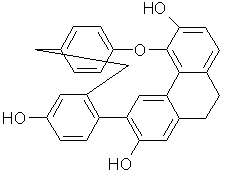
Cavicularin
Encyclopedia
Cavicularin is a natural phenol
ic secondary metabolite
isolated from the liverwort
Cavicularia densa. This macrocycle
is unusual because it was the first compound isolated from nature displaying optical activity due to the presence of planar chirality
and axial chirality
. The specific rotation
for (+)-cavicularin is +168.2°. It is also a very strained
molecule. It incorporates a benzene ring that is bent 17° out of planarity. This type of angle strain
in aromatic compounds is normally reserved for synthetic cyclophane
s.
The liverwort
was obtained from Mt. Ishizuchi in the district of Shikoku
. The material was dried for one day, ground to a powder and 5 grams were reflux
ed in methanol
for 4 months to yield 2.5 mg (0.049%) of cavicularin after column chromatography
and preparative TLC. In 2005, the compound was prepared by total synthesis
together with the unstrained compound riccardin C. .
Natural phenol
Natural phenols, bioavailable phenols, plant phenolics, low molecular weight phenols or phenoloids are a class of natural products. They are small molecules containing one or more phenolic group. These molecules are smaller in size than polyphenols, containing less than 12 phenolic groups...
ic secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds that are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of an organism. Unlike primary metabolites, absence of secondary metabolities does not result in immediate death, but rather in long-term impairment of the organism's...
isolated from the liverwort
Marchantiophyta
The Marchantiophyta are a division of bryophyte plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like other bryophytes, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information....
Cavicularia densa. This macrocycle
Macrocycle
A macrocycle is, as defined by IUPAC, "a cyclic macromolecule or a macromolecular cyclic portion of a molecule." In the chemical literature, organic chemists may consider any molecule containing a ring of nine or more atoms to be a macrocycle...
is unusual because it was the first compound isolated from nature displaying optical activity due to the presence of planar chirality
Planar chirality
Planar chirality is the special case of chirality for two dimensions.Most fundamentally, planar chirality is a mathematical term, finding use in chemistry, physics and related physical sciences, for example, in astronomy, optics and metamaterials...
and axial chirality
Axial chirality
Axial chirality is a special case of chirality in which a molecule does not possess a stereogenic center but an axis of chirality – an axis about which a set of substituents is held in a spatial arrangement that is not superposable on its mirror image...
. The specific rotation
Specific rotation
In stereochemistry, the specific rotation of a chemical compound [α] is defined as the observed angle of optical rotation α when plane-polarized light is passed through a sample with a path length of 1 decimeter and a sample concentration of 1 gram per 1 millilitre. It is the main property used to...
for (+)-cavicularin is +168.2°. It is also a very strained
Strain (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule experiences strain when its chemical structure undergoes some stress which raises its internal energy in comparison to a strain-free reference compound. The internal energy of a molecule consists of all the energy stored within it. A strained molecule has an additional...
molecule. It incorporates a benzene ring that is bent 17° out of planarity. This type of angle strain
Angle strain
Angle strain, also called Baeyer strain in cyclic molecules, is the resistance associated with bond angle compression or bond angle expansion. It occurs when bond angles deviate from the ideal bond angles to achieve maximum bond strength in a specific chemical conformation...
in aromatic compounds is normally reserved for synthetic cyclophane
Cyclophane
A cyclophane is a hydrocarbon consisting of an aromatic unit and an aliphatic chain that forms a bridge between two non-adjacent positions of the aromatic ring. More complex derivatives with multiple aromatic units and bridges forming cagelike structures are also known...
s.
The liverwort
Marchantiophyta
The Marchantiophyta are a division of bryophyte plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like other bryophytes, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information....
was obtained from Mt. Ishizuchi in the district of Shikoku
Shikoku
is the smallest and least populous of the four main islands of Japan, located south of Honshū and east of the island of Kyūshū. Its ancient names include Iyo-no-futana-shima , Iyo-shima , and Futana-shima...
. The material was dried for one day, ground to a powder and 5 grams were reflux
Reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations...
ed in methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
for 4 months to yield 2.5 mg (0.049%) of cavicularin after column chromatography
Column chromatography
Column chromatography in chemistry is a method used to purify individual chemical compounds from mixtures of compounds. It is often used for preparative applications on scales from micrograms up to kilograms.The main advantage of column chromatography is the relatively low cost and disposability...
and preparative TLC. In 2005, the compound was prepared by total synthesis
Total synthesis
In organic chemistry, a total synthesis is, in principle, the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simpler pieces, usually without the aid of biological processes. In practice, these simpler pieces are commercially available in bulk and semi-bulk quantities, and are often...
together with the unstrained compound riccardin C. .