
Caldwell catalogue
Encyclopedia
The Caldwell Catalogue is an astronomical catalog
of 109 bright star cluster
s, nebula
e, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers
. The list was compiled by Sir Patrick Caldwell-Moore, better known as Patrick Moore
, as a complement to the Messier Catalogue.
The Messier Catalogue is used frequently by amateur astronomers as a list of interesting deep-sky objects for observations, but Moore noted that the list did not include many of the sky's brightest deep-sky objects, including the Hyades
, the Double Cluster
(NGC 869
and NGC 884
), and NGC 253. Moreover, Moore observed that the Messier Catalogue, which was compiled based on observations in the Northern Hemisphere, excluded bright deep-sky objects visible in the Southern Hemisphere such as Omega Centauri
, Centaurus A
, the Jewel Box, and 47 Tucanae
. He quickly compiled a list of 109 objects (to match the number of objects in the Messier Catalogue) and published it in Sky & Telescope in December 1995.
Since its publication, the catalogue has grown in popularity and usage within the amateur astronomical
community. Small compilation errors in the original 1995 version of the list have since been corrected. Moore used his other surname to name the list as M for Moore was already taken by Messier, and the catalogue adopts "C" numbers to rename objects with more common designations.
As stated above, the list was compiled from objects already identified by professional astronomers and commonly observed by amateur astronomers. Unlike objects in the Messier catalogue, which are listed in the order they were discovered, the Caldwell catalogue is ordered by declination
, with C1 being the most northerly and C109 being the most southerly, although two objects (NGC 4244
and the Hyades
) are listed out of sequence. The original list also incorrectly identified S Norma Cluster (NGC 6087
) as NGC 6067
and incorrectly labelled the Lambda Centauri Cluster (IC 2944
) as the Gamma Centauri Cluster.
A natural progression for the amateur astronomer wishing to observe deep sky objects would be to view the Messier catalogue, followed by the Caldwell catalogue, and then the Herschel 400 Catalogue
. At the end of this exercise the observer would have viewed nearly 600 objects. Although there are 618 objects listed in these three catalogues the Herschel 400 Catalogue does contain some objects from the Messier and Caldwell catalogues.
Astronomical catalog
An astronomical catalog or catalogue is a list or tabulation of astronomical objects, typically grouped together because they share a common type, morphology, origin, means of detection, or method of discovery...
of 109 bright star cluster
Star cluster
Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than...
s, nebula
Nebula
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases...
e, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers
Amateur astronomy
Amateur astronomy, also called backyard astronomy and stargazing, is a hobby whose participants enjoy watching the night sky , and the plethora of objects found in it, mainly with portable telescopes and binoculars...
. The list was compiled by Sir Patrick Caldwell-Moore, better known as Patrick Moore
Patrick Moore
Sir Patrick Alfred Caldwell-Moore, CBE, FRS, FRAS is a British amateur astronomer who has attained prominent status in astronomy as a writer, researcher, radio commentator and television presenter of the subject, and who is credited as having done more than any other person to raise the profile of...
, as a complement to the Messier Catalogue.
The Messier Catalogue is used frequently by amateur astronomers as a list of interesting deep-sky objects for observations, but Moore noted that the list did not include many of the sky's brightest deep-sky objects, including the Hyades
Hyades (star cluster)
The Hyades is the nearest open cluster to the Solar System and one of the best-studied of all star clusters. The Hipparcos satellite, the Hubble Space Telescope, and infrared color-magnitude diagram fitting have been used to establish a distance to the cluster's center of ~153 ly...
, the Double Cluster
Double Cluster
The Double Cluster is the common name for the naked-eye open clusters NGC 884 and NGC 869 , which are close together in the constellation Perseus. NGC 884 and NGC 869 are at distances of 7600 and 6800 light-years away, respectively, so they are also close to one another in space...
(NGC 869
NGC 869
NGC 869 is an open cluster located 7600 light years away in the constellation of Perseus. The cluster is most likely around 13 million years old. It is the westernmost of the Double Cluster with NGC 884. Located in the Perseus OB1 association both clusters are located physically close to one...
and NGC 884
NGC 884
NGC 884 is an open cluster located 7600 light years away in the constellation of Perseus. The cluster is most likely around 12.5 million years old. It is the easternmost of the Double Cluster with NGC 869. Located in the Perseus OB1 association both clusters are located physically close to one...
), and NGC 253. Moreover, Moore observed that the Messier Catalogue, which was compiled based on observations in the Northern Hemisphere, excluded bright deep-sky objects visible in the Southern Hemisphere such as Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri or NGC 5139 is a globular clusterin the constellation of Centaurus, discovered by Edmond Halley in 1677 who listed it as a nebula. Omega Centauri had been listed in Ptolemy's catalog 2000 years ago as a star. Lacaille included it in his catalog as number I.5...
, Centaurus A
Centaurus A
Centaurus A is a prominent galaxy in the constellation of Centaurus. There is considerable debate in the literature regarding the galaxy's fundamental properties such as its Hubble type and distance...
, the Jewel Box, and 47 Tucanae
47 Tucanae
47 Tucanae or just 47 Tuc is a globular cluster located in the constellation Tucana. It is about 16,700 light years away from Earth, and 120 light years across. It can be seen with the naked eye, with a visual magnitude of 4.0...
. He quickly compiled a list of 109 objects (to match the number of objects in the Messier Catalogue) and published it in Sky & Telescope in December 1995.
Since its publication, the catalogue has grown in popularity and usage within the amateur astronomical
Amateur astronomy
Amateur astronomy, also called backyard astronomy and stargazing, is a hobby whose participants enjoy watching the night sky , and the plethora of objects found in it, mainly with portable telescopes and binoculars...
community. Small compilation errors in the original 1995 version of the list have since been corrected. Moore used his other surname to name the list as M for Moore was already taken by Messier, and the catalogue adopts "C" numbers to rename objects with more common designations.
