Cajun French
Encyclopedia

Variety (linguistics)
In sociolinguistics a variety, also called a lect, is a specific form of a language or language cluster. This may include languages, dialects, accents, registers, styles or other sociolinguistic variation, as well as the standard variety itself...
or dialects of the French language
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
spoken primarily in Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
, specifically in the southern and southwestern parishes.
While historically other Louisiana French dialects, including Colonial or Plantation Society French
Colonial French
Colonial French or Colonial Louisiana French is one of the three dialects into which Louisiana French is typically divided . Formerly spoken widely in what is now the U.S...
, have been spoken in the state, these are now considered to have largely merged with the original Cajun dialects. However, there are still significant populations of Louisiana Creoles, from White-Americans, African-Americans, and Native American tribes who continue to speak this variety of French. Parishes where this dialect is found include, but are not limited to, Avoyelles
Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana
Avoyelles is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Marksville. In 2000, its population was 41,481. The parish is named for the Avoyel Indian tribe.-History:...
, Iberia
Iberia Parish, Louisiana
Iberia Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is New Iberia. As of 2000, the population was 73,266.Iberia Parish is part of the New Iberia Micropolitan Statistical Area as well as the Lafayette–Acadiana Combined Statistical Area.Iberia, along with...
, Pointe Coupée
Pointe Coupee Parish, Louisiana
Pointe Coupee Parish, pronounced "Pwent Koo-Pay" and , is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is New Roads. As of 2000, the population was 22,763....
, St. Martin
St. Martin Parish, Louisiana
St. Martin Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is St. Martinville. As of the 2000 census, the population was 48,583.St...
, St. Landry
St. Landry Parish, Louisiana
St. Landry Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is at the heart of Acadian/Cajun culture and heritage in Louisiana. The parish seat is Opelousas. According to the 2010 census, the population of St. Landry Parish is 83,384.St...
, St. Mary, St. Tammany, Terrebonne
Terrebonne Parish, Louisiana
Terrebonne Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Houma. Its population was 111,860...
, Plaquemines, and other parishes south of Orleans.
Cajun French is not the same as Louisiana Creole
Louisiana Creole French
Louisiana Creole is a French Creole language spoken by the Louisiana Creole people of the state of Louisiana. The language consists of elements of French, Spanish, African, and Native American roots.-Geography:...
. Cajun French is almost solely derived from Acadian French
Acadian French
Acadian French , is a regionalized dialect of Canadian French. It is spoken by the francophone population of the Canadian province of New Brunswick, by small minorities in areas in the Gaspé region of eastern Quebec, by small groups of francophones in Prince Edward Island, in several tiny pockets...
as it was spoken in the French colony of Acadia
Acadia
Acadia was the name given to lands in a portion of the French colonial empire of New France, in northeastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine. At the end of the 16th century, France claimed territory stretching as far south as...
(located in what are now the Maritime provinces of Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
and in Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
) at the time of the expulsion of the Acadians in the mid 18th century; however, a significant amount of cultural vocabulary is derived from Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
, and Haitian Creole.
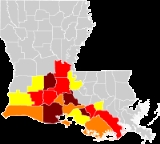
Parishes where Cajun French is spoken
- AcadiaAcadia Parish, LouisianaAcadia Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Crowley. According to the 2010 census, the population of Acadia Parish is 61,773. The parish was founded from parts of St...
- AscensionAscension Parish, LouisianaAscension Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is the fastest growing parish in the state. Its population is 107,215 which is 39.9% greater than the 2000 census...
- AllenAllen Parish, LouisianaAllen Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Oberlin. As of the 2000 census, the population was 25,440. Allen Parish is in southwestern Louisiana, southwest of Alexandria....
- AssumptionAssumption Parish, LouisianaAssumption Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana, and was formed in 1807 as an original parish of the Louisiana Territory. Its parish seat is Napoleonville. In 2000, its population was 23,388. Assumption is one of the 22 Acadiana parishes. Its major product is sugarcane...
- AvoyellesAvoyelles Parish, LouisianaAvoyelles is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Marksville. In 2000, its population was 41,481. The parish is named for the Avoyel Indian tribe.-History:...
