
Bernoulli distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
and statistics
, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss scientist Jacob Bernoulli, is a discrete probability distribution
, which takes value 1 with success probability and value 0 with failure probability
and value 0 with failure probability  . So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have:
. So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have:
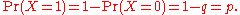
The probability mass function
f of this distribution is
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss scientist Jacob Bernoulli, is a discrete probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
, which takes value 1 with success probability
 and value 0 with failure probability
and value 0 with failure probability  . So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have:
. So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have: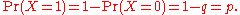
The probability mass function
Probability mass function
In probability theory and statistics, a probability mass function is a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value...
f of this distribution is
-
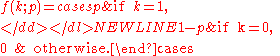
This can also be expressed as

The expected valueExpected valueIn probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
of a Bernoulli random variable X is , and its varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
, and its varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
is
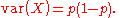
The kurtosisKurtosisIn probability theory and statistics, kurtosis is any measure of the "peakedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable...
goes to infinity for high and low values of p, but for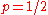 the Bernoulli distribution has a lower kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namely -2.
the Bernoulli distribution has a lower kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namely -2.
The Bernoulli distribution is a member of the exponential familyExponential familyIn probability and statistics, an exponential family is an important class of probability distributions sharing a certain form, specified below. This special form is chosen for mathematical convenience, on account of some useful algebraic properties, as well as for generality, as exponential...
.
The maximum likelihood estimator of p based on a random sample is the sample mean.
Related distributions
- If
 are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli distributed with success probability p, then
are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli distributed with success probability p, then  (binomial distribution). The Bernoulli distribution is simply
(binomial distribution). The Bernoulli distribution is simply 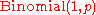 .
. - The categorical distributionCategorical distributionIn probability theory and statistics, a categorical distribution is a probability distribution that describes the result of a random event that can take on one of K possible outcomes, with the probability of each outcome separately specified...
is the generalization of the Bernoulli distribution for variables with any constant number of discrete values. - The Beta distribution is the conjugate priorConjugate priorIn Bayesian probability theory, if the posterior distributions p are in the same family as the prior probability distribution p, the prior and posterior are then called conjugate distributions, and the prior is called a conjugate prior for the likelihood...
of the Bernoulli distribution. - The geometric distribution is the number of Bernoulli trials needed to get one success.
See also
- Bernoulli trialBernoulli trialIn the theory of probability and statistics, a Bernoulli trial is an experiment whose outcome is random and can be either of two possible outcomes, "success" and "failure"....
- Bernoulli processBernoulli processIn probability and statistics, a Bernoulli process is a finite or infinite sequence of binary random variables, so it is a discrete-time stochastic process that takes only two values, canonically 0 and 1. The component Bernoulli variables Xi are identical and independent...
- Bernoulli samplingBernoulli samplingIn the theory of finite population sampling, Bernoulli sampling is a sampling process where each element of the population that is sampled is subjected to an independent Bernoulli trial which determines whether the element becomes part of the sample during the drawing of a single sample...
- Binary entropy function
External links
- If

