
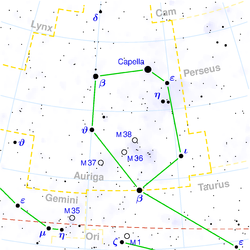
Beta Aurigae
Encyclopedia
Beta Aurigae (β Aur, β Aurigae), traditionally named Menkalinan, is a white subgiant
ternary
star
system approximately 85 light-year
s away in the constellation
Auriga
.
 The name Menkalinan is shortened from the Arabic منكب ذي العنان mankib ðī-l-‘inān "shoulder of the rein-holder". It is known as 五車三 (the Third Star of the Five Chariots) in feudal Chinese astronomy.
The name Menkalinan is shortened from the Arabic منكب ذي العنان mankib ðī-l-‘inān "shoulder of the rein-holder". It is known as 五車三 (the Third Star of the Five Chariots) in feudal Chinese astronomy.
, which is a G2-type subgiant star.
The third star, Beta Aurigae C, is a red dwarf
star that is invisible to the naked eye. The C component is about 330 AU
from the AB pair.
varies over a period of 3.96004 day
s between +1.85 and +1.93, as every 47.5 hour
s one of the stars partially eclipse
s the other from Earth
's perspective.
Beta Aurigae is believed to be a stream star member of the Ursa Major Moving Group
.
Subgiant star
A subgiant star is a star that is slightly brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as true giant stars...
ternary
Star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars which orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large number of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a star cluster or galaxy, although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems.-Binary star systems:A stellar...
star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
system approximately 85 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s away in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Auriga
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'charioteer' and its stars form a shape that has been associated with the pointed helmet of a charioteer. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains among the 88 modern...
.
Nomenclature

System components
Beta Aurigae is actually a ternary (triple) star system, although the light that the star system releases forges the appearance of a single star in the night sky. The two brightest components, Beta Aurigae A and B, are both white subgiants falling under the A-type stellar classification; Beta Aurigae B is about the same mass and radius as A. A-type entities are hot stars that release a blue-white light; these two stars burn brighter and with more heat than the SunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, which is a G2-type subgiant star.
The third star, Beta Aurigae C, is a red dwarf
Red dwarf
According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a red dwarf star is a small and relatively cool star, of the main sequence, either late K or M spectral type....
star that is invisible to the naked eye. The C component is about 330 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
from the AB pair.
Variability
Beta Aurigae's primary and secondary stars constitute an eclipsing spectroscopic binary; the combined apparent magnitudeApparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
varies over a period of 3.96004 day
Day
A day is a unit of time, commonly defined as an interval equal to 24 hours. It also can mean that portion of the full day during which a location is illuminated by the light of the sun...
s between +1.85 and +1.93, as every 47.5 hour
Hour
The hour is a unit of measurement of time. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minutes, or 3,600 seconds...
s one of the stars partially eclipse
Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object is temporarily obscured, either by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer...
s the other from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's perspective.
Beta Aurigae is believed to be a stream star member of the Ursa Major Moving Group
Ursa Major Moving Group
The Ursa Major Moving Group, also known as Collinder 285 or Ursa Major association, is a nearby stellar moving group, a set of stars with common velocities in space and thought to have a common origin. Its core is located roughly 80 light years away...
.
See also
- Algol
- Beta Aurigae in fiction
- CapellaCapella (star)Capella is the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, the sixth brightest star in the night sky and the third brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus and Vega. Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, it is actually a star system of four stars in...