As stated above, the list was compiled from objects already identified by professional astronomers and commonly observed by amateur astronomers. Unlike objects in the Messier catalogue, which are listed in the order they were discovered, the Caldwell catalogue is ordered by declination
Declination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
, with C1 being the most northerly and C109 being the most southerly, although two objects (NGC 4244
NGC 4244
NGC 4244, also Caldwell 26, is an edge-on loose Spiral galaxy and Caldwell object in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is part of the M94 Group , a galaxy group relatively close to the Local Group containing the Milky Way. It shines at magnitude +10.2/+10.6. Its celestial cooridinates are RA ,...
and the Hyades
Hyades (star cluster)
The Hyades is the nearest open cluster to the Solar System and one of the best-studied of all star clusters. The Hipparcos satellite, the Hubble Space Telescope, and infrared color-magnitude diagram fitting have been used to establish a distance to the cluster's center of ~153 ly...
) are listed out of sequence. The original list also incorrectly identified S Norma Cluster (NGC 6087
NGC 6087
NGC 6087 is one of the brightest open clusters in the constellation Norma with a magnitude of 5.4. It is approximately 3500 light-years away and contains about 40 stars of the seventh to the eleventh magnitude, the brightest being 6.5 magnitude S Normae....
) as NGC 6067
NGC 6067
NGC 6067 is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Norma. It is located to the north of Kappa Normae, with an angular diameter of 12′. The cluster can be observed with binoculars or a small telescope, while a 12-inch aperture telescope will reveal about 250 stars....
and incorrectly labelled the Lambda Centauri Cluster (IC 2944
IC 2944
IC 2944, also known as the Running Chicken Nebula or the Lambda Cen Nebula, is an open cluster with an associated emission nebula found in the constellation Centaurus, near the star Lambda Centauri...
) as the Gamma Centauri Cluster.
A natural progression for the amateur astronomer wishing to observe deep sky objects would be to view the Messier catalogue, followed by the Caldwell catalogue, and then the Herschel 400 Catalogue
Herschel 400 Catalogue
The Herschel 400 catalogue is a subset of William Herschel's original deep sky catalogue of 2,500 deep sky objects, selected by Brenda F. Guzman , Lydel Guzman, Paul Jones, James Morrison, Peggy Taylor and Sara Saey of the Ancient City Astronomy Club in St. Augustine, Florida, USA circa 1980...
. At the end of this exercise the observer would have viewed nearly 600 objects. Although there are 618 objects listed in these three catalogues the Herschel 400 Catalogue does contain some objects from the Messier and Caldwell catalogues.
Number of objects by type in the Caldwell catalogue.
| Dark nebulae | 1 |
| Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
35 |
| Globular clusters | 18 |
| Nebulae | 9 |
| Star Clusters Star cluster Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than... |
25 |
| Star Clusters and Nebulae | 6 |
| Planetary Nebulae Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
13 |
| Supernova remnant Supernova remnant A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two... |
2 |
| Total | 109 |
Key
| Star cluster Star cluster Star clusters or star clouds are groups of stars. Two types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters, more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally contain less than... |
| Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
| Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
1-10
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | NGC 188 NGC 188 NGC 188 is an open cluster in the constellation Cepheus. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1825.Unlike most open clusters that drift apart after a few million years because of the gravitational interaction of our galaxy, NGC 188 lies far above the plane of the galaxy and is one of the most... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.8 | Cepheus Cepheus (constellation) Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
8.1 | ||
| C2 | NGC 40 NGC 40 NGC 40 is a planetary nebula discovered by W.F.Herschel Nov 25 1788, and is composed of hot gas around a dying star. The star has ejected its outer layer which has left behind a smaller, hot star with a temperature on the surface of about 50,000 degrees... |
Bow-Tie Nebula | Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
3.5 | Cepheus Cepheus (constellation) Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
11 | |
| C3 | NGC 4236 NGC 4236 NGC 4236 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Draco.-Galaxy group information:NGC 4236 is a member of the M81 Group, a group of galaxies located at a distance of approximately 11.7 Mly from Earth. The group also contains the well-known spiral galaxy Messier 81 and the... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
7,000 | Draco Draco (constellation) Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. Draco is circumpolar for many observers in the northern hemisphere... |
9.7 | ||
| C4 | NGC 7023 | Iris Nebula Iris nebula The Iris Nebula, also NGC 7023 and Caldwell 4, is a bright reflection nebula and Caldwell object in the constellation Cepheus. NGC 7023 is actually the cluster within the nebula, LBN 487, and the nebula is lit by a magnitude +7 star, SAO 19158. It shines at magnitude +6.8... |
 |
Open Cluster and Nebula Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.4 | Cepheus Cepheus (constellation) Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
7 |
| C5 | IC 342 IC 342 IC 342 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Camelopardalis. The galaxy is located near the galactic equator where dust obscuration makes it a difficult object for both amateur and professional astronomers to observe.IC 342 is one of the brightest two galaxies in the IC 342/Maffei... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
13,000 | Camelopardalis | 9 | ||
| C6 | NGC 6543 | Cat's Eye Nebula Cat's Eye Nebula The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Draco. Structurally, it is one of the most complex nebulae known, with high-resolution Hubble Space Telescope observations revealing remarkable structures such as knots, jets, bubbles and sinewy arc-like features... |
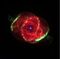 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
3 | Draco Draco (constellation) Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. Draco is circumpolar for many observers in the northern hemisphere... |
9 |
| C7 | NGC 2403 NGC 2403 NGC 2403 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Camelopardalis. NGC 2403 is an outlying member of the M81 Group, and is approximately 8 million light-years distant... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
14,000 | Camelopardalis | 8.4 | |
