
Book design
Encyclopedia
Book design is the art of incorporating the content, style, format
, design
, and sequence of the various components of a book
into a coherent whole.
In the words of Jan Tschichold
, book design "though largely forgotten today, methods and rules upon which it is impossible to improve have been developed over centuries. To produce perfect books these rules have to be brought back to life and applied." Richard Hendel describes book design as "an arcane subject" and refers to the need for a context to understand what that means.
Front matter generally only appears in the first volume in a series, although some elements (such as a table of contents or index) may appear in each volume.
The following table will help distinguish between some of the different types of front matter:
The following are two instructive examples:
 The front cover is the front of the book, and is marked appropriately, by text and/or graphics, in order to identify it as such, namely as the very beginning of the book. The front cover usually contains at least the title
The front cover is the front of the book, and is marked appropriately, by text and/or graphics, in order to identify it as such, namely as the very beginning of the book. The front cover usually contains at least the title
and/or author
, with possibly an appropriate illustration
.
On the inside of the cover page, extending to the facing page is the front endpaper
sometimes referred as FEP. The free half of the end paper is called a flyleaf. Traditionally, in hand-bound books, the endpaper was just a sheet of blank or ornamented paper physically masking and reinforcing the connection between the cover and the body of the book. In modern publishing it can be either plain, as in many text-oriented books, or variously ornamented and illustrated in books such as Picture books, other children's literature, some arts and craft and hobbyist books, novelty/gift-market and coffee table books, and Graphic novels. These books have an audience and traditions of their own where the graphic design
and immediacy is especially important and publishing tradition and formality are less important.
The spine is the vertical edge of a book as it normally stands on a bookshelf. It is customary for it to have printed text on it. In texts published and/or printed in the United States, the spine text, when vertical, runs from the top to the bottom, such that it is right side up when the book is lying flat with the front cover on top. In books of Europe, vertical spine text traditionally runs from the bottom up, though this convention has been changing lately. The spine usually contains all, or some, of four elements (besides decoration, if any), and in the following order: (1) author, editor, or compiler; (2) title; (3) publisher; and (4) publisher logo.
On the inside of the back cover page, extending from the facing page before it, is the endpaper. Its design matches the front endpaper and, in accordance with it, contains either plain paper or pattern, image etc.
The back cover often contains biographical matter about the author or editor, and quotes from other sources praising the book. It may also contain a summary or description of the book
(or hardback) refers to books with stiff
covers, as opposed to flexible
ones. The binding of a hardcover book usually includes boards (often made of paperboard
) covered in cloth, leather, or other materials. The binding is usually sewn to the pages using string stitching.
A less expensive binding method is that used for paperback
books (sometimes called softback or softcover). Most paperbacks are bound with paper or light cardboard, though other materials (such as plastic) are used. The covers are flexible and usually bound to the pages using glue (perfect binding). Some small paperback books are sub-classified as pocketbooks. These paperbacks are smaller than usual - small enough to barely fit into a pocket (especially the back pocket of one's trousers). However, this capacity to fit into a pocket diminishes with increasing number of pages and increasing thickness of the book. Such a book may still be designated as a pocketbook.
to help find material quickly.
Gold leaf may also be applied to the edges of the pages, so that when closed, the side, top, and bottom of the book have a golden color. On some books, a design may be printed on the edges. Some artist's books go even further, by using fore-edge painting
.
Pop-up
elements and fold-out pages may be used to add dimensions to the page in different ways.
Children's books commonly incorporate a wide array of design features built into the fabric of the book. Die-cut techniques in the work of Eric Carle
are one example.
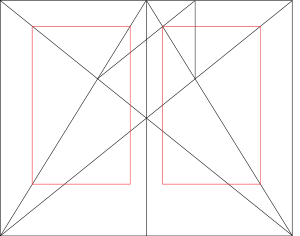 A basic unit in book design is the page spread. The left page (called verso) and right page (called recto
A basic unit in book design is the page spread. The left page (called verso) and right page (called recto
) are of the same size and aspect ratio, and are centered on the gutter where they are bound together at the spine
.