- CalcasieuCalcasieu Parish, LouisianaCalcasieu Parish[p] is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Lake Charles. As of 2010, the parish population was 192,768...
- CameronCameron Parish, LouisianaCameron Parish is the parish with the most land area in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Cameron and as of 2010, the population was 6,839...
- EvangelineEvangeline Parish, Louisiana-Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 35,434 people, 12,736 households, and 9,157 families residing in the parish. The population density was 53 people per square mile . There were 14,258 housing units at an average density of 22 per square mile...
- IberiaIberia Parish, LouisianaIberia Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is New Iberia. As of 2000, the population was 73,266.Iberia Parish is part of the New Iberia Micropolitan Statistical Area as well as the Lafayette–Acadiana Combined Statistical Area.Iberia, along with...
- Jefferson DavisJefferson Davis Parish, LouisianaJefferson Davis Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Jennings. As of 2000, its population was 31,435. Jefferson Davis Parish is named after the president of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, Jefferson Davis. It is located in southwestern...
- LafayetteLafayette Parish, LouisianaLafayette Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Lafayette. According to the 2010 Census, its population was recorded as 221,578....
- LafourcheLafourche Parish, LouisianaLafourche Parish is a parish located in the south of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It was originally the northern part of Lafourche Interior Parish, which consisted of the present parishes of Lafourche and Terrebonne. The parish seat is Thibodaux...
- Pointe CoupeePointe Coupee Parish, LouisianaPointe Coupee Parish, pronounced "Pwent Koo-Pay" and , is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is New Roads. As of 2000, the population was 22,763....
- St. CharlesSt. Charles Parish, LouisianaSt. Charles Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Hahnville. In 2010, its population was 52,780. In the eighteenth and nineteenth century, this was part of the German Coast, an area along the Mississippi River settled by numerous German pioneers in the...
- St. James
- St. LandrySt. Landry Parish, LouisianaSt. Landry Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is at the heart of Acadian/Cajun culture and heritage in Louisiana. The parish seat is Opelousas. According to the 2010 census, the population of St. Landry Parish is 83,384.St...
- St. MartinSt. Martin Parish, LouisianaSt. Martin Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is St. Martinville. As of the 2000 census, the population was 48,583.St...
- St. MarySt. Mary Parish, LouisianaSt. Mary Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Franklin. As of 2000, the population was 53,500.The Morgan City Micropolitan Statistical Area includes all of St. Mary Parish.-Geography:...
- TerrebonneTerrebonne Parish, LouisianaTerrebonne Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Houma. Its population was 111,860...
- VermilionVermilion Parish, LouisianaVermilion Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Abbeville. As of the 2010 census, the population was 57,999....
History
The French resettled in Louisiana, establishing the culture and language there. Through the Acadian FrenchAcadian French
Acadian French , is a regionalized dialect of Canadian French. It is spoken by the francophone population of the Canadian province of New Brunswick, by small minorities in areas in the Gaspé region of eastern Quebec, by small groups of francophones in Prince Edward Island, in several tiny pockets...
language, Cajun is ultimately descended from the dialects of Anjou
Anjou
Anjou is a former county , duchy and province centred on the city of Angers in the lower Loire Valley of western France. It corresponds largely to the present-day département of Maine-et-Loire...
and Poitou
Poitou
Poitou was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers.The region of Poitou was called Thifalia in the sixth century....
. The word "Cajun" is an anglicization of "Cadien," itself a shortened pronunciation of "Acadien."
French immigration continued in the 19th century until the start of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, bringing large numbers of francophones speaking something more similar to today's Metropolitan French into Louisiana. Over time, through contact between groups, including a high rate of intermarriage, the dialects would mix, to produce the French we today call Cajun French.
Over time Cajun became the firmly established language of many south Louisiana parishes. Cajun was not only spoken by the Cajun
Cajun
Cajuns are an ethnic group mainly living in the U.S. state of Louisiana, consisting of the descendants of Acadian exiles...
people but also by other ethnic groups that lived in Acadian settled areas. Creoles
Louisiana Creole people
Louisiana Creole people refers to those who are descended from the colonial settlers in Louisiana, especially those of French and Spanish descent. The term was first used during colonial times by the settlers to refer to those who were born in the colony, as opposed to those born in the Old World...
