Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency
Encyclopedia
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency is a rare metabolic disorder that prevents the body from converting certain fats called long-chain fatty acid
s into energy, particularly during periods without food.
Carnitine
, a natural substance acquired mostly through the diet, is used by cells to process fats and produce energy. People with this disorder have a faulty enzyme, Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I
, that prevents these long-chain fatty acids from being transported into the mitochondria to be broken down.
s (products of fat breakdown that are used for energy) and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia
). Together these signs are called hypoketotic hypoglycemia. People with this disorder typically also have an enlarged liver
(hepatomegaly
), muscle weakness, and elevated levels of carnitine in the blood.
 Mutations in the CPT1A gene cause carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency.
Mutations in the CPT1A gene cause carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency.
Mutations in the CPT1A gene lead to the production of a defective version of an enzyme called carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Without this enzyme, long-chain fatty acids from food and fats stored in the body cannot be transported into mitochondria to be broken down and processed. As a result, excessive levels of long-chain fatty acids may build up in tissues, damaging the liver, heart, and brain.
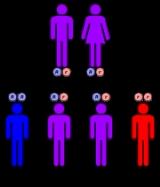
This condition has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers
of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s into energy, particularly during periods without food.
Carnitine
Carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound biosynthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine. In living cells, it is required for the transport of fatty acids from the cytosol into the mitochondria during the breakdown of lipids for the generation of metabolic energy. It is widely...
, a natural substance acquired mostly through the diet, is used by cells to process fats and produce energy. People with this disorder have a faulty enzyme, Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I also known as carnitine acyltransferase I or CAT1 is a mitochondrial enzyme. It is part of a family of enzymes called carnitine acyltransferases. Three isoforms of CPT1 are currently known: CPT1A, CPT1B, and CPT1C...
, that prevents these long-chain fatty acids from being transported into the mitochondria to be broken down.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of this disorder include low levels of ketoneKetone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s (products of fat breakdown that are used for energy) and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
). Together these signs are called hypoketotic hypoglycemia. People with this disorder typically also have an enlarged liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
(hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a nonspecific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, direct toxicity, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass...
), muscle weakness, and elevated levels of carnitine in the blood.
Differential diagnosis
This condition is sometimes mistaken for Reye syndrome, a severe disorder that develops in children while they appear to be recovering from viral infections such as chicken pox or flu. Most cases of Reye syndrome are associated with the use of aspirin during these viral infections.Genetics

Mutations in the CPT1A gene lead to the production of a defective version of an enzyme called carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Without this enzyme, long-chain fatty acids from food and fats stored in the body cannot be transported into mitochondria to be broken down and processed. As a result, excessive levels of long-chain fatty acids may build up in tissues, damaging the liver, heart, and brain.
This condition has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.