The design of each individual page, on the other hand, is governed by the canons of page construction
.
The possible layout of the sets of letters of the alphabet, or words, on a page is determined by the so-called print space, and is also an element in the design of the page of the book. Clearly, there must be sufficient space, at the spine of the book, if the text is to be visible. On the other hand, the other three margin
s of the page, which frame the book, are made of the appropriate size for both practical and aesthetic reasons.
The term comes originally from hot metal typesetting
: above the desktop was a mirror (German: Spiegel) where the typesetter could read the inverted letters.
Word processor
A word processor is a computer application used for the production of any sort of printable material....
, design
Design
Design as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
, and sequence of the various components of a book
Book
A book is a set or collection of written, printed, illustrated, or blank sheets, made of hot lava, paper, parchment, or other materials, usually fastened together to hinge at one side. A single sheet within a book is called a leaf or leaflet, and each side of a leaf is called a page...
into a coherent whole.
In the words of Jan Tschichold
Jan Tschichold
Jan Tschichold was a typographer, book designer, teacher and writer.-Life:Tschichold was the son of a provincial signwriter, and he was trained in calligraphy...
, book design "though largely forgotten today, methods and rules upon which it is impossible to improve have been developed over centuries. To produce perfect books these rules have to be brought back to life and applied." Richard Hendel describes book design as "an arcane subject" and refers to the need for a context to understand what that means.
Front matter
Front matter, or preliminaries ("prelims", for short), is the first section of a book, and is usually the smallest section in terms of the number of pages. The pages are numbered in lower-case Roman numerals. Each page is counted; but no folio or page number is expressed, or printed, on either display pages, or blank pages.Front matter generally only appears in the first volume in a series, although some elements (such as a table of contents or index) may appear in each volume.
The following table will help distinguish between some of the different types of front matter:
| Name | Voice | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Contents Table of contents A table of contents, usually headed simply "Contents" and abbreviated informally as TOC, is a list of the parts of a book or document organized in the order in which the parts appear... |
Publisher | This is a list of chapter headings, and nested subheadings, together with their respective page numbers. This includes all front-matter items listed below together with chapters in the body matter and back matter. The number of levels of subheadings shown should be limited so as to keep the contents list short, ideally one page or possibly a double-page spread. |
| Foreword Foreword A foreword is a piece of writing sometimes placed at the beginning of a book or other piece of literature. Written by someone other than the primary author of the work, it often tells of some interaction between the writer of the foreword and the book's primary author or the story the book tells... |
Some real person other than the author of the book | Often, a foreword will tell of some interaction between the writer of the foreword and the story or the writer of the story. A foreword to later editions of a work often explains in what respects that edition differs from previous ones. |
| Preface Preface A preface is an introduction to a book or other literary work written by the work's author. An introductory essay written by a different person is a foreword and precedes an author's preface... |
The author | A preface generally covers the story of how the book came into being, or how the idea for the book was developed; this is often followed by thanks and acknowledgments to people who were helpful to the author during the time of writing. |
| Acknowledgement Acknowledgment (creative arts) In the creative arts and scientific literature, an acknowledgment is an expression of gratitude for assistance in creating a literary or artistic work.... |
The author | Often part of the Preface, rather than a separate section in its own right, it acknowledges those who contributed to the creation of the book. |
| Introduction Introduction (essay) An introduction is a beginning section which states the purpose and goals of the following writing. The introduction is usually interesting and it intrigues the reader and causes him or her to want to read on. The sentence in which the introduction begins can be a question or just a statement... |
The author | A beginning section which states the purpose and goals of the following writing. |
| Dedication | The author | A dedication page is a page in a book that precedes the text, in which the author names the person or people for whom he/she has written the book. |
| Prologue Prologue A prologue is an opening to a story that establishes the setting and gives background details, often some earlier story that ties into the main one, and other miscellaneous information. The Greek prologos included the modern meaning of prologue, but was of wider significance... |
The narrator (or a character in the book) | A prologue is an opening to a story that establishes the setting and gives background details, often some earlier story that ties into the main one, and other miscellaneous information. |
Body matter
The structure of a work (and especially of its body matter) is often described hierarchically.- Volumes
- A volume is a set of leaves that are bound together. Thus each work is either a volume, or is divided into volumes.