| C8 | NGC 559 NGC 559 NGC 559, also Caldwell 8, is an open cluster and Caldwell object in the constellation Cassiopeia. It shines at magnitude +9.5. Its celestial coordinates are RA , dec . It is located near the open cluster NGC 637, and the bright magnitude +2.2 irregular variable star Gamma Cassiopeiae. The cluster... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3.7 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
9.5 | ||
| C9 | Sh2-155 | Cave Nebula Cave Nebula The Cave Nebula, Sh2-155 or Caldwell 9, is a dim and very diffuse bright nebula within a larger nebula complex containing emission, reflection, and dark nebulosity. It is located in the constellation Cepheus.... |
 |
Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
2.8 | Cepheus Cepheus (constellation) Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
7.7 |
| C10 | NGC 663 NGC 663 NGC 663, also known as Caldwell 10, is young open cluster of about 400 stars in the Cassiopeia constellation. It has an estimated 400 stars and spans about a quarter of a degree across the sky. It can reportedly be detected with the unaided eye, although a telescope is recommended for best viewing.... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
7.2 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
7.1 |
11-20
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11 | NGC 7635 NGC 7635 NGC 7635, also called the Bubble Nebula, Sharpless 162, or Caldwell 11, is a H II region emission nebula in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies close to the direction of the open cluster Messier 52. The "bubble" is created by the stellar wind from a massive hot, 8.7 magnitude young central... |
Bubble nebula |  |
Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
7.1 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
- |
| C12 | NGC 6946 NGC 6946 NGC 6946, , is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 22 million light-years away, on the border between the constellations Cepheus and Cygnus. It was discovered by William Herschel on September 9, 1798... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
18,000 | Cepheus Cepheus (constellation) Cepheus is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
8.9 | ||
| C13 | NGC 457 NGC 457 NGC 457 is an open star cluster in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel in 1787. and lies over 7,900 light years away from the Sun. It has an estimated age of 21 million years... |
Owl Cluster, E.T. Cluster |  |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
- | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
6.4 |
| C14 | NGC 869 NGC 869 NGC 869 is an open cluster located 7600 light years away in the constellation of Perseus. The cluster is most likely around 13 million years old. It is the westernmost of the Double Cluster with NGC 884. Located in the Perseus OB1 association both clusters are located physically close to one... & NGC 884 NGC 884 NGC 884 is an open cluster located 7600 light years away in the constellation of Perseus. The cluster is most likely around 12.5 million years old. It is the easternmost of the Double Cluster with NGC 869. Located in the Perseus OB1 association both clusters are located physically close to one... |
Double Cluster Double Cluster The Double Cluster is the common name for the naked-eye open clusters NGC 884 and NGC 869 , which are close together in the constellation Perseus. NGC 884 and NGC 869 are at distances of 7600 and 6800 light-years away, respectively, so they are also close to one another in space... , H & χ Persei |
 |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
7.3 | Perseus Perseus (constellation) Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek hero Perseus. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union... |
4 |
| C15 | NGC 6826 NGC 6826 NGC 6826 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Cygnus. It is commonly referred to as the "blinking planetary", although many other nebulae exhibit such "blinking". When viewed through a small telescope, the brightness of the central star overwhelms the eye when viewed directly,... |
Blinking Planetary | 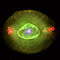 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
2.2 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
10 |
| C16 | NGC 7243 NGC 7243 NGC 7243, also Caldwell 16, is an open cluster and Caldwell object in the constellation Lacerta. It shines at magnitude +6.4. Its celestial coordinates are RA , dec . It is located near the naked-eye stars Alpha Lacertae, 4 Lacertae, an A-class double star, and planetary nebula IC 5217... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2.5 | Lacerta | 6.4 | ||
| C17 | NGC 147 NGC 147 NGC 147 is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy about 2.58 Mly away in the constellation Cassiopeia. NGC 147 is a member of the Local group of galaxies and a satellite galaxy of the Andromeda Galaxy . It forms a physical pair with the nearby galaxy NGC 185,another remote satellite of M31. It was... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
2,300 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
9.3 | |
| C18 | NGC 185 NGC 185 NGC 185 is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy about 2.08 million light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is a member of the Local group, and is a satellite galaxy of the Andromeda Galaxy . NGC 185 was discovered by William Herschel on November 30, 1787, and he cataloged it "H II.707"... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
2,300 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
9.2 | |
| C19 | IC 5146 IC 5146 IC 5146 is a reflection/emission nebula and Caldwell object in the constellation Cygnus. IC 5146 refers specifically to the star cluster and Sh2-125 to the nebula. It shines at magnitude +10.0/+9.3/+7.2. Its celestial coordinates are RA , dec... |
Cocoon Nebula |  |
Open Cluster and Nebula Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3.3 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
7.2 |
| C20 | NGC 7000 | North America Nebula North America Nebula The North America Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, close to Deneb . The remarkable shape of the emission nebula resembles that of the continent of North America, complete with a prominent Gulf of Mexico... |
 |
Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
1.8 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
4 |
21-30
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C21 | NGC 4449 NGC 4449 NGC 4449 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is located about 12 million light-years away, part of the M94 Group , a galaxy group relatively close to the Local Group containing the Milky Way... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
10,000 | Canes Venatici | 9.4 | ||
| C22 | NGC 7662 NGC 7662 NGC 7662 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Andromeda.... |
Blue Snowball | 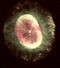 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
3.2 | Andromeda Andromeda (constellation) Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus... |
9 |
