Beta-2 microglobulin
Encyclopedia
β2 microglobulin also known as B2M is a component of MHC class I
molecules, which are present on all nucleated cells (excludes red blood cell
s). In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein
is encoded by the B2M gene
.
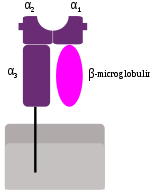 β2 microglobulin lies lateral to the α3 chain on the cell surface. Unlike α3, β2 has no transmembrane
β2 microglobulin lies lateral to the α3 chain on the cell surface. Unlike α3, β2 has no transmembrane
region. Directly above β2 (i.e. away from the cell) lies the α1 chain, which itself is lateral to the α2.
β2 microglobulin associates not only with the alpha chain of MHC class I molecules, but also with class I-like molecules such as CD1
and Qa
.
An additional function is association with the HFE protein, together regulating endocytosis of iron into intestinal cells. Loss of this function causes iron excess and hemochromatosis.
, it can aggregate into amyloid
fibers that deposit in joint spaces, a disease known as dialysis-related amyloidosis.
Mice models deficient for the β2 microglobulin gene have been engineered. These mice demonstrate that β2 microglobulin is necessary for cell surface expression of MHC class I and stability of the peptide binding groove. In fact, in the absence of β2 microglobulin, very limited amounts of MHC class I (classical and non-classical) molecules can be detected on the surface. In the absence of MHC class I, CD8
T cells cannot develop. (CD8 T cells are a subset of T cells involved in the development of acquired immunity.)Low levels of β2 microglobulin can indicate non-progression of HIV.
Levels of beta-2 microglobulin can be elevated in multiple myeloma
and lymphoma
, though in these cases primary amyloidosis (amyloid light chain) and secondary amyloidosis (Amyloid associated protein) are more common.
the normal value of beta-2 microglobulin ranges from( 1 - 2.1 )
MHC class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex molecules and are found on every nucleated cell of the body...
molecules, which are present on all nucleated cells (excludes red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
s). In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
is encoded by the B2M gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
.
Structure and function

Transmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein is a protein that goes from one side of a membrane through to the other side of the membrane. Many TPs function as gateways or "loading docks" to deny or permit the transport of specific substances across the biological membrane, to get into the cell, or out of the cell as...
region. Directly above β2 (i.e. away from the cell) lies the α1 chain, which itself is lateral to the α2.
β2 microglobulin associates not only with the alpha chain of MHC class I molecules, but also with class I-like molecules such as CD1
CD1
For the album by Throbbing Gristle, see CD1 CD1 is a family of glycoproteins expressed on the surface of various human antigen-presenting cells. They are related to the class I MHC molecules, and are involved in the presentation of lipid antigens to T cells...
and Qa
QA
QA may stand for:* Qatar, ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code** .qa, the country code top level domain for Qatar* Quality assurance, the process or set of processes used to measure and assure the quality of a product...
.
An additional function is association with the HFE protein, together regulating endocytosis of iron into intestinal cells. Loss of this function causes iron excess and hemochromatosis.
Clinical significance
In patients on long-term hemodialysisHemodialysis
In medicine, hemodialysis is a method for removing waste products such as creatinine and urea, as well as free water from the blood when the kidneys are in renal failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies .Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy...
, it can aggregate into amyloid
Amyloid
Amyloids are insoluble fibrous protein aggregates sharing specific structural traits. Abnormal accumulation of amyloid in organs may lead to amyloidosis, and may play a role in various neurodegenerative diseases.-Definition:...
fibers that deposit in joint spaces, a disease known as dialysis-related amyloidosis.
Mice models deficient for the β2 microglobulin gene have been engineered. These mice demonstrate that β2 microglobulin is necessary for cell surface expression of MHC class I and stability of the peptide binding groove. In fact, in the absence of β2 microglobulin, very limited amounts of MHC class I (classical and non-classical) molecules can be detected on the surface. In the absence of MHC class I, CD8
CD8
CD8 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T cell receptor . Like the TCR, CD8 binds to a major histocompatibility complex molecule, but is specific for the class I MHC protein. There are two isoforms of the protein, alpha and beta, each encoded by a different gene...
T cells cannot develop. (CD8 T cells are a subset of T cells involved in the development of acquired immunity.)Low levels of β2 microglobulin can indicate non-progression of HIV.
Levels of beta-2 microglobulin can be elevated in multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma , also known as plasma cell myeloma or Kahler's disease , is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell normally responsible for the production of antibodies...
and lymphoma
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
, though in these cases primary amyloidosis (amyloid light chain) and secondary amyloidosis (Amyloid associated protein) are more common.
the normal value of beta-2 microglobulin ranges from( 1 - 2.1 )

