
Battle of South Mountain
Encyclopedia
The Battle of South Mountain (known in several early Southern
accounts as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap) was fought September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign
of the American Civil War
. Three pitched battles were fought for possession of three South Mountain
passes: Crampton's
, Turner's
, and Fox's Gap
s. Maj. Gen.
George B. McClellan
, commanding the Union
Army of the Potomac
, needed to pass through these gaps in his pursuit of Confederate
General Robert E. Lee
's Army of Northern Virginia
. Despite being significantly outnumbered, Lee's army delayed McClellan's advance for a day before withdrawing.
after they enter Maryland
. It is a natural obstacle that separates the Hagerstown Valley
and Cumberland Valley
from the eastern part of Maryland.
After Lee invaded Maryland, a copy of an order, known as order 191, detailing troop movements that he wrote fell into the hands of McClellan. From this, McClellan learned that Lee had split his forces and the Union general hoped to attack and defeat some of these isolated forces before they could concentrate against him. To reach Lee, McClellan had to move across South Mountain. Lee learned of McClellan's intelligence coup and quickly sent forces to reinforce the passes to block his advance.
McClellan temporarily organized his army into three wings for the attacks on the passes. Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
, the Right Wing, commanded the I Corps (Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker
) and IX Corps (Maj. Gen. Jesse L. Reno
). The Right Wing was sent to Turner's Gap and Fox's Gap in the north. The Left Wing, commanded by Maj. Gen. William B. Franklin
, consisting of his own VI Corps and Maj. Gen. Darius N. Couch
's division of the IV Corps, was sent to Crampton's Gap in the south. The Center Wing (II Corps and XII Corps), under Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner, was in reserve.
, Confederate cavalry and a small portion of Maj. Gen. Lafayette McLaws
's division defended Brownsville Pass and Crampton's Gap
. McLaws was unaware of the approach of 12,000 Federals and had only 500 men under Col. William A. Parham thinly deployed behind a three quarter-mile-long stone wall at the eastern base of Crampton's Gap
. Franklin spent three hours deploying his forces. A Confederate later wrote of a "lion making exceedingly careful preparations to spring on a plucky little mouse." Franklin deployed the division of Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum on the right and Maj. Gen. William F. "Baldy" Smith
on the left. They seized the gap and captured 400 prisoners, mostly men who were arriving as late reinforcements from Brig. Gen.
Howell Cobb
's brigade.
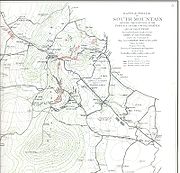 Confederate Maj. Gen. D.H. Hill, deploying 5,000 men over more than 2 miles, defended both Turner's Gap and Fox's Gap. Burnside sent Hooker's I Corps to the right and Turner's Gap. The Union Iron Brigade
Confederate Maj. Gen. D.H. Hill, deploying 5,000 men over more than 2 miles, defended both Turner's Gap and Fox's Gap. Burnside sent Hooker's I Corps to the right and Turner's Gap. The Union Iron Brigade
attacked Colonel
Alfred H. Colquitt
's brigade along the National Road
, driving it back up the mountain, but it refused to yield the pass. Hooker positioned three divisions opposite two peaks located one mile north of the gap. The Alabama Brigade of Brig. Gen. Robert E. Rodes
was forced to withdraw because of his isolated position, despite the arrival of reinforcements from Brig. Gen. David R. Jones's division and Brig. Gen. Nathan G. Evans's brigade. Darkness and the difficult terrain prevented the complete collapse of Lee's line. At nightfall, the Confederates still held the gap.
Brigade ) defended Fox's Gap against Reno's IX Corps. A 9 a.m. attack by Union Brig. Gen. Jacob D. Cox
's Kanawha Division secured much of the land south of the gap. In the movement, Lt. Col. Rutherford B. Hayes
of the 23rd Ohio led a flank attack and was seriously wounded. Cox pushed through the North Carolinians positioned behind a stone wall at the gap's crest, but he failed to capitalize on his gains as his men were exhausted, allowing Confederate reinforcements to deploy in the gap around the Daniel Wise farm. Reno sent forward the rest of his corps, but due to the timely arrival of Southern reinforcements under Confederate Brig. Gen. John Bell Hood
, they failed to dislodge the defenders. Union Maj. Gen. Jesse Reno and Confederate Brig. Gen. Samuel Garland, Jr.