- Books and parts
- (Single-volume works account for most of the non-academic consumer market in books.) A single volume may embody either a part of a book or the whole of a book; in some works, parts include multiple books, and in some others books include multiple parts.
- Chapters and sections
- A chapter or section may be contained within a part and/or a book; when both chapters and sections are used in the same work, the sections are more often contained within chapters than the reverse.
The following are two instructive examples:
- The Lord of the RingsThe Lord of the RingsThe Lord of the Rings is a high fantasy epic written by English philologist and University of Oxford professor J. R. R. Tolkien. The story began as a sequel to Tolkien's earlier, less complex children's fantasy novel The Hobbit , but eventually developed into a much larger work. It was written in...
has three parts (either in a single volume, or in one volume each), with each part containing two books, each containing in turn multiple chapters. - The ChristianChristianityChristianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
BibleBibleThe Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
(usually bound as a single volume) is divided into two "testaments" (which might more typically be described as "parts", and differ in length by a factor of three or four), each containing dozens of books, each in turn containing multiple chapters, which are most often divided (for purposes of citationCitationBroadly, a citation is a reference to a published or unpublished source . More precisely, a citation is an abbreviated alphanumeric expression Broadly, a citation is a reference to a published or unpublished source (not always the original source). More precisely, a citation is an abbreviated...
) into "verseChapters and verses of the BibleThe Bible is a compilation of many shorter books written at different times and later assembled into the Biblical canon. All but the shortest of these books have been divided into chapters, generally a page or so in length, since the early 13th century. Since the mid-16th century, each chapter has...
s" each containing roughly one independent clauseIndependent clauseAn independent clause is a clause that can stand by itself, also known as a simple sentence. An independent clause contains a subject and a predicate; it makes sense by itself....
.
Back matter
The back matter, if used, normally consists of one or more of the following components:- An epilogueEpilogueAn epilogue, epilog or afterword is a piece of writing at the end of a work of literature or drama, usually used to bring closure to the work...
is a piece of writing at the end of a work of literature or drama, usually used to bring closure to the work. - An extro or outro is the conclusion to a piece of work and is considered the opposite of the intro. These terms are more commonly used in music.
- An afterwordAfterwordAn afterword is a literary device that is often found at the end of a piece of literature. It generally covers the story of how the book came into being, or of how the idea for the book was developed....
is frequently a piece of writing describing a time well after the time frame of the main story. - A conclusionConclusion-Logic:*Logical consequence*Affirmative conclusion from a negative premise, a logical fallacy-Music:*Conclusion , the end of a musical composition*The Conclusion, an album by Bombshell Rocks*Conclusion of an Age, an album by the band Sylosis...
. - A postscriptPostscriptA postscript, abbreviated P.S., is writing added after the main body of a letter . The term comes from the Latin post scriptum, an expression meaning "written after" .A postscript may be a sentence, a paragraph, or occasionally many paragraphs added, often hastily and...