| C23 | NGC 891 NGC 891 NGC 891 is an edge-on unbarred spiral galaxy about 30 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 6 1784. The galaxy is a member of the NGC 1023 group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
31,000 | Andromeda Andromeda (constellation) Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus... |
10 | |
| C24 | NGC 1275 NGC 1275 NGC 1275 is a type 1.5 Seyfert galaxy located around 237 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation Perseus. NGC 1275 corresponds to the radio galaxy Perseus A and is situated near the centre of the large Perseus Cluster of galaxies... |
Perseus A |  |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
230,000 | Perseus Perseus (constellation) Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek hero Perseus. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union... |
11.6 |
| C25 | NGC 2419 NGC 2419 NGC 2419 is a globular cluster in the constellation Lynx. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 31, 1788... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
275 | Lynx Lynx (constellation) Lynx is a constellation in the northern sky, introduced in the 17th century by Johannes Hevelius. It is named after the lynx, a genus of cat. It is a very faint constellation; its brightest stars form a zigzag line.-History:... |
10.4 | ||
| C26 | NGC 4244 NGC 4244 NGC 4244, also Caldwell 26, is an edge-on loose Spiral galaxy and Caldwell object in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is part of the M94 Group , a galaxy group relatively close to the Local Group containing the Milky Way. It shines at magnitude +10.2/+10.6. Its celestial cooridinates are RA ,... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
10,000 | Canes Venatici | 10.2 | |
| C27 | NGC 6888 | Crescent Nebula Crescent Nebula The Crescent Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, about 5000 light years away. It is formed by the fast stellar wind from the Wolf-Rayet star WR 136 colliding with and energizing the slower moving wind ejected by the star when it became a red giant around 400,000 years ago... |
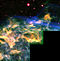 |
Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
4.7 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
7.4 |
| C28 | NGC 752 NGC 752 NGC 752 is an open cluster in the constellation Andromeda. The cluster was discovered by Caroline Herschel in 1783 and cataloged by her brother William Herschel in 1786, although an object that may have been NGC 752 was described by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654.The large cluster lies... |
 |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.2 | Andromeda Andromeda (constellation) Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus... |
5.7 | |
| C29 | NGC 5005 NGC 5005 NGC 5005 is an inclined spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. The galaxy has a relatively bright nucleus and a bright disk that contains multiple dust lanes... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
69,000 | Canes Venatici | 9.8 | |
| C30 | NGC 7331 NGC 7331 NGC 7331 is a spiral galaxy about away in the constellation Pegasus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
47,000 | Pegasus Pegasus (constellation) Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
9.5 |
31-40
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C31 | IC 405 IC 405 IC 405 is an emission/reflection nebula in the constellation Auriga, surrounding the bluish star AE Aurigae. It shines at magnitude +6.0. Its celestial coordinates are RA dec... |
Flaming Star Nebula | Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
1.6 | Auriga Auriga (constellation) Auriga is a constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'charioteer' and its stars form a shape that has been associated with the pointed helmet of a charioteer. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains among the 88 modern... |
- | |
| C32 | NGC 4631 NGC 4631 NGC 4631 is an edge-on spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. This galaxy's slightly distorted wedge shape gives it the appearance of a herring or a whale, whence its nickname... |
Whale Galaxy |  |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
22,000 | Canes Venatici | 9.3 |
| C33 | NGC 6992 | Veil Nebula Veil Nebula The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus. It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop , a large but relatively faint supernova remnant... |
Supernova Remnant Supernova remnant A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two... |
2.5 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
- | |
| C34 | NGC 6960 | Veil Nebula Veil Nebula The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus. It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop , a large but relatively faint supernova remnant... |
 |
Supernova Remnant Supernova remnant A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two... |
2.5 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
- |
| C35 | NGC 4889 NGC 4889 NGC 4889, also known as Caldwell 35, is a supergiant class-4 elliptical galaxy, the brightest within the Coma cluster and a Caldwell object in the constellation Coma Berenices. It shines at magnitude +11.4. Its celestial coordinates are RA 13h00.1m, DEC +27°59'... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
300,000 | Coma Berenices | 11.4 | ||
| C36 | NGC 4559 NGC 4559 NGC 4559 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Berenices. Distance estimates for NCG 4559 range from about 29 million light-years to 51 million light-years, averaging about 29 million light-years.... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
32,000 | Coma Berenices | 9.9 | |
| C37 | NGC 6885 NGC 6885 NGC 6885, also Caldwell 37, is an open cluster and Caldwell object in the constellation Vulpecula. It shines at magnitude +5.7/+8.1. Its celestial coordinates are RA , dec . It surrounds a naked-eye O or B-class star, and is located near M27 , the nebula IC 4954, and open clusters NGC 6882 and NGC... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.95 | Vulpecula | 6 | ||
| C38 | NGC 4565 NGC 4565 NGC 4565 is an edge-on spiral galaxy about 30 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices.... |
Needle Galaxy |  |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
32,000 | Coma Berenices | 9.6 |
| C39 | NGC 2392 | Eskimo Nebula Eskimo Nebula The Eskimo Nebula , also known as the Clownface Nebula or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula . It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of... /Clown Face Nebula |
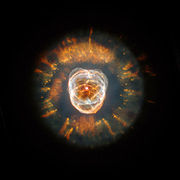 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
4 | Gemini Gemini (constellation) Gemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for "twins", and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology... |
10 |
| C40 | NGC 3626 NGC 3626 NGC 3626, also Caldwell 40, is a medium-tightness spiral galaxy and Caldwell object in the constellation Leo. It shines at magnitude +10.6/+10.9. Its celestial coordinates are RA , dec . It is located near the naked-eye class A4 star Zosma, as well as galaxies NGC 3608, NGC 3607, NGC 3659, NGC... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
