
Brazilian wine
Encyclopedia
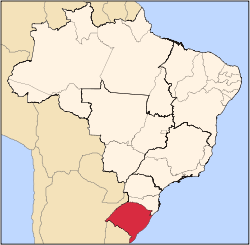
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
has a relatively large amounts of vineyard
Vineyard
A vineyard is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice...
s, a large part of them produce table grape
Table grape
Table grapes are grapes intended for consumption while they are fresh, as opposed to grapes grown for wine production, juice production, or for drying into raisins....
s, and only some produce Brazilian wine. As much of Brazil is close to the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
, traditional rules of thumb brand most of the country unsuitable for viticulture
Viticulture
Viticulture is the science, production and study of grapes which deals with the series of events that occur in the vineyard. When the grapes are used for winemaking, it is also known as viniculture...
, due to too much heat and humidity. Most of the wine production of Brazil is concentrated in the south of the country, away from the equator, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul is the southernmost state in Brazil, and the state with the fifth highest Human Development Index in the country. In this state is located the southernmost city in the country, Chuí, on the border with Uruguay. In the region of Bento Gonçalves and Caxias do Sul, the largest wine...
, which is close to Uruguay
Uruguay
Uruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
and Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
. In that area, many of the vineyards are also located in cooler high and hilly locations, to a large part in Serra Gaúcha
Serra Gaúcha
The Serra Gaúcha, The Gaucho Highlands, is the mountainous region in the northeastern portion of Rio Grande do Sul state in southern Brazil. This mountainous region is home to many Brazilians of German and Italian descent...
region.
While better quality wines (vinho fino) are produced from the European grapevine Vitis vinifera
Vitis vinifera
Vitis vinifera is a species of Vitis, native to the Mediterranean region, central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran....
, in 2003 only some 5000 hectares (12,355.3 acre) out of Brazil's 68000 hectares (168,031.5 acre) were planted with such vines. The rest is American vines or hybrid vines, many of which are easier to cultivate under Brazilian growing conditions.
History
Several less successful attempts at introducing European vines into Brazil were made during the centuries. The first vines were brought to Brazil by the Portuguese in 1532, who planted them in the state São PauloSão Paulo (state)
São Paulo is a state in Brazil. It is the major industrial and economic powerhouse of the Brazilian economy. Named after Saint Paul, São Paulo has the largest population, industrial complex, and economic production in the country. It is the richest state in Brazil...
. Jesuits brought Spanish vines to Rio Grande do Sul in 1626, and 18th century settlers from the Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
brought vine cuttings from Madeira
Madeira
Madeira is a Portuguese archipelago that lies between and , just under 400 km north of Tenerife, Canary Islands, in the north Atlantic Ocean and an outermost region of the European Union...
and the Azores. 1840 plantations of Isabella
Isabella (grape)
The Isabella grape is a cultivar derived from the grape species Vitis labrusca or 'fox grape' which is used for table, juice and wine production.-Appearance and use:...
(a cultivar of the species Vitis labrusca
Vitis labrusca
Vitis labrusca is a species of grapevines belonging to the Vitis genus in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The vines are native to the eastern United States and are the source of many grape cultivars, including Catawba and Concord grapes, and many hybrid grape varieties such as Agawam,...
) on the south coast of Rio Grande are considered the first successful vine plantations in Brazil. By the late 1870s, winemaking was more definitely established and had taken hold in Serra Gaúcha, where Italian immigrants did much of the vine-growing, and mostly American vines were produced. Some Italian varieties and Tannat
Tannat
Tannat is a red wine grape, historically grown in South West France in the Madiran AOC and is now one of the most prominent grapes in Uruguay, where it is considered the "national grape". It is also grown in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Peru, and in Italy's Puglia region where it is used as a...
were later added.
Wine production with higher quality ambitions started in the 1970s, when several international wine companies invested in Brazil and brought in know-how and modern equipment.