, Amerindian ethnic groups such as the Houma
Houma Tribe
The Houma people are a Native America tribe. They belong to the United Houma Nation, a state recognized tribe in Louisiana. They primarily live in East and West Feliciana, and Pointe Coupee Parishes, about 100 miles north of the town of Houma named for them, west of the mouth of the Mississippi...
, Chitimacha
Chitimacha
The Chitimacha are a Native American federally recognized tribe that lives in the U.S. state of Louisiana, mainly in St. Mary Parish. They currently number about 720 people. The Chitimacha language is a language isolate.- History :The Chitimacha's historic home was the southern Louisiana coast...
, Pointe-au-Chien, Bayougoula, Tunica-Biloxi
Tunica-Biloxi
The modern Tunica-Biloxi tribe live in Mississippi and east central Louisiana. The modern tribe is composed of descendants of Tunica, Biloxi , Ofo , Avoyel , and Muskogean Choctaw. They speak mostly English and French...
, Atakapa
Atakapa
The Atakapan people are a Southeastern culture of Native American tribes who spoke Atakapa and historically lived along the Gulf of Mexico. They called themselves the Ishak, pronounced "ee-SHAK", which translates as "The People". Although the people were decimated by infectious disease after...
, Opelousa, Okelousa
Okelousa
The Okelousa are Native American people originally from the Southern United States . The name is taken from the Chocktaw word for "black water"-External links:***...
, and Avoyel
Avoyel
The Avoyel or Avoyelles was a small Natchez-speaking tribe who inhabited land near the mouth of the Red River in the area of present-day Marksville, Louisiana. The indigenous name for this tribe is Tamoucougoula. The word Avoyel is of French derivation and means either "Flint People" or "the...
, through their cohabitation in south Louisiana's parishes eventually became proficient in Cajun French. Creoles and Amerindians already spoke French prior to the arrival of the Acadian people in Louisiana.
The term "Cajun
Cajun
Cajuns are an ethnic group mainly living in the U.S. state of Louisiana, consisting of the descendants of Acadian exiles...
" is reported to have derived from the English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
pronunciation of the French word Acadien. Some Cajuns call themselves "Cadiens" or "Cadjins" in French. The first spelling is derived from the French spelling "Acadien" and the second is an approximation, using French phonetics, of the pronunciation of the group name in Cajun French. "Cadien" is the French spelling preferred by Cajun academics. "Cajun" is an English word which is not accepted by Cajun academics to designate the group in French. The primary region where Cajun French is spoken is called Acadiana
Acadiana
Acadiana, or The Heart of Acadiana, is the official name given to the French Louisiana region that is home to a large Francophone population. Of the 64 parishes that make up Louisiana, 22 named parishes and other parishes of similar cultural environment, make up the intrastate...
(not to be confused with Acadia
Acadia
Acadia was the name given to lands in a portion of the French colonial empire of New France, in northeastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine. At the end of the 16th century, France claimed territory stretching as far south as...
, which refers to the region where Acadian French is spoken). Cajun areas of Louisiana sometimes form partnerships with Acadians in Canada who send French teachers to teach the language in schools.
In 1984, Jules O. Daigle, a Roman Catholic priest, published A Dictionary of the Cajun Language the first dictionary devoted to Cajun French. Once considered an authority on the language, it is not exhaustive; it omits alternate spellings and synonyms which Father Daigle deemed "perversions" of the language, but which are nonetheless popular among Cajun speakers and writers. Though remaining useful today, Daigle's dictionary has been superseded by Dictionary of Louisiana French (2010) edited by Albert Valdman and other authorities on the language.
Decline and resurgence
Many residents of Acadiana are bilingualMultilingualism
Multilingualism is the act of using, or promoting the use of, multiple languages, either by an individual speaker or by a community of speakers. Multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. Multilingualism is becoming a social phenomenon governed by the needs of...