86,000 | Leo Leo (constellation) Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for lion. Its symbol is . Leo lies between dim Cancer to the west and Virgo to the east.-Stars:... |
10.9 |
41-50
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C41 | Mel 25 | Hyades Hyades (star cluster) The Hyades is the nearest open cluster to the Solar System and one of the best-studied of all star clusters. The Hipparcos satellite, the Hubble Space Telescope, and infrared color-magnitude diagram fitting have been used to establish a distance to the cluster's center of ~153 ly... |
 |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
0.151 | Taurus Taurus (constellation) Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is a Latin word meaning 'bull', and its astrological symbol is a stylized bull's head:... |
0.5 |
| C42 | NGC 7006 NGC 7006 NGC 7006 is a globular cluster in the constellation Delphinus. NGC 7006 resides in the outskirts of the Milky Way. It is about 135.000 light-years away, five times the distance between the Sun and the centre of the galaxy, and it is part of the galactic halo... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
135 | Delphinus | 10.6 | |
| C43 | NGC 7814 NGC 7814 NGC 7814 is a spiral galaxy about 40 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. The galaxy is seen edge-on from Earth. It is sometimes referred to as "the little sombrero", a miniature version of Messier 104... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
49,000 | Pegasus Pegasus (constellation) Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
10.5 | |
| C44 | NGC 7479 NGC 7479 NGC 7479 is a barred spiral galaxy about 105 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784. Supernovae SN 1990U and SN2009jf occurred in NGC 7479. NGC 7479 is also recognized as a Seyfert galaxy undergoing starburst activity in the nucleus... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
106,000 | Pegasus Pegasus (constellation) Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
11 | |
| C45 | NGC 5248 NGC 5248 NGC 5248 is a compact intermediate spiral galaxy about 59 million light-years away in the constellation Boötes. It is a member of the NGC 5248 Group of galaxies, itself one of the Virgo III Groups strung out to the east of the Virgo Supercluster of galaxies... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
74,000 | Boötes | 10.2 | ||
| C46 | NGC 2261 NGC 2261 NGC 2261 is a variable nebula located in the constellation Monoceros. It is illuminated by the star R Monocerotis , which is not directly visible itself.... |
Hubble's Variable Nebula | Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
2.5 | Monoceros | - | |
| C47 | NGC 6934 NGC 6934 NGC 6934 is a globular cluster in the constellation Delphinus, about 50,000 light years distant. It was discovered by William Herschel on .-External links:* — ESA/Hubble Picture of the Week... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
57 | Delphinus | 8.9 | ||
| C48 | NGC 2775 NGC 2775 NGC 2775 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Cancer. This galaxy has a bulge and multiple spiral arms, on which few HII regions can be detected, implying recent star formation... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
55,000 | Cancer Cancer (constellation) Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as such. Its symbol is . Cancer is small and its stars are faint... |
10.3 | ||
| C49 | NGC 2237 | Rosette Nebula Rosette Nebula The Rosette Nebula is a large, circular H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy... |
 |
Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
4.9 | Monoceros | 9.0 |
| C50 | NGC 2244 NGC 2244 NGC 2244 is an open cluster in the Rosette Nebula, which is located in the constellation Monoceros. This cluster has several O-type stars, super hot stars that generate large amounts of radiation and stellar wind.... |
 |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.9 | Monoceros | 4.8 |
51-60
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C51 | IC 1613 IC 1613 IC 1613 is an irregular dwarf galaxy in the constellation Cetus near the star 26 Ceti. It was discovered in 1906 by Max Wolf, and is approaching Earth at 234 km/s.... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
2,300 | Cetus | 9.3 | ||
| C52 | NGC 4697 NGC 4697 NGC 4697 is an elliptical galaxy some 40 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It is a member of the NGC 4697 Group, a group of galaxies also containing NGC 4731 and several generally much smaller galaxies This group is about 55 million light-years away; it is one of the... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
76,000 | Virgo Virgo (constellation) Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for virgin, and its symbol is . Lying between Leo to the west and Libra to the east, it is the second largest constellation in the sky... |
9.3 | ||
| C53 | NGC 3115 NGC 3115 NGC 3115 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Sextans. The galaxy was discovered by William Herschel on February 22, 1787. At about 32 million light-years away from us it is several times bigger than our Milky Way... |
Spindle Galaxy Spindle Galaxy Spindle Galaxy may refer to one of two galaxies:* NGC 5866 in the constellation Draco * NGC 3115 in the constellation Sextans... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
22,000 | Sextans | 9.2 | |
| C54 | NGC 2506 NGC 2506 NGC 2506 is an open cluster in the constellation Monoceros. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1791.... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
10 | Monoceros | 7.6 | ||
| C55 | NGC 7009 | Saturn Nebula Saturn Nebula The Saturn Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation Aquarius. It was discovered by William Herschel on September 7, 1782, using a telescope of his own design in the garden at his home in Datchet, England, and was one of his earliest discoveries in his sky survey... |
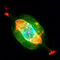 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
1.4 | Aquarius Aquarius (constellation) Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-bearer" or "cup-bearer", and its symbol is , a representation of water.... |
8 |
| C56 | NGC 246 NGC 246 NGC 246 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Cetus. The nebula and the stars associated with it are listed in several catalogs, as summarized by the SIMBAD database. The nebula's central star is the white dwarf HIP 3678.... |
 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
1.6 | Cetus | 8 | |
| C57 | NGC 6822 NGC 6822 NGC 6822 is a barred irregular galaxy approximately 1.6 million light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. Part of the Local Group of galaxies, it was discovered by E. E. Barnard in 1881 , with a six-inch refractor telescope. It is one of the closer galaxies to the Milky Way... |
