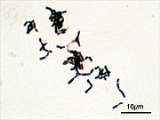
Bifidobacterium
Encyclopedia
Bifidobacterium is a genus
of Gram-positive
, non-motile
, often branched anaerobic
bacteria
. They are ubiquitous, endosymbiotic
inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract
, vagina
and mouth (B. dentium
) of mammals and other animals. Bifidobacteria are one of the major genera of bacteria that make up the colon
flora in mammals. Some bifidobacteria are used as probiotics.
Before the 1960s, Bifidobacterium species were collectively referred to as "Lactobacillus bifidus".
Bifidobacterium spp. are known to discourage the growth of Gram-negative pathogens in infants.
Mother's milk contains high concentrations of lactose and lower quantities of phosphate (pH Buffer). Therefore, when mother's milk is fermented by lactic acid bacteria (incl. bifidobacteria) in the infant's GI tract, the pH may be reduced, making it more difficult for Gram-negative bacteria to grow.
Much metabolic research on bifidobacteria has focused on oligosaccharide metabolism as these carbohydrates are available in their otherwise nutrient-limited habitats. Interestingly, infant-associated bifidobacterial phylotypes appear to have evolved the ability to ferment milk oligosaccharides, whereas adult-associated species utilize plant oligosaccharides, consistent with what they encounter in their respective environments. As breast-fed infants often harbor bifidobacteria dominated gut consortia, there have been numerous applications to mimic the bifidogenic properties of milk oligosaccharides. These are broadly classified as plant-derived fructo-oligosaccharides or dairy-derived galacto-oligosaccharides, which are differentially metabolized and distinct from milk oligosaccharide catabolism.
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of Gram-positive
Gram-positive
Gram-positive bacteria are those that are stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining. This is in contrast to Gram-negative bacteria, which cannot retain the crystal violet stain, instead taking up the counterstain and appearing red or pink...
, non-motile
Motility
Motility is a biological term which refers to the ability to move spontaneously and actively, consuming energy in the process. Most animals are motile but the term applies to single-celled and simple multicellular organisms, as well as to some mechanisms of fluid flow in multicellular organs, in...
, often branched anaerobic
Anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. It could possibly react negatively and may even die if oxygen is present...
bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. They are ubiquitous, endosymbiotic
Endosymbiont
An endosymbiont is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism, i.e. forming an endosymbiosis...
inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
, vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
and mouth (B. dentium
Bifidobacterium dentium
Bifidobacterium dentium is a species of bacteria in the genus of Bifidobacterium, branched anaerobic bacteria from the Bifidobacteriaceae family....
) of mammals and other animals. Bifidobacteria are one of the major genera of bacteria that make up the colon
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
flora in mammals. Some bifidobacteria are used as probiotics.
Before the 1960s, Bifidobacterium species were collectively referred to as "Lactobacillus bifidus".
Probiotics
Some Bifidobacterium strains are considered as important probiotics and used in the food industry. Different species and/or strains of Bifidobacteria may exert a range of beneficial health effects, including the regulation of intestinal microbial homeostasis, the inhibition of pathogens and harmful bacteria that colonize and/or infect the gut mucosa, the modulation of local and systemic immune responses, the repression of procarcinogenic enzymatic activities within the microbiota, the production of vitamins, and the bioconversion of a number of dietary compounds into bioactive molecules.Bifidobacterium spp. are known to discourage the growth of Gram-negative pathogens in infants.
Mother's milk contains high concentrations of lactose and lower quantities of phosphate (pH Buffer). Therefore, when mother's milk is fermented by lactic acid bacteria (incl. bifidobacteria) in the infant's GI tract, the pH may be reduced, making it more difficult for Gram-negative bacteria to grow.
Metabolism
The genus Bifidobacterium possesses a unique fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase pathway employed to ferment carbohydrates.Much metabolic research on bifidobacteria has focused on oligosaccharide metabolism as these carbohydrates are available in their otherwise nutrient-limited habitats. Interestingly, infant-associated bifidobacterial phylotypes appear to have evolved the ability to ferment milk oligosaccharides, whereas adult-associated species utilize plant oligosaccharides, consistent with what they encounter in their respective environments. As breast-fed infants often harbor bifidobacteria dominated gut consortia, there have been numerous applications to mimic the bifidogenic properties of milk oligosaccharides. These are broadly classified as plant-derived fructo-oligosaccharides or dairy-derived galacto-oligosaccharides, which are differentially metabolized and distinct from milk oligosaccharide catabolism.
Response to oxygen
The sensitivity of members of the genus Bifidobacterium to O2 limits probiotic activity to solely anaerobic habitats. Recent research has reported that the Bifidobacterium strains exhibit various types of oxic growth. Low concentrations of O2 and CO2 can have a stimulatory effect on the growth of Bifidobacterium strains. Based on the growth profiles under different O2 concentrations, the Bifidobacterium species were classified into four classes: O2-hypersensitive, O2-sensitive, O2-tolerant, and microaerophilic. The primary factor responsible for aerobic growth inhibition is proposed to be the production of H2O2 in the growth medium. A H2O2-forming NADH oxidase was purified from O2-sensitive Bifidobacterium bifidum and was identified as a b-type dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. The kinetic parameters suggested that the enzyme could be involved in H2O2 production in highly aerated environments.External links
- Bifidobacterium at Microbe Wiki
http://www.genomesonline.org/search.cgi?colcol=all&goldstamp=ALL&gen_type=ALL&org_name1=genus&gensp=Bifidobacterium&org_domain=ALL&org_status=ALL&size2=ALL&org_size=Kb&gen_gc=ALL&phylogeny2=ALL&gen_institution=ALL&gen_funding=ALL&gen_data=ALL&cont=ALL&gen_country=ALL&gen_pheno=ALL&gen_eco=ALL&gen_disease=ALL&gen_relevance=ALL&gen_avail=ALL&selection=submit+search Bifidobacterium Genome Projects] (from http://www.genomesonline.orgGenomes OnLine Database)- Comparative Analysis of Bifidobacterium Genomes (at DOE'sUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
IMG systemIntegrated Microbial Genomes SystemThe Integrated Microbial Genomes is a genome browsing and annotation system developed by the DOE-Joint Genome Institute. IMG contains all the draft and complete microbial genomes sequenced by the DOE-JGI integrated with other publicly available genomes...
)

