
Binodal
Encyclopedia
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
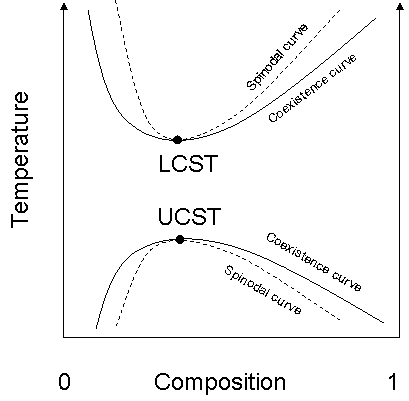
, the binodal, also known as the coexistence curve or binodal curve, denotes the condition at which two distinct phases
Phase (matter)
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space , throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, and chemical composition...
may coexist. Equivalently, it is the boundary between the set of conditions in which it is thermodynamically favorable for the system to be fully mixed and the set of conditions in which it is thermodynamically favorable for it to phase separate. In general, the binodal is defined by the condition at which the chemical potential
Chemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
of all solution components is equal in each phase. The extremum of a binodal curve in temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
coincides with the one of the spinodal
Spinodal
In thermodynamics, the spinodal is the limit of stability of a solution, denoting the boundary of absolute instability of a solution to decomposition into multiple phases. Within this curve, infinitesimally small fluctuations in composition and density will lead to phase separation via spinodal...
curve and is known as a critical point
Critical point (thermodynamics)
In physical chemistry, thermodynamics, chemistry and condensed matter physics, a critical point, also called a critical state, specifies the conditions at which a phase boundary ceases to exist...
.