, were killed at Fox's Gap. Union soldiers dumped 60 Confederate bodies down Farmer Wise's dry well, paying him $60 in compensation.
to capture and gave Lee time to unite his scattered divisions at Sharpsburg
for the Battle of Antietam
on September 17.
The battlefields are preserved within the South Mountain State Park
, Gathland State Park
, and the Appalachian National Scenic Trail. Crampton's Gap Historic District
and Turner's and Fox's Gaps Historic District
are listed on the National Register of Historic Places
.
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
accounts as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap) was fought September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign
Maryland Campaign
The Maryland Campaign, or the Antietam Campaign is widely considered one of the major turning points of the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's first invasion of the North was repulsed by Maj. Gen. George B...
of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. Three pitched battles were fought for possession of three South Mountain
South Mountain (Maryland and Pennsylvania)
South Mountain is the northern extension of the Blue Ridge Mountain range in Maryland and Pennsylvania. From the Potomac River near Knoxville, Maryland in the south, to Dillsburg, Pennsylvania in the north, the long range separates the Hagerstown and Cumberland valleys from the Piedmont regions of...
passes: Crampton's
Crampton's Gap
Crampton's Gap, also known as Crampton Gap, is a wind gap on South Mountain in Maryland.The gap connects Burkittsville in the Middletown Valley to the east with Gapland and Rohrersville in the Pleasant Valley to the west....
, Turner's
Turner's Gap
Turner's Gap is a wind gap in the South Mountain Range of the Blue Ridge Mountains, located in Frederick County and Washington County, Maryland. The gap is traversed by U.S. Route 40 Alt, the Old National Pike. The Appalachian Trail also crosses the gap....
, and Fox's Gap
Fox's Gap
Fox's Gap, also known as Fox Gap, is a wind gap in the South Mountain Range of the Blue Ridge Mountains, located in Frederick County and Washington County, Maryland. The gap is traversed by Reno Monument Road...
s. Maj. Gen.
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
George B. McClellan
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
, commanding the Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
, needed to pass through these gaps in his pursuit of Confederate
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
General Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
's Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
. Despite being significantly outnumbered, Lee's army delayed McClellan's advance for a day before withdrawing.
Background
South Mountain is the name given to the continuation of the Blue Ridge MountainsBlue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. This province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. The mountain range is located in the eastern United States, starting at its southern-most...
after they enter Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
. It is a natural obstacle that separates the Hagerstown Valley
Hagerstown Valley
Hagerstown Valley is located in Maryland in the United States. It is part of the Great Appalachian Valley, which continues northward as Cumberland Valley in Pennsylvania, and southward as Shenandoah Valley in West Virginia and Virginia....
and Cumberland Valley
Cumberland Valley
The Cumberland Valley is a constituent valley of the Great Appalachian Valley and a North American agricultural region within the Atlantic Seaboard watershed in Pennsylvania and Maryland....
from the eastern part of Maryland.
After Lee invaded Maryland, a copy of an order, known as order 191, detailing troop movements that he wrote fell into the hands of McClellan. From this, McClellan learned that Lee had split his forces and the Union general hoped to attack and defeat some of these isolated forces before they could concentrate against him. To reach Lee, McClellan had to move across South Mountain. Lee learned of McClellan's intelligence coup and quickly sent forces to reinforce the passes to block his advance.
McClellan temporarily organized his army into three wings for the attacks on the passes. Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside was an American soldier, railroad executive, inventor, industrialist, and politician from Rhode Island, serving as governor and a U.S. Senator...
, the Right Wing, commanded the I Corps (Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker
Joseph Hooker
Joseph Hooker was a career United States Army officer, achieving the rank of major general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Although he served throughout the war, usually with distinction, Hooker is best remembered for his stunning defeat by Confederate General Robert E...
) and IX Corps (Maj. Gen. Jesse L. Reno
Jesse L. Reno
Jesse Lee Reno was a career United States Army officer who served in the Mexican-American War, the western frontier, and as a Union General during the American Civil War...
). The Right Wing was sent to Turner's Gap and Fox's Gap in the north. The Left Wing, commanded by Maj. Gen. William B. Franklin
William B. Franklin
William Buel Franklin was a career United States Army officer and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He rose to the rank of a corps commander in the Army of the Potomac, fighting in several notable early battles in the Eastern Theater.-Early life:William B. Franklin was born in York,...
, consisting of his own VI Corps and Maj. Gen. Darius N. Couch
Darius N. Couch
Darius Nash Couch was an American soldier, businessman, and naturalist. He served as a career U.S. Army officer during the Mexican-American War, the Second Seminole War, and as a general officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War.During the Civil War, Couch fought notably in the...
