that interact over a periodic boundary can also use a periodic correction vector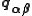 . This vector, which can be stored or computed for every cell pair
. This vector, which can be stored or computed for every cell pair 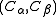 contains the correction which needs to be applied to "wrap" one cell around the domain to neighbour the other. The pairwise distance between two particles
contains the correction which needs to be applied to "wrap" one cell around the domain to neighbour the other. The pairwise distance between two particles 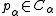 and
and 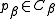 is then computed as
is then computed as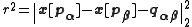 .
.This approach, although more efficient than using ghost cells, is less straightforward to implement (the cell pairs need to be identified over the periodic boundaries and the vector
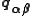 needs to be computed/stored).
needs to be computed/stored).Improvements
Despite reducing the computational cost of finding all pairs within a given cut-off distance from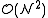 to
to 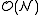 , the cell list algorithm listed above still has some inefficiencies.
, the cell list algorithm listed above still has some inefficiencies.Consider a computational cell with edge length equal to the cut-off radius
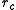 . The pairwise distance between all particles in the cell and in one of the neighbouring cells is computed. The cell has 26 neighbours: 6 sharing a common face, 12 sharing a common edge and 8 sharing a common corner. Of all the pairwise distances computed, only about 16% percent will actually be less than or equal to
. The pairwise distance between all particles in the cell and in one of the neighbouring cells is computed. The cell has 26 neighbours: 6 sharing a common face, 12 sharing a common edge and 8 sharing a common corner. Of all the pairwise distances computed, only about 16% percent will actually be less than or equal to 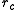 . In other words, 84% of all pairwise distance computations are spurious.
. In other words, 84% of all pairwise distance computations are spurious.One way of overcoming this inefficiency is to partition the domain into cells of edge length smaller than
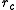 . The pairwise interactions are then not just computed between neighboring cells, but between all cells within
. The pairwise interactions are then not just computed between neighboring cells, but between all cells within 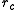 of each other (first suggested in and implemented and analysed in , and ). This approach can be
of each other (first suggested in and implemented and analysed in , and ). This approach can betaken to the limit wherein each cell holds at most one single particle, therefore reducing the number of spurious pairwise distance evaluations to zero. This gain in efficiency, however, is quickly offset by the number of cells
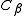 that need to be inspected for every interaction with a cell
that need to be inspected for every interaction with a cell 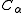 , which, for example in 3d, grows cubically with the inverse of the cell edge length. Setting the edge length to
, which, for example in 3d, grows cubically with the inverse of the cell edge length. Setting the edge length to 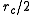 , however, already reduces the number of spurious distance evaluations to 63%.
, however, already reduces the number of spurious distance evaluations to 63%.Another approach is outlined and tested in , in which the particles are first sorted along the axis connecting the cell centers. This approach generates only about 40% spurious pairwise distance computations, yet carries an additional cost due to sorting the particles.

