
Buckley–Leverett equation
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
, the Buckley–Leverett equation is a transport equation
used to model two-phase flow in porous media. The Buckley–Leverett equation or the Buckley–Leverett displacement can be interpreted as a way of incorporating the microscopic effects to due capillary pressure in two-phase flow into Darcy's law
.
In a 1D sample (control volume
), let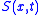 be the water saturation, then the Buckley–Leverett equation is
be the water saturation, then the Buckley–Leverett equation is
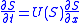
where
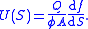
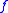 is the fractional flow rate,
is the fractional flow rate, 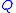 is the total flow,
is the total flow, 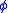 is porosity
is porosity
and is area of the cross-section in the sample volume.
is area of the cross-section in the sample volume.
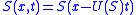 which means that
which means that 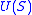 is the front velocity
is the front velocity
of the fluids at saturation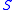 .
.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, the Buckley–Leverett equation is a transport equation
Generic scalar transport equation
The generic scalar transport equation is a general partial differential equation that describes transport phenomena such as heat transfer, mass transfer, fluid dynamics , etc. A general form of the equation is \big...
used to model two-phase flow in porous media. The Buckley–Leverett equation or the Buckley–Leverett displacement can be interpreted as a way of incorporating the microscopic effects to due capillary pressure in two-phase flow into Darcy's law
Darcy's law
Darcy's law is a phenomenologically derived constitutive equation that describes the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. The law was formulated by Henry Darcy based on the results of experiments on the flow of water through beds of sand...
.
In a 1D sample (control volume
Control volume
In fluid mechanics and thermodynamics, a control volume is a mathematical abstraction employed in the process of creating mathematical models of physical processes. In an inertial frame of reference, it is a volume fixed in space or moving with constant velocity through which the fluid flows...
), let
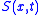 be the water saturation, then the Buckley–Leverett equation is
be the water saturation, then the Buckley–Leverett equation is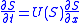
where
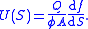
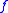 is the fractional flow rate,
is the fractional flow rate,  is the total flow,
is the total flow,  is porosity
is porosityPorosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
and
 is area of the cross-section in the sample volume.
is area of the cross-section in the sample volume.Assumptions for validity
The Buckley–Leverett equation is derived for a 1D sample given- mass conservationConservation of massThe law of conservation of mass, also known as the principle of mass/matter conservation, states that the mass of an isolated system will remain constant over time...
- capillary pressure
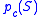 is a function of water saturation
is a function of water saturation 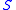 only
only -
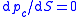 causing the pressure gradients of the two phases to be equal.
causing the pressure gradients of the two phases to be equal. - Flow is Linear
- Flow is Steady-State
- Formation is one Layer
General solution
The solution of the Buckley–Leverett equation has the form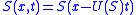 which means that
which means that 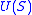 is the front velocity
is the front velocityFront velocity
In physics, front velocity is the speed at which the first rise of a pulse above zero moves forward.In mathematics, it is also used to describe the velocity of a possibly propagating front in the solution of hyperbolic partial differential equation....
of the fluids at saturation
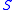 .
.See also
- Capillary pressure
- Permeability (fluid)Permeability (fluid)Permeability in fluid mechanics and the earth sciences is a measure of the ability of a porous material to allow fluids to pass through it.- Units :...
- Relative permeabilityRelative permeabilityIn multiphase flow in porous media, the relative permeability of a phase is a dimensionless measure of the effective permeability of that phase. It is the ratio of the effective permeability of that phase to the absolute permeability...
- Darcy's lawDarcy's lawDarcy's law is a phenomenologically derived constitutive equation that describes the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. The law was formulated by Henry Darcy based on the results of experiments on the flow of water through beds of sand...

