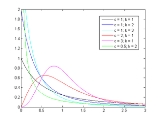
Burr distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, statistics
and econometrics
, the Burr Type XII distribution or simply the Burr distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a non-negative random variable
. It is also known as the Singh-Maddala distribution and is one of a number of different distributions sometimes called the "generalized log-logistic distribution
". It is most commonly used to model household income
(See: Household income in the U.S. and compare to magenta
graph at right).
The Burr distribution has probability density function
:
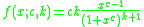
and cumulative distribution function
:
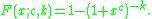
The Dagum distribution, also known as the inverse Burr Distribution.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
and econometrics
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
, the Burr Type XII distribution or simply the Burr distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a non-negative random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
. It is also known as the Singh-Maddala distribution and is one of a number of different distributions sometimes called the "generalized log-logistic distribution
Log-logistic distribution
In probability and statistics, the log-logistic distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a non-negative random variable. It is used in survival analysis as a parametric model for events whose rate increases initially and decreases later, for example mortality from cancer following...
". It is most commonly used to model household income
Household income
Household income is a measure of the combined incomes of all people sharing a particular household or place of residence. It includes every form of income, e.g., salaries and wages, retirement income, near cash government transfers like food stamps, and investment gains.Average household income can...
(See: Household income in the U.S. and compare to magenta
Magenta
Magenta is a color evoked by light stronger in blue and red wavelengths than in yellowish-green wavelengths . In light experiments, magenta can be produced by removing the lime-green wavelengths from white light...
graph at right).
The Burr distribution has probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
:
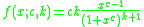
and cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
:
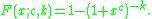
See also
Log-logistic distributionLog-logistic distribution
In probability and statistics, the log-logistic distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a non-negative random variable. It is used in survival analysis as a parametric model for events whose rate increases initially and decreases later, for example mortality from cancer following...
The Dagum distribution, also known as the inverse Burr Distribution.