Barnard's Galaxy |  |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
2,300 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
9 |
| C58 | NGC 2360 NGC 2360 NGC 2360 is an open cluster in the constellation Canis Major. It was discovered by Caroline Herschel in 1783.... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3.7 | Canis Major | 7.2 | ||
| C59 | NGC 3242 NGC 3242 NGC 3242 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Hydra.William Herschel discovered the nebula on February 7, 1785, and cataloged it as H IV.27... |
Ghost of Jupiter |  |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
1.4 | Hydra Hydra (constellation) Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees. It has a long history, having been included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake... |
9 |
| C60 | NGC 4038 | Antennae Galaxies Antennae Galaxies The Antennae Galaxies are a pair of interacting galaxies in the constellation Corvus. They are currently going through a phase of starburst. They were discovered by William Herschel in 1785... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
83,000 | Corvus Corvus (constellation) Corvus is a small constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for raven or crow. It includes only 11 stars visible to the naked eye... |
10.7 |
61-70
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C61 | NGC 4039 | Antennae Galaxies Antennae Galaxies The Antennae Galaxies are a pair of interacting galaxies in the constellation Corvus. They are currently going through a phase of starburst. They were discovered by William Herschel in 1785... |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
83,000 | Corvus Corvus (constellation) Corvus is a small constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for raven or crow. It includes only 11 stars visible to the naked eye... |
13 | |
| C62 | NGC 247 NGC 247 NGC 247 is an Intermediate spiral galaxy about 11.1 Mly away in the constellation Cetus. This distance was confirmed in late February 2011. Previous measurements showed that the galaxy was about 12.2 Mly away, but was proved to be wrong... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
6,800 | Cetus | 8.9 | |
| C63 | NGC 7293 | Helix Nebula Helix Nebula The Helix Nebula is a large planetary nebula located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, probably before 1824, this object is one of the closest to the Earth of all the bright planetary nebulae. The estimated distance is about 215 parsecs or 700 light-years... |
 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
0.522 | Aquarius Aquarius (constellation) Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-bearer" or "cup-bearer", and its symbol is , a representation of water.... |
7.3 |
| C64 | NGC 2362 NGC 2362 NGC 2362 is an open cluster in the constellation Canis Major. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654. Its brightest star is Tau Canis Majoris, and therefore it is sometimes called the Tau Canis Majoris Cluster. NGC 2362 has a distance of 1.48 kpc and is a relatively young 4–5... |
Open Cluster and Nebula Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
5.1 | Canis Major | 4.1 | ||
| C65 | NGC 253 | Sculptor Galaxy/Silver Coin Galaxy |  |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
9,800 | Sculptor Sculptor (constellation) Sculptor is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. It represents a sculptor. It was introduced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. He originally named it Apparatus Sculptoris , but the name was later shortened.-Notable features:No stars brighter than 3rd magnitude are... |
7.1 |
| C66 | NGC 5694 NGC 5694 NGC 5694 is a globular cluster in the constellation Hydra. It was discovered in 1784 by William Herschel.... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
113 | Hydra Hydra (constellation) Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees. It has a long history, having been included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake... |
10.2 | ||
| C67 | NGC 1097 NGC 1097 NGC 1097 is a barred spiral galaxy about 45 million light-years away in the constellation Fornax. As of 2006, three supernovae have been observed in NGC 1097.... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
47,000 | Fornax | 9.3 | |
| C68 | NGC 6729 NGC 6729 NGC 6729 is a reflection/emission nebula in the constellation Corona Australis. It was discovered by Johann Friedrich Julius Schmidt in 1861.... |
Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
0.424 | Corona Australis | - | ||
| C69 | NGC 6302 NGC 6302 NGC 6302 is a bipolar planetary nebula in the constellation Scorpius. The structure in the nebula is among the most complex ever observed in planetary nebulae... |
Bug Nebula |  |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
5.2 | Scorpius | 13 |
| C70 | NGC 300 NGC 300 NGC 300 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Sculptor. It is one of the closest galaxies to the Local Group, and probably lies between us and the Sculptor Group. It is the brightest of the five main spirals in the direction of the Sculptor Group... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
3,900 | Sculptor Sculptor (constellation) Sculptor is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. It represents a sculptor. It was introduced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. He originally named it Apparatus Sculptoris , but the name was later shortened.-Notable features:No stars brighter than 3rd magnitude are... |
9 |
71-80
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C71 | NGC 2477 NGC 2477 NGC 2477 is an open cluster in the constellation Puppis. It contains about 300 stars, and was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751. The cluster's age has been estimated at about 700 million years.- Visual appearance :... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3.7 | Puppis | 5.8 | ||
| C72 | NGC 55 NGC 55 NGC 55 is a barred irregular galaxy located about 7 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. Along with its neighbor NGC 300, it is one the closest galaxies to the Local Group, probably lying between us and the Sculptor Group.-Nearby galaxies and group information:NGC 55 and the... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
4,200 | Sculptor Sculptor (constellation) Sculptor is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. It represents a sculptor. It was introduced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. He originally named it Apparatus Sculptoris , but the name was later shortened.-Notable features:No stars brighter than 3rd magnitude are... |
8 | |
| C73 | NGC 1851 NGC 1851 NGC 1851 is a globular cluster located in the constellation Columba.- External links :*... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
39.4 | Columba Columba (constellation) Columba is a small, faint constellation created in the late sixteenth century. Its name is Latin for dove. It is located just south of Canis Major and Lepus.-History:... |
7.3 | |