's division of the IV Corps, was sent to Crampton's Gap in the south. The Center Wing (II Corps and XII Corps), under Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner, was in reserve.
Crampton's Gap
At the southernmost point of the battle, near BurkittsvilleBurkittsville, Maryland
Burkittsville is a town in Frederick County, Maryland, United States. The population was 171 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Burkittsville is located at ....
, Confederate cavalry and a small portion of Maj. Gen. Lafayette McLaws
Lafayette McLaws
Lafayette McLaws was a United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War.-Early life:...
's division defended Brownsville Pass and Crampton's Gap
Battle of Crampton's Gap
The Battle of Crampton's Gap or Battle of Burkittsville was a battle fought between forces under Confederate Brig. Gen. Howell Cobb and Union Maj. Gen. William B...
. McLaws was unaware of the approach of 12,000 Federals and had only 500 men under Col. William A. Parham thinly deployed behind a three quarter-mile-long stone wall at the eastern base of Crampton's Gap
Crampton's Gap
Crampton's Gap, also known as Crampton Gap, is a wind gap on South Mountain in Maryland.The gap connects Burkittsville in the Middletown Valley to the east with Gapland and Rohrersville in the Pleasant Valley to the west....
. Franklin spent three hours deploying his forces. A Confederate later wrote of a "lion making exceedingly careful preparations to spring on a plucky little mouse." Franklin deployed the division of Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum on the right and Maj. Gen. William F. "Baldy" Smith
William Farrar Smith
William Farrar Smith , was a civil engineer, a member of the New York City police commission, and Union general in the American Civil War.-Early life:...
on the left. They seized the gap and captured 400 prisoners, mostly men who were arriving as late reinforcements from Brig. Gen.
Brigadier General
Brigadier general is a senior rank in the armed forces. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000...
Howell Cobb
Howell Cobb
Howell Cobb was an American political figure. A Southern Democrat, Cobb was a five-term member of the United States House of Representatives and Speaker of the House from 1849 to 1851...
's brigade.
Turner's Gap

Iron Brigade
The Iron Brigade, also known as the Iron Brigade of the West or the Black Hat Brigade, was an infantry brigade in the Union Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Although it fought entirely in the Eastern Theater, it was composed of regiments from Western states...
attacked Colonel
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
Alfred H. Colquitt
Alfred H. Colquitt
Alfred Holt Colquitt was a lawyer, preacher, soldier, 49th Governor of Georgia and two term U.S. Senator from Georgia where he died in office. He served as an officer in the Confederate army, reaching the rank of major general....
's brigade along the National Road
National Road
The National Road or Cumberland Road was the first major improved highway in the United States to be built by the federal government. Construction began heading west in 1811 at Cumberland, Maryland, on the Potomac River. It crossed the Allegheny Mountains and southwestern Pennsylvania, reaching...
, driving it back up the mountain, but it refused to yield the pass. Hooker positioned three divisions opposite two peaks located one mile north of the gap. The Alabama Brigade of Brig. Gen. Robert E. Rodes
Robert E. Rodes
Robert Emmett Rodes was a railroad civil engineer and a promising young Confederate general in the American Civil War, killed in battle in the Shenandoah Valley.-Education, antebellum career:...
was forced to withdraw because of his isolated position, despite the arrival of reinforcements from Brig. Gen. David R. Jones's division and Brig. Gen. Nathan G. Evans's brigade. Darkness and the difficult terrain prevented the complete collapse of Lee's line. At nightfall, the Confederates still held the gap.
Fox's Gap
Just to the south, other elements of Hill's division (most notably Drayton'sThomas Drayton
Thomas Fenwick Drayton was a plantation owner, politician, railroad president, and military officer, serving in the United States Army and then as a brigadier general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.-Early life and career:Drayton was a native of South Carolina, most...
Brigade ) defended Fox's Gap against Reno's IX Corps. A 9 a.m. attack by Union Brig. Gen. Jacob D. Cox
Jacob Dolson Cox
Jacob Dolson Cox, was a lawyer, a Union Army general during the American Civil War, and later a Republican politician from Ohio. He served as the 28th Governor of Ohio and as United States Secretary of the Interior....
