
Bond dipole moment
Encyclopedia
The bond dipole moment uses the idea of electric dipole moment
to measure the polarity
of a chemical bond within a molecule
. The bond dipole μ is given by:
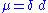 .
.
The bond dipole is modeled as +δ — δ- with a distance d between the partial charges +δ and δ-. It is a vector, parallel to the bond axis, pointing from minus to plus, as is conventional for electric dipole moment vectors. (Some chemists draw the vector the other way around, pointing from plus to minus, but only in situations where the direction doesn't matter.) This vector can be physically interpreted as the movement undergone by electrons when the two atoms are placed a distance d apart and allowed to interact, the electrons will move from their free state positions to be localised more around the more electronegative
atom.
The SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb-meter, but that is much too large to be practical on the molecular scale.
Bond dipole moments are commonly measured in debye
s, represented by the symbol D, which is what
you get if you measure the charge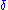 in units of 10-10 statcoulomb
in units of 10-10 statcoulomb
and measure the distance d in Angstrom
s. Note that
10-10 statcoulomb is 0.48 units of elementary charge.
Another useful conversion factor is 1 C m = 2.9979 D.
Typical dipole moments for simple diatomic molecules are in the range of 0 to 11D. At one extreme, a symmetrical molecule such as chlorine
, Cl2, has zero dipole moment, while near the other extreme, gas phase potassium bromide
, KBr, which is highly ionic, has a dipole moment of 10.5D.
For a complete molecule the total molecular dipole moment may be approximated as the vector sum of individual bond dipole moments.
Often bond dipoles are obtained by the reverse process: a known total dipole of a molecule can be decomposed into bond dipoles. The reason for doing this is the transfer of bond dipole moments to molecules that have the same bonds, but for which the total dipole moment is not yet known. The vector sum of the transferred bond dipoles gives an estimate for the total (unknown) dipole of the molecule.
The Bond Dipole is two atoms in a bond, such that the electronegativity of one atom causes electrons to be drawn towards the other, in turn causing a partial negative charge. There is therefore a difference in polarity across the bond, which causes a dipole moment.
Electric dipole moment
In physics, the electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges in a system of charges, that is, a measure of the charge system's overall polarity with SI units of Coulomb-meter...
to measure the polarity
Chemical polarity
In chemistry, polarity refers to a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multipole moment. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Molecular polarity is dependent on the difference in...
of a chemical bond within a molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
. The bond dipole μ is given by:
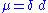 .
.The bond dipole is modeled as +δ — δ- with a distance d between the partial charges +δ and δ-. It is a vector, parallel to the bond axis, pointing from minus to plus, as is conventional for electric dipole moment vectors. (Some chemists draw the vector the other way around, pointing from plus to minus, but only in situations where the direction doesn't matter.) This vector can be physically interpreted as the movement undergone by electrons when the two atoms are placed a distance d apart and allowed to interact, the electrons will move from their free state positions to be localised more around the more electronegative
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ , is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus...
atom.
The SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb-meter, but that is much too large to be practical on the molecular scale.
Bond dipole moments are commonly measured in debye
Debye
The debye is a CGS unit of electric dipole momentElectric dipole moment is defined as charge times displacement: Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10-10 statcoulomb10-10 statcoulomb is approximately 0.2083...
s, represented by the symbol D, which is what
you get if you measure the charge
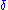 in units of 10-10 statcoulomb
in units of 10-10 statcoulombStatcoulomb
The statcoulomb or franklin or electrostatic unit of charge is the physical unit for electrical charge used in the centimetre-gram-second system of units and Gaussian units. It is a derived unit given by...
and measure the distance d in Angstrom
Ångström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
s. Note that
10-10 statcoulomb is 0.48 units of elementary charge.
Another useful conversion factor is 1 C m = 2.9979 D.
Typical dipole moments for simple diatomic molecules are in the range of 0 to 11D. At one extreme, a symmetrical molecule such as chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
, Cl2, has zero dipole moment, while near the other extreme, gas phase potassium bromide
Potassium bromide
Potassium bromide is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the United States. Its action is due to the bromide ion...
, KBr, which is highly ionic, has a dipole moment of 10.5D.
For a complete molecule the total molecular dipole moment may be approximated as the vector sum of individual bond dipole moments.
Often bond dipoles are obtained by the reverse process: a known total dipole of a molecule can be decomposed into bond dipoles. The reason for doing this is the transfer of bond dipole moments to molecules that have the same bonds, but for which the total dipole moment is not yet known. The vector sum of the transferred bond dipoles gives an estimate for the total (unknown) dipole of the molecule.
The Bond Dipole is two atoms in a bond, such that the electronegativity of one atom causes electrons to be drawn towards the other, in turn causing a partial negative charge. There is therefore a difference in polarity across the bond, which causes a dipole moment.

