
Bülach fibula
Encyclopedia
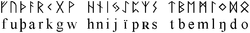
Fibulae and ancient brooches
A fibula is an ancient brooch. Technically, the Latin term, fibulae, refers to Roman brooches; however, the term is widely used to refer to brooches from the entire ancient and early medieval world that continue Roman forms...
with almandine inlay found in Bülach
Bülach
Bülach is a municipality in Switzerland in the canton of Zurich, located in the district of the same name, and belongs to the Glatt Valley .-History:Bülach is first mentioned in 811 as Pulacha...
, Canton Zürich
Canton of Zürich
The Canton of Zurich has a population of . The canton is located in the northeast of Switzerland and the city of Zurich is its capital. The official language is German, but people speak the local Swiss German dialect called Züritüütsch...
in 1927. The Alemannic
Alamanni
The Alamanni, Allemanni, or Alemanni were originally an alliance of Germanic tribes located around the upper Rhine river . One of the earliest references to them is the cognomen Alamannicus assumed by Roman Emperor Caracalla, who ruled the Roman Empire from 211 to 217 and claimed thereby to be...
grave in which it was found (no. 249) dates to 6th century and contained the remains of an adult woman. The fibula, dated to between the 3rd and 6th centuries, bears an Elder Futhark
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark is the oldest form of the runic alphabet, used by Germanic tribes for Northwest Germanic and Migration period Germanic dialects of the 2nd to 8th centuries for inscriptions on artifacts such as jewellery, amulets, tools, weapons and runestones...
inscription, the only one found in Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
to date.
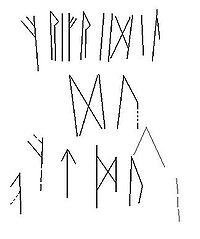
Inscription
The inscription begins- frifridil du aftm[...
with the first and the third f runes as well as the a rune mirrored.
Frifridil is a pet name for a male friend or lover (OHG
Old High German
The term Old High German refers to the earliest stage of the German language and it conventionally covers the period from around 500 to 1050. Coherent written texts do not appear until the second half of the 8th century, and some treat the period before 750 as 'prehistoric' and date the start of...
fridil, MHG
Middle High German
Middle High German , abbreviated MHG , is the term used for the period in the history of the German language between 1050 and 1350. It is preceded by Old High German and followed by Early New High German...
friedel). du is the 2nd person singular pronoun, already differentiated from the common West Germanic þu, lending the inscription an early Old High German
Old High German
The term Old High German refers to the earliest stage of the German language and it conventionally covers the period from around 500 to 1050. Coherent written texts do not appear until the second half of the 8th century, and some treat the period before 750 as 'prehistoric' and date the start of...
or Alemannic German
Alemannic German
Alemannic is a group of dialects of the Upper German branch of the Germanic language family. It is spoken by approximately ten million people in six countries: Switzerland, Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, France and Italy...
character.
The remaining part of the inscription is read differently by various authors. Also, the mirrored runes have suggested change of reading direction to some. Krause and Jankuhn (1966) read
- fri[d]fridil du fat mik l l
with only two l runes
Laguz
*Laguz or *Laukaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the l-rune , *laguz meaning "water" or "lake" and *laukaz meaning "leek". In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem, it is called lagu "ocean". In the Younger Futhark, the rune is called lögr "waterfall" in Icelandic and logr "water" in Norse.The...
, translating "you, my lover, embrace me, leek! leek!", interpreting the l runes as abbreviating "leek" (*laukaz), symbolizing fertility or prosperity (leek is strongly associated with nubile women in Old Norse
Old Norse
Old Norse is a North Germanic language that was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and inhabitants of their overseas settlements during the Viking Age, until about 1300....
skaldic poetry)
Klingenberg (1976) has
- frifridil [lid] du [fud] f[a]t[o] mik. (l)[au]k (l)[i]d l l
reading the first lid as implied by mirroring the dil and the fud as implied by mirroring the du f in conscious obscuring of the obscene content, lid meaning "penis" and fud meaning "vulva", and interpreting the l runes as phallic symbols, again abbreviating lid, resulting in a translation of "[I, your] lover with the penis, you with the vulva: receive me; leek! penis! leek! penis!".
Opitz (1977) similarly has
- fri[d]fridil [lid] du [fud] f[a]t[.] mik (l[id]) l[id] l[id]
- "lover - penis; you - vulva; receive me; (penis) penis penis"
dismissing Klingenberg's k and d at the end of the inscription as conjectured.
Later interpreters have dismissed the "l runes" as mere accidental scratches, and the sexual reading of Klingenberg and Opitz as the product of an excited imagination. Looijenga (1997) reads a mere uninterpretable aftmu. The undisputed reading of frifridil however establishes the inscription as a dedication among lovers.