's Kanawha Division secured much of the land south of the gap. In the movement, Lt. Col. Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford Birchard Hayes was the 19th President of the United States . As president, he oversaw the end of Reconstruction and the United States' entry into the Second Industrial Revolution...
of the 23rd Ohio led a flank attack and was seriously wounded. Cox pushed through the North Carolinians positioned behind a stone wall at the gap's crest, but he failed to capitalize on his gains as his men were exhausted, allowing Confederate reinforcements to deploy in the gap around the Daniel Wise farm. Reno sent forward the rest of his corps, but due to the timely arrival of Southern reinforcements under Confederate Brig. Gen. John Bell Hood
John Bell Hood
John Bell Hood was a Confederate general during the American Civil War. Hood had a reputation for bravery and aggressiveness that sometimes bordered on recklessness...
, they failed to dislodge the defenders. Union Maj. Gen. Jesse Reno and Confederate Brig. Gen. Samuel Garland, Jr.
Samuel Garland, Jr.
Samuel Garland, Jr., was an American attorney from Virginia and Confederate general during the American Civil War. He was killed in action during the Maryland Campaign while defending Fox's Gap at the Battle of South Mountain.-Early life and career:The grandnephew of James Madison, Garland was...
, were killed at Fox's Gap. Union soldiers dumped 60 Confederate bodies down Farmer Wise's dry well, paying him $60 in compensation.
Aftermath
By dusk, with Crampton's Gap lost and his position at Fox's and Turner's Gaps precarious, Lee ordered his outnumbered forces to withdraw from South Mountain. McClellan was now in position to destroy Lee's army before it could concentrate. Union casualties of 28,000 engaged were 2,325 (443 killed, 1,807 wounded, and 75 missing); Confederates lost 2,685 (325 killed, 1560 wounded, and 800 missing) of 18,000. The Battle of South Mountain was an important morale booster for the defeat-stricken Army of the Potomac. The New York World wrote that the battle "turn[ed] back the tide of rebel successes" and "the strength of the rebels is hopelessly broken." Lee contemplated the end of his Maryland campaign. However, McClellan's limited activity on September 15 after his victory at South Mountain condemned the garrison at Harpers FerryBattle of Harpers Ferry
The Battle of Harpers Ferry was fought September 12–15, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War. As Gen. Robert E. Lee's Confederate army invaded Maryland, a portion of his army under Maj. Gen. Thomas J...
to capture and gave Lee time to unite his scattered divisions at Sharpsburg
Sharpsburg, Maryland
Sharpsburg is a town in Washington County, Maryland, United States, approximately south of Hagerstown. The population was 691 at the 2000 census....
for the Battle of Antietam
Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam , fought on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, and Antietam Creek, as part of the Maryland Campaign, was the first major battle in the American Civil War to take place on Northern soil. It was the bloodiest single-day battle in American history, with about 23,000...
on September 17.
The battlefields are preserved within the South Mountain State Park
South Mountain State Park
South Mountain State Park is a state park in Washington and Frederick county, Maryland. The park encompasses nearly the entire length of South Mountain through Maryland and is contiguous with several other national, state and local parks on the mountain, including the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal...
, Gathland State Park
Gathland State Park
Gathland State Park is a small state park located near Burkittsville, Maryland, in the United States. The park is composed of the remains of the estate of George Alfred Townsend , a correspondent during the American Civil War who wrote under the pen name "Gath"...
, and the Appalachian National Scenic Trail. Crampton's Gap Historic District
Crampton's Gap Historic District
The Crampton's Gap Historic District comprises the Civil War-era battlefield involved in the Battle of Crampton's Gap, which took place on September 14, 1862, part of the larger Battle of South Mountain. The district extends on the west to the foot of South Mountain, and to the east of...
and Turner's and Fox's Gaps Historic District
Turner's and Fox's Gaps Historic District
The Turner's and Fox's Gaps Historic District comprises the Civil War-era battlefield involved in the Battle of South Mountain, which took place on September 14, 1862. The district extends on the west to the slopes of South Mountain in the area of Zittlestown, and to the east beyond the foot of the...
are listed on the National Register of Historic Places
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places is the United States government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures, and objects deemed worthy of preservation...
.
Further reading
- Carman, Ezra AyersEzra A. CarmanEzra Ayers Carman was an officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War, commanding a New Jersey infantry regiment and a brigade.-Early life:...
. The Maryland Campaign of September 1862. Vol. 1, South Mountain. Edited by Thomas G. Clemens. El Dorado Hills, CA: Savas Beatie, 2010. ISBN 978-1-932714-81-4.
External links
- Battle of South Mountain: Maps, photos, histories, and preservation news (CWPT)

