
Capillary length
Encyclopedia
In fluid mechanics
, capillary length is a characteristic length scale for fluid subject to a body force from gravity and a surface force due to surface tension
.
The capillary length is defined as: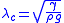 ,
,
where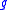 is the acceleration due to gravity and
is the acceleration due to gravity and 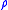 is the density of the fluid, and
is the density of the fluid, and 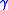 is the surface tension
is the surface tension
of the fluid-fluid interface.
For clean water at standard temperature and pressure, the capillary length is ~2mm.
A capillary surface
that has a characteristic length smaller than the capillary length can be considered a low Bond number surface. A sessile drop whose largest dimension is smaller than the capillary length, for example, will take the shape of spherical cap
, which is the solution to the Young-Laplace equation with gravity completely absent.
Fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the study of fluids and the forces on them. Fluid mechanics can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; fluid kinematics, the study of fluids in motion; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion...
, capillary length is a characteristic length scale for fluid subject to a body force from gravity and a surface force due to surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
.
The capillary length is defined as:
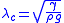 ,
,where
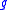 is the acceleration due to gravity and
is the acceleration due to gravity and  is the density of the fluid, and
is the density of the fluid, and  is the surface tension
is the surface tensionSurface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
of the fluid-fluid interface.
For clean water at standard temperature and pressure, the capillary length is ~2mm.
A capillary surface
Capillary surface
In fluid mechanics and mathematics, a capillary surface is a surface that represents the interface between two different fluids. As a consequence of being a surface, a capillary surface has no thickness in slight contrast with most real fluid interfaces....
that has a characteristic length smaller than the capillary length can be considered a low Bond number surface. A sessile drop whose largest dimension is smaller than the capillary length, for example, will take the shape of spherical cap
Spherical cap
In geometry, a spherical cap is a portion of a sphere cut off by a plane. If the plane passes through the center of the sphere, so that the height of the cap is equal to the radius of the sphere, the spherical cap is called a hemisphere....
, which is the solution to the Young-Laplace equation with gravity completely absent.