. - An appendix or addendumAddendumAn addendum, in general, is an addition required to be made to a document by its reader subsequent to its printing or publication. It comes from the Latin verbal phrase addendum est, being the gerundive form of the verb addo, addere, addidi, additum, "to give to, add to", meaning " must be added"...
is a supplemental addition to a given main work. It may correct errors, explain inconsistencies or otherwise detail or update the information found in the main work. - The glossaryGlossaryA glossary, also known as an idioticon, vocabulary, or clavis, is an alphabetical list of terms in a particular domain of knowledge with the definitions for those terms...
consists of a set of definitions of words of importance to the work. They are normally alphabetized. The entries may consist of places and characters, which is common for longer works of fiction. - The bibliographyBibliographyBibliography , as a practice, is the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects; in this sense, it is also known as bibliology...
cites others used in the body. Most common in non-fiction books or research papers. - An indexIndex (publishing)An index is a list of words or phrases and associated pointers to where useful material relating to that heading can be found in a document...
is used to find terms used in the text. Most common in non-fiction books. - The colophonColophon (publishing)In publishing, a colophon is either:* A brief description of publication or production notes relevant to the edition, in modern books usually located at the reverse of the title page, but can also sometimes be located at the end of the book, or...
is a brief description usually located at the end of a book, describing production notes relevant to the edition and may include a printer's mark or logotype.
Front cover, spine, and back cover of the dust-jacket

Title
A title is a prefix or suffix added to someone's name to signify either veneration, an official position or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may even be inserted between a first and last name...
and/or author
Author
An author is broadly defined as "the person who originates or gives existence to anything" and that authorship determines responsibility for what is created. Narrowly defined, an author is the originator of any written work.-Legal significance:...
, with possibly an appropriate illustration
Illustration
An illustration is a displayed visualization form presented as a drawing, painting, photograph or other work of art that is created to elucidate or dictate sensual information by providing a visual representation graphically.- Early history :The earliest forms of illustration were prehistoric...
.
On the inside of the cover page, extending to the facing page is the front endpaper
Endpaper
The endpapers or end-papers of a book are the leaves of paper before the title page and after the text. Booksellers sometimes refer to the front end paper as FEP....
sometimes referred as FEP. The free half of the end paper is called a flyleaf. Traditionally, in hand-bound books, the endpaper was just a sheet of blank or ornamented paper physically masking and reinforcing the connection between the cover and the body of the book. In modern publishing it can be either plain, as in many text-oriented books, or variously ornamented and illustrated in books such as Picture books, other children's literature, some arts and craft and hobbyist books, novelty/gift-market and coffee table books, and Graphic novels. These books have an audience and traditions of their own where the graphic design
Graphic design
Graphic design is a creative process – most often involving a client and a designer and usually completed in conjunction with producers of form – undertaken in order to convey a specific message to a targeted audience...
and immediacy is especially important and publishing tradition and formality are less important.
The spine is the vertical edge of a book as it normally stands on a bookshelf. It is customary for it to have printed text on it. In texts published and/or printed in the United States, the spine text, when vertical, runs from the top to the bottom, such that it is right side up when the book is lying flat with the front cover on top. In books of Europe, vertical spine text traditionally runs from the bottom up, though this convention has been changing lately. The spine usually contains all, or some, of four elements (besides decoration, if any), and in the following order: (1) author, editor, or compiler; (2) title; (3) publisher; and (4) publisher logo.
On the inside of the back cover page, extending from the facing page before it, is the endpaper. Its design matches the front endpaper and, in accordance with it, contains either plain paper or pattern, image etc.
The back cover often contains biographical matter about the author or editor, and quotes from other sources praising the book. It may also contain a summary or description of the book
Binding
Books are classified under two categories according to the physical nature of their binding. The designation hardcoverHardcover
A hardcover, hardback or hardbound is a book bound with rigid protective covers...
(or hardback) refers to books with stiff
Stiffness
Stiffness is the resistance of an elastic body to deformation by an applied force along a given degree of freedom when a set of loading points and boundary conditions are prescribed on the elastic body.-Calculations:...
covers, as opposed to flexible
Flexibility
Flexibility may refer to:* Flexibility , the distance of motion of a joint, which may be increased by stretching* Flexibility , in the field of engineering systems design, designs that can adapt when external changes occur...
ones. The binding of a hardcover book usually includes boards (often made of paperboard
Paperboard
Paperboard is a thick paper based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a basis weight above 224 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single...