| C74 | NGC 3132 NGC 3132 NGC 3132 is a bright and extensively studied planetary nebula in the constellation Vela. Its distance from Earth is estimated at about 550 kpc... |
Eight Burst Nebula | 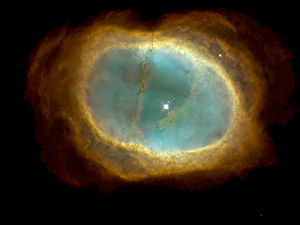 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
2 | Vela Vela (constellation) Vela is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship Argo Navis, which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis.-Stars:... |
8 |
| C75 | NGC 6124 NGC 6124 NGC 6124 is an open cluster located 18,600 light years away in the constellation Scorpius. It was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751 during his South African tour.The cluster is large and bright, with about 125 stars visible.... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.5 | Scorpius | 5.8 | ||
| C76 | NGC 6231 NGC 6231 NGC 6231 is an open cluster located near Zeta Scorpii. Zeta1 is a member of this star cluster.... |
Open Cluster and Nebula Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
6 | Scorpius | 2.6 | ||
| C77 | NGC 5128 | Centaurus A Centaurus A Centaurus A is a prominent galaxy in the constellation of Centaurus. There is considerable debate in the literature regarding the galaxy's fundamental properties such as its Hubble type and distance... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
16,000 | Centaurus | 7 |
| C78 | NGC 6541 | Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
22.3 | Corona Australis | 6.6 | ||
| C79 | NGC 3201 NGC 3201 NGC 3201 is a low galactic latitude globular cluster in the Vela constellation. It has a very low central concentration of stars.It was discovered by James Dunlop on May 28, 1826.-External links:* *... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
17 | Vela Vela (constellation) Vela is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship Argo Navis, which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis.-Stars:... |
6.8 | |
| C80 | NGC 5139 | Omega Centauri Omega Centauri Omega Centauri or NGC 5139 is a globular clusterin the constellation of Centaurus, discovered by Edmond Halley in 1677 who listed it as a nebula. Omega Centauri had been listed in Ptolemy's catalog 2000 years ago as a star. Lacaille included it in his catalog as number I.5... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
17.3 | Centaurus | 3.7 |
81-90
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C81 | NGC 6352 NGC 6352 NGC 6352 is a globular cluster in the southern constellation Ara. A telescope with a 150mm primary mirror is required to resolve the stars within this loose cluster.... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
18.6 | Ara Ara (constellation) Ara is a southern constellation situated between Scorpius and Triangulum Australe. Its name is Latin for "altar". Ara was one of the 48 Greek constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical... |
8.2 | ||
| C82 | NGC 6193 NGC 6193 NGC 6193 is open cluster containing 27 stars in the constellation Ara, visible to the unaided eye. The cluster is associated with a nearby nebulosity, NGC 6188.-List of stars in cluster:-References:* * * * * * *... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.3 | Ara Ara (constellation) Ara is a southern constellation situated between Scorpius and Triangulum Australe. Its name is Latin for "altar". Ara was one of the 48 Greek constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical... |
5.2 | ||
| C83 | NGC 4945 NGC 4945 NGC 4945 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Centaurus. It is thought to be quite similar to the Milky Way Galaxy, but X-ray observations show that NGC 4945 has an unusual, energetic, Seyfert 2 nucleus that might house a large black hole... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
17,000 | Centaurus | 9 | |
| C84 | NGC 5286 | Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
36 | Centaurus | 7.6 | ||
| C85 | IC 2391 IC 2391 IC 2391 is an open cluster in the constellation Vela. It has been purported to be first described by the Persian astronomer Al Sufi in about 964. It was also found by Abbe Lacaille and has been cataloged as Lac II 5. The cluster is at a distance of about 500 light-years away from Earth and can be... |
Omicron Vel Cluster | Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
0.5 | Vela Vela (constellation) Vela is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship Argo Navis, which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis.-Stars:... |
2.5 | |
| C86 | NGC 6397 NGC 6397 NGC 6397 is a globular cluster in the constellation Ara. It is located about 7,200 light-years from Earth, making it one of the two nearest globular clusters to Earth... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
7.5 | Ara Ara (constellation) Ara is a southern constellation situated between Scorpius and Triangulum Australe. Its name is Latin for "altar". Ara was one of the 48 Greek constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical... |
5.7 | |
| C87 | NGC 1261 NGC 1261 -External links:****... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
55.5 | Horologium | 8.4 | ||
| C88 | NGC 5823 | Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3.4 | Circinus | 7.9 | ||
| C89 | NGC 6087 NGC 6087 NGC 6087 is one of the brightest open clusters in the constellation Norma with a magnitude of 5.4. It is approximately 3500 light-years away and contains about 40 stars of the seventh to the eleventh magnitude, the brightest being 6.5 magnitude S Normae.... (mistakenly written as NGC 6067 in the original, but description is that of NGC 6087) |
S Norma Cluster | Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3.3 | Norma Norma (constellation) Norma is a small and inconspicuous constellation in the southern hemisphere between Scorpius and Centaurus. Its name is Latin for normal, referring to a right angle, and is variously considered to represent a rule, a carpenter's square, a set square or a level.... |
5.4 | |
| C90 | NGC 2867 NGC 2867 NGC 2867 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Carina. It was discovered by John Herschel on April 1, 1834.... |
 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
5.5 | Carina Carina (constellation) Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:... |
10 |
91-100
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C91 | NGC 3532 NGC 3532 NGC 3532, also known as the Wishing Well Cluster, is an open cluster in the constellation Carina. It got the name because through a telescope's eyepiece it appears like dozens of silver coins twinkling at the bottom of a wishing well.... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.6 | Carina Carina (constellation) Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:... |
3 | ||
| C92 | NGC 3372 | Eta Carinae Nebula | Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... |
7.5 | Carina Carina (constellation) Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:... |
- | |
| C93 | NGC 6752 NGC 6752 NGC 6752 is a globular cluster in the constellationPavo. It is the third brightest in the sky, after 47 Tucanae and Omega Centauri.-References:* *... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