, having learned French at home and English in school. In recent years the number of speakers of Cajun French has diminished considerably, but efforts are being made to reintroduce the language in schools. The Council for the Development of French in Louisiana
Council for the Development of French in Louisiana
The Council for the Development of French in Louisiana, or CODOFIL — known in French as le Conseil pour le développement du français en Louisiane and Konséy pou Dévelopmen di françé en Lwizyàn in Creole — is a state agency created in 1968 by the Louisiana legislature...
(CODOFIL) was established in 1968 to promote the preservation of French language and culture in Louisiana. In addition to this, some Louisiana universities, such as LSU, offer courses in Cajun French in the hopes of preserving the language.
Some people question whether the Cajun language will survive another generation. The number of people who speak Cajun has declined dramatically over the last fifty years. Many parents intentionally did not teach their children the Cajun language to encourage English language fluency, in hopes that the children would have a better life in an English-speaking nation. However, many of these grandparents are discovering that their grandchildren are researching and trying to learn the language.
Many young adults are learning enough Cajun to understand Cajun music lyrics. Also, there is now a trend to use Cajun language websites to learn the dialect. Culinary words and terms of endearment such as "cher" /ʃæ/ (dear) and "nonc" (uncle) are still heard among otherwise English-speaking Cajuns. Some of the language will continue to exist, but whether many people will be able to conduct a full and fluent conversation in the language is still uncertain. Currently, Cajun French is considered an endangered language
Endangered language
An endangered language is a language that is at risk of falling out of use. If it loses all its native speakers, it becomes a dead language. If eventually no one speaks the language at all it becomes an "extinct language"....
.
The Louisiana state legislature has greatly shifted its stance on the status of French. With the passage of Legislative Act No. 409 in 1968, the Louisiana governor was, and still is granted the authorization "to establish the Council for the Development of Louisiana-French" and that the agency is to consist of no more than fifty members including a chairman. The name was soon changed to CODOFIL and was granted the power to "do anything possible and necessary to encourage the development, usage and preservation of French as it exists in Louisiana.
An article written online by the Université Laval
Université Laval
Laval University is the oldest centre of education in Canada and was the first institution in North America to offer higher education in French...
argues that the state of Louisiana's shift from anti-French to softly promoting the language has been of great importance to the survival of the language. The article states that it is advantageous to invigorate the revival of the language in order to better cherish the state's rich heritage as well as protect a francophone minority that has suffered greatly from negligence by political and religious leaders. Furthermore, the university's article claims that it is CODOFIL and not the state itself that retains language politics
Language politics
Language politics is a term used to describe political consequences of linguistic differences between people, or on occasion the political consequences of the way a language is spoken and what words are used. It means language can express some authority. Examples include:*Recognition of a...
and that the only political stance the state of Louisiana makes is that of non interference. All of this culminates in the fact that outside of the extreme southern portions of the state, French remains a secondary language that retains heavy cultural and identity values.
According to Jacques Henry, chairman of CODOFIL, much progress has been made for francophones and that the future of French in Louisiana is not merely a symbolic one. According to statistics gathered by CODOFIL, the past twenty years has seen widespread acceptance of French immersion programs. Mr. Henry goes further to write that the official recognition, appreciation by parents, and inclusion of French in schools reflects growing valorization of the language and francophone culture. Henry ends his article by writing that ultimately the survival of French in Louisiana will be guaranteed by Cajun parents and politicians, stating that the French language's survival is by no means guaranteed but that there is still hope.