) covered in cloth, leather, or other materials. The binding is usually sewn to the pages using string stitching.
A less expensive binding method is that used for paperback
Paperback
Paperback, softback or softcover describe and refer to a book by the nature of its binding. The covers of such books are usually made of paper or paperboard, and are usually held together with glue rather than stitches or staples...
books (sometimes called softback or softcover). Most paperbacks are bound with paper or light cardboard, though other materials (such as plastic) are used. The covers are flexible and usually bound to the pages using glue (perfect binding). Some small paperback books are sub-classified as pocketbooks. These paperbacks are smaller than usual - small enough to barely fit into a pocket (especially the back pocket of one's trousers). However, this capacity to fit into a pocket diminishes with increasing number of pages and increasing thickness of the book. Such a book may still be designated as a pocketbook.
Other items
Some books such as Bibles or dictionaries may have a thumb indexThumb index
A thumb index, also called a cut-in index, is a round cut-out in the pages of a dictionary, encyclopedia, or other alphabetized reference work, used to locate entries starting at a particular letter...
to help find material quickly.
Gold leaf may also be applied to the edges of the pages, so that when closed, the side, top, and bottom of the book have a golden color. On some books, a design may be printed on the edges. Some artist's books go even further, by using fore-edge painting
Fore-edge painting
A fore-edge painting is a scene painted on the edges of the pages of a book. There are two basic forms, including paintings on edegs that have been fanned and edges that are closed; thus with the first instance a book edge must be fanned to see the painting and in the second the painting is on the...
.
Pop-up
Pop-Up
Pop Up is the debut album by French electropop trio Yelle. It was released in France on 3 September 2007 by the EMI-owned label Source Etc. The album peaked at number sixty-one on the French Albums Chart, and went on to sell 20,000 copies.-Promotion:...
elements and fold-out pages may be used to add dimensions to the page in different ways.
Children's books commonly incorporate a wide array of design features built into the fabric of the book. Die-cut techniques in the work of Eric Carle
Eric Carle
Eric Carle is a children's book author and illustrator who is most famous for his book The Very Hungry Caterpillar, which has been translated into over 50 languages...
are one example.
Page spread

Recto
The recto and verso are respectively the "front" and "back" sides of a leaf of paper in a bound item such as a codex, book, broadsheet, or pamphlet. In languages written from left to right the recto is the right-hand page and the verso the left-hand page...
) are of the same size and aspect ratio, and are centered on the gutter where they are bound together at the spine
Bookbinding
Bookbinding is the process of physically assembling a book from a number of folded or unfolded sheets of paper or other material. It usually involves attaching covers to the resulting text-block.-Origins of the book:...
.
The design of each individual page, on the other hand, is governed by the canons of page construction
Canons of page construction
The canons of page construction are a set of principles in the field of book design used to describe the ways that page proportions, margins and type areas of books are constructed....
.
The possible layout of the sets of letters of the alphabet, or words, on a page is determined by the so-called print space, and is also an element in the design of the page of the book. Clearly, there must be sufficient space, at the spine of the book, if the text is to be visible. On the other hand, the other three margin
Margin (typography)
In typography, a margin is the space that surrounds the content of a page. The margin helps to define where a line of text begins and ends. When a page is justified the text is spread out to be flush with the left and right margins...
s of the page, which frame the book, are made of the appropriate size for both practical and aesthetic reasons.
Print space
The print space (German Satzspiegel) is a typographic term and determines the effective area on the paper of a book, journal or other press work. The print space is limited by the surrounding borders, or in other words the gutters outside the printed area.The term comes originally from hot metal typesetting
Hot metal typesetting
In printing and typography, hot metal typesetting refers to 19th-century technologies for typesetting text in letterpress printing. This method injects molten type metal into a mold that has the shape of one or more glyphs...
: above the desktop was a mirror (German: Spiegel) where the typesetter could read the inverted letters.