13 | Pavo Pavo (constellation) Pavo is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for peacock. It is one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 in... |
5.4 | ||
| C94 | NGC 4755 | Jewel Box | Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.9 | Crux | 4.2 | |
| C95 | NGC 6025 NGC 6025 NGC 6025 is an open cluster located 2,700 light years away in the Triangulum Australe constellation. It was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751 or 1752 during his South Africa tour.-External links:**-References:... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2.5 | Triangulum Australe | 5.1 | ||
| C96 | NGC 2516 NGC 2516 NGC 2516 is an open cluster in the southern sky in the constellation Carina near Volans discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751-1752. From its catalog numbers it is called NGC 2516 or C 96; its popular name is The Diamond Cluster.... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.3 | Carina Carina (constellation) Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:... |
3.8 | ||
| C97 | NGC 3766 NGC 3766 NGC 3766, the Pearl Cluster, is an open star cluster in the constellation Centaurus, visible in the Southern hemisphere. It was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751-1752.-External links:* * *... |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
5.8 | Centaurus | 5.3 | ||
| C98 | NGC 4609 | Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.2 | Crux | 6.9 | ||
| C99 | - | Coalsack Nebula Coalsack Nebula The Coalsack Dark Nebula is the most prominent dark nebula in the skies, easily visible to the naked eye as a dark patch silhouetted against the southern Milky Way. It was known pre-historically in the Southern Hemisphere and was observed by Vicente Yáñez Pinzón in 1499... |
 |
Dark Nebula Dark nebula A dark nebula is a type of interstellar cloud that is so dense that it obscures the light from the background emission or reflection nebula or that it blocks out background stars . The extinction of the light is caused by interstellar dust grains located in the coldest, densest parts of larger... |
0.61 | Crux | - |
| C100 | IC 2944 IC 2944 IC 2944, also known as the Running Chicken Nebula or the Lambda Cen Nebula, is an open cluster with an associated emission nebula found in the constellation Centaurus, near the star Lambda Centauri... |
Lambda Centauri Nebula |  |
Open Cluster and Nebula Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
6 | Centaurus | 4.5 |
101-109
| Caldwell number | NGC number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance to object in thousands of light years | Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C101 | NGC 6744 NGC 6744 NGC 6744 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 30 million light-years away in the constellation Pavo. It is considered one of the most Milky Way-like spiral galaxies in our immediate vicinity, with flocculent arms and an elongated core... |
 |
Galaxy Galaxy A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a... |
34,000 | Pavo Pavo (constellation) Pavo is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for peacock. It is one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 in... |
9 | |
| C102 | IC 2602 IC 2602 IC 2602 is an open cluster in the constellation Carina. It was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751 from South Africa. The cluster is at a distance of about 479 light-years away from Earth and can be seen with the naked eye... |
Theta Car Cluster |  |
Open Cluster Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
0.492 | Carina Carina (constellation) Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was formerly part of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until that constellation was divided in three.-Stars:... |
1.9 |
| C103 | NGC 2070 | Tarantula Nebula Tarantula Nebula The Tarantula Nebula is an H II region in the Large Magellanic Cloud . It was originally thought to be a star, but in 1751 Nicolas Louis de Lacaille recognized its nebular nature.... |
 |
Open Cluster and Nebula Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
170 | Dorado | 8.2 |
| C104 | NGC 362 NGC 362 NGC 362 is a globular cluster located in the constellation Tucana in the Southern Hemisphere. It was discovered on August 1, 1826 by James Dunlop.... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
27.7 | Tucana | 6.6 | ||
| C105 | NGC 4833 NGC 4833 NGC 4833 is a globular cluster discovered by Abbe Lacaille during his 1751-1752 journey to South Africa, and catalogued in 1755. It was subsequently observed and catalogued by James Dunlop and Sir John Herschel whose instruments could resolve it into individual stars.The globular cluster is... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
19.6 | Musca | 7.4 | |
| C106 | NGC 104 | 47 Tucanae 47 Tucanae 47 Tucanae or just 47 Tuc is a globular cluster located in the constellation Tucana. It is about 16,700 light years away from Earth, and 120 light years across. It can be seen with the naked eye, with a visual magnitude of 4.0... |
 |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
14.7 | Tucana | 4 |
| C107 | NGC 6101 NGC 6101 NGC 6101 is a globular cluster in the constellation Apus. It requires a telescope of at least 200 mm aperture to resolve individual stars.... |
Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
49.9 | Apus | 9.3 | ||
| C108 | NGC 4372 | Globular Cluster Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
18.9 | Musca | 7.8 | ||
| C109 | NGC 3195 NGC 3195 NGC 3195 is a planetary nebulae located in the constellation Chamaeleon. It is the most southern of all the bright planetary nebula in the sky, and remains completely invisible to all northern observers... |
 |
Planetary Nebula Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
5.4 | Chamaeleon | - |
See also
- Messier Catalogue
- Herschel 400 CatalogueHerschel 400 CatalogueThe Herschel 400 catalogue is a subset of William Herschel's original deep sky catalogue of 2,500 deep sky objects, selected by Brenda F. Guzman , Lydel Guzman, Paul Jones, James Morrison, Peggy Taylor and Sara Saey of the Ancient City Astronomy Club in St. Augustine, Florida, USA circa 1980...
- New General CatalogueNew General CatalogueThe New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects...
(NGC) - Index CatalogueIndex CatalogueThe Index Catalogue —also known as the Index Catalogue of Nebulae, the Index Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, IC I, or IC II— is a catalogue of galaxies, nebulae and star clusters that serves as a supplement to the New General Catalogue...
(IC) - Revised New General CatalogueRevised New General CatalogueThe Revised New General Catalogue and companion Revised Index Catalogue is a revision to the original New General Catalogue and Index Catalogues made by J. L. E. Dreyer. Some of the brightnesses of objects measured by Dreyer were not accurate or the description of the object was not accurate....
(RNGC) - Revised Index Catalogue (RIC)

