Carbomer
Overview
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
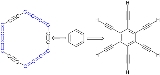
, a carbomer is an expanded molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
obtained by insertion of a C2 unit in a given molecule. Carbomers differ from their templates in size but not in symmetry when each C–C single bond is replaced by at least one alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
bond, and when a double bond is replaced by an allene
Allene
An allene is a compound in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon centres. Allenes are classified as polyenes with cumulated dienes. The parent compound of allene is propadiene. Compounds with an allene-type structure but with more than three carbon atoms are...
bond. The size of the carbomer will continue to increase when more alkyne bonds are introduced and for this reason carbomers are also called carbon-molecules, where "n" is the number of acetylene or allene groups in an n-expansion unit.

