
Bunsen cell
Encyclopedia
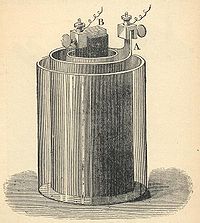
Primary cell
A primary cell is any kind of battery in which the electrochemical reaction is not reversible, rendering the cell non-rechargeable. A common example of a primary cell is the disposable battery. Unlike a secondary cell, the reaction cannot be reversed by running a current into the cell; the chemical...
(colloquially called a "battery") composed of a zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
in dilute sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
separated by a porous pot from a carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
in nitric
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
or chromic acid
Chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the...
.
Cell details
The Bunsen cell is about 1.9 voltVolt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s and arises from the following reaction:
-
- Zn + H2SO4 + 2HNO3 → ZnSO4 + 2 H2O + 2 NO2↑
The cell is named after its inventor, German chemist Robert Wilhelm Bunsen, who improved upon the Grove cell
Grove cell
The Grove cell was an early electric primary cell named after its inventor, British chemist William Robert Grove, and consisted of a zinc anode in dilute sulfuric acid and a platinum cathode in concentrated nitric acid, the two separated by a porous ceramic pot.-Cell details:The Grove cell voltage...
by replacing Grove
William Robert Grove
Sir William Robert Grove PC QC FRS was a judge and physical scientist. He anticipated the general theory of the conservation of energy, and was a pioneer of fuel cell technology.-Early life:...
's platinum
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
cathode with carbon in the form of pulverized coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
and coke
Coke (fuel)
Coke is the solid carbonaceous material derived from destructive distillation of low-ash, low-sulfur bituminous coal. Cokes from coal are grey, hard, and porous. While coke can be formed naturally, the commonly used form is man-made.- History :...
. Like Grove's battery, Bunsen's emitted noxious fumes.
Bunsen used this cell to extract metals.
Henri Moissan
Henri Moissan
Ferdinand Frederick Henri Moissan was a French chemist who won the 1906 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work in isolating fluorine from its compounds.-Biography:...
used a stack of 90 cells for the electrolysis of hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula HF. This colorless gas is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the aqueous form as hydrofluoric acid, and thus is the precursor to many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers . HF is widely used in the...
to obtain the element fluorine
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
for the first time.
See also
- History of the batteryHistory of the batteryThe history of the development of electrochemical cells is crucial to the scientific study and industrial applications of electricity, for prior to the rise of electrical grids around the end of the 19th century, they were the main source of electricity...
- List of battery types
- Battery nomenclatureBattery nomenclatureStandard battery nomenclature describes portable dry cell batteries that are interchangeable in physical dimensions and electrical characteristics between manufacturers. The long history of disposable dry cells means that many different manufacturer-specific and national standards were used to...