See also
Books by type- Canons of page constructionCanons of page constructionThe canons of page construction are a set of principles in the field of book design used to describe the ways that page proportions, margins and type areas of books are constructed....
- Galley proofGalley proofIn printing and publishing, proofs are the preliminary versions of publications meant for review by authors, editors, and proofreaders, often with extra wide margins. Galley proofs may be uncut and unbound, or in some cases electronic...
- Walter HamadyWalter HamadyWalter Hamady or, in full, Walter Samuel Haatoum Hamady, is an American artist, book designer, papermaker, poet and teacher. He is especially known for his innovative efforts in letterpress printing, bookbinding, and papermaking...
- ImprintImprintIn the publishing industry, an imprint can mean several different things:* As a piece of bibliographic information about a book, it refers to the name and address of the book's publisher and its date of publication as given at the foot or on the verso of its title page.* It can mean a trade name...
- Letterpress
- Page numberingPage numberingPage numbering is the process of applying a sequence of numbers to the pages of a book or other document. The number itself, which may appear in various places on the page, can be referred to as a page number or as a folio...
- PublishingPublishingPublishing is the process of production and dissemination of literature or information—the activity of making information available to the general public...
- Visual design
- Epigraph (literature)Epigraph (literature)In literature, an epigraph is a phrase, quotation, or poem that is set at the beginning of a document or component. The epigraph may serve as a preface, as a summary, as a counter-example, or to link the work to a wider literary canon, either to invite comparison or to enlist a conventional...
Other types of book
- Graphic NovelGraphic novelA graphic novel is a narrative work in which the story is conveyed to the reader using sequential art in either an experimental design or in a traditional comics format...
- Interactive children's bookInteractive children's bookInteractive children's books are a subset of children's books which require participation and interaction by the reader. Participation can range from books with texture to those with special devices used to help teach children certain tools. Interactive children's books may also incorporate modern...
- Interactive fictionInteractive fictionInteractive fiction, often abbreviated IF, describes software simulating environments in which players use text commands to control characters and influence the environment. Works in this form can be understood as literary narratives and as video games. In common usage, the term refers to text...
- Picture books
- Pop-up bookPop-up bookThe term pop-up book is often applied to any three-dimensional or movable book, although properly the umbrella term movable book covers pop-ups, transformations, tunnel books, volvelles, flaps, pull-tabs, pop-outs, pull-downs, and more, each of which performs in a different manner...
Further reading
- Hendel, Richard, On Book Design, Yale University Press (1998) ISBN 0-300-07570-7.
- Hochuli, Jost, and Robin Kinross, Designing Books: Practice and Theory, Hyphen Press (1996) ISBN 0-907259-08-1.
- Bruno, Michael H., Pocket Pal: The Handy Little Book of Graphic Arts Production, 19th Edition, Graphic Arts Technical Foundation (2004) ISBN 0-88362-488-5.
- Lee, Marshal, Bookmaking: Editing, Design, Production, Third Edition, W. W. Norton and Company (2004) ISBN 0-393-73018-2.
- University of Chicago Press,The Chicago Manual of Style, 15th ed. (Chicago: 2003) ISBN 0226104036 (hardcover); ISBN 0226104052 (hardcover with CD-ROM): ISBN 0226104044 (CD-ROM).
- University of Chicago Press, The Chicago Manual of StyleThe Chicago Manual of StyleThe Chicago Manual of Style is a style guide for American English published since 1906 by the University of Chicago Press. Its 16 editions have prescribed writing and citation styles widely used in publishing...
, 15th ed., Online ed. (Chicago: Released September 29.)
External links
- Walter Hamady and the Perishable Press Limited
- Designing The Painted Bird
- Alcuin Society Book Design Awards
- Elbert Hubbard, Dard Hunter and Book Design at Roycroft Press
- Five Simple Steps to Designing Grid Systems
- Foreword: A Book Design Blog
- Merle Armitage: Impresario of Book Design
- A Tribute to Richard Eckersley: An Exemplary Book Designer

