
Spinodal
Encyclopedia
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
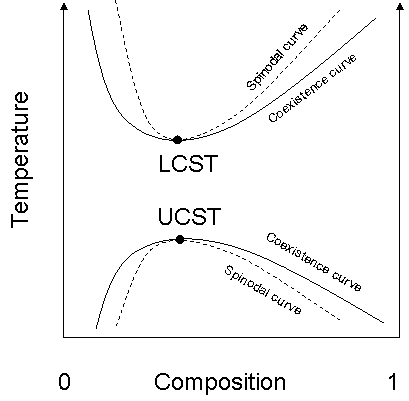
, the spinodal is the limit of stability of a solution, denoting the boundary of absolute instability of a solution to decomposition into multiple phases. Within this curve, infinitesimally small fluctuations in composition and density will lead to phase separation via spinodal decomposition
Spinodal decomposition
Spinodal decomposition is a mechanism by which a solution of two or more components can separate into distinct regions with distinctly different chemical compositions and physical properties...
. Outside of the curve, the solution will be at least metastable with respect to fluctuations. In other words, outside of the spinodal curve some careful process may at least in theory obtain a single phase system. Inside of it, no process will. In general, the spinodal lies inside of a binodal
Binodal
In thermodynamics, the binodal, also known as the coexistence curve or binodal curve, denotes the condition at which two distinct phases may coexist...
(coexistence) curve, which denotes the minimum-energy equilibrium state of the system.
Criterion
For binary solutions, the thermodynamic criterion which defines the spinodal curve is that the second derivative of free energy with respect to density or some composition variable is zero.Critical point
Extrema of the spinodal in temperature with respect to the composition variable coincide with ones of the binodal curve and are known as critical pointsCritical point (thermodynamics)
In physical chemistry, thermodynamics, chemistry and condensed matter physics, a critical point, also called a critical state, specifies the conditions at which a phase boundary ceases to exist...
.