Subdialects
Cajun French often varies by community and ethnic group. However, Cajun French can be said to have two general dialects: Prairie French and Bayou French.Prairie French
Prairie French is spoken among Cajun, Creole and Black residents in southwest Louisiana.Bayou French
Bayou French is primarily spoken among Cajuns and American Indians in southeast Louisiana. The Black population of southeast Louisiana now only has a few speakers and those are mostly non-fluent. It has a thicker creole influence, and bilingual speakers of creole tend to switch back and forth in this accent.Words of Native American origin
| Words of Native American Origin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Term | Gloss | Origin |
| Bayou | Choctaw bayuk | |
| Raccoon | Choctaw or Mobilian shaui | |
| Bowfin | Choctaw shupik, "mudfish" | |
| Palmetto | Carib allatani | |
| Pecan | Algonquian via Mobilian | |
| Sunfish | Choctaw patàssa "flat" | |
| Persimmon | Illinois piakimin, via Mobilian | |
| (Black)bird | Possibly Atakapa t'sak | |
See also
- Acadian FrenchAcadian FrenchAcadian French , is a regionalized dialect of Canadian French. It is spoken by the francophone population of the Canadian province of New Brunswick, by small minorities in areas in the Gaspé region of eastern Quebec, by small groups of francophones in Prince Edward Island, in several tiny pockets...
- List of Louisiana parishes by French-speaking population
- French in the United StatesFrench in the United StatesThe French language is spoken as a minority language in the United States. According to year 2000 census figures, 1.6 million Americans over the age of five speak the language at home; making French the fourth most-spoken language in the country behind English, Spanish, and Chinese...
- Canadian FrenchCanadian FrenchCanadian French is an umbrella term referring to the varieties of French spoken in Canada. French is the mother tongue of nearly seven million Canadians, a figure constituting roughly 22% of the national population. At the federal level it has co-official status alongside English...
- Cajun EnglishCajun EnglishCajun English is the dialect of English spoken by Cajuns living in southern Louisiana and, to some extent, in eastern Texas. Cajun English is significantly influenced by Cajun French, the historical language of the Cajun people, a direct descendant of Acadian French, which differs somewhat from...
- Endangered languageEndangered languageAn endangered language is a language that is at risk of falling out of use. If it loses all its native speakers, it becomes a dead language. If eventually no one speaks the language at all it becomes an "extinct language"....
- List of endangered languages
General references
Cajun French Dictionary and Phrasebook by Clint Bruce and Jennifer Gipson ISBN 0-7818-0915-0. Hippocrene Books Inc.Tonnerre mes chiens! A glossary of Louisiana French figures of speech by Amanda LaFleur ISBN 0-9670838-9-3. Renouveau Publishing.
A Dictionary of the Cajun Language by Rev. Msgr. Jules O. Daigle, M.A., S.T.L. ISBN 0-9614245-3-2. Swallow Publications, Inc.
Cajun Self-Taught by Rev. Msgr. Jules O. Daigle, M.A., S.T.L. ISBN 0-9614245-4-0. Swallow Publications, Inc.
Language Shift in the Coastal Marshes of Louisiana by Kevin J. Rottet ISBN 0-8204-4980-6. Peter Lang Publishing, Inc.
Conversational Cajun French I by Harry Jannise and Randall P. Whatley ISBN 0-8828-9316-5. The Chicot Press.
Dictionary of Louisiana French as Spoken in Cajun, Creole, and American Indian Communities, senior editor Albert Valdman. ISBN 978-1604734034 Jackson: University Press of Mississippi, 2010.
External links
- LSU Cajun Pages
- A beginner's introduction: What is Cajun French?
- Le français cadien par thèmes: Cajun French by Themes
- Faux amis: How to Speak French in Louisiana Without Getting in Trouble
- Glossaire Français Cadien-Français Européen: Cajun-Standard French Glossary
- L'interrogatif en français cadien: Forming questions in Cajun French
- Les pronoms personnels cadiens: Cajun personal pronouns
- Les pronoms sujets et le système verbal: The Basics of Verb Conjugation
- Les animaux dans la métaphore populaire: Cajun animal metaphors
- Un glossaire cadien-anglais: Cajun French to English glossary
- La Base de données lexicographiques de la Louisiane
- TVTL.tv Télévision Terrebonne-LaFourche
- Council for the Development of French in Louisiana (CODOFIL)
- Cajun language websites
- Ethnologue report for Cajun French
- Cane River Valley French
- Cajun French Language Tutorials
- Terrebonne Parish French Online!

