
Baryonic dark matter
Encyclopedia
In astronomy
and cosmology
, baryonic dark matter is dark matter
(matter that is undetectable by its emitted radiation
, but whose presence can be inferred from gravitational effects on visible matter) composed of baryon
s, i.e. proton
s and neutron
s and combinations of these, such as non-emitting ordinary atoms. Candidates for baryonic dark matter include non-luminous gas, Massive Astrophysical Compact Halo Objects
(MACHOs: condensed objects such as black hole
s, neutron star
s, white dwarf
s, very faint star
s, or non-luminous objects like planet
s), and brown dwarf
s.
The total amount of baryonic dark matter can be inferred from Big Bang nucleosynthesis
, and observations of the cosmic microwave background. Both indicate that the amount of baryonic dark matter is much smaller than the total amount of dark matter.
In the case of big bang nucleosynthesis
, the problem is that large amounts of ordinary matter means a denser early universe, more efficient conversion of matter to helium-4
and less unburned deuterium
that can remain. If one assumes that all of the dark matter in the universe consists of baryons, then there is far too much deuterium in the universe. This could be resolved if there were some means of generating deuterium, but large efforts in the 1970s failed to come up with plausible mechanisms for this to occur. For instance, MACHOs, which include, for example, brown dwarfs (balls of hydrogen and helium with masses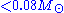 ), never begin nuclear fusion of hydrogen, but they do burn deuterium. Other possibilities that were examined include "Jupiters", which are similar to brown dwarf but have masses
), never begin nuclear fusion of hydrogen, but they do burn deuterium. Other possibilities that were examined include "Jupiters", which are similar to brown dwarf but have masses 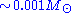 and do not burn anything, and white dwarf
and do not burn anything, and white dwarf
s.
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
and cosmology
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
, baryonic dark matter is dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
(matter that is undetectable by its emitted radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
, but whose presence can be inferred from gravitational effects on visible matter) composed of baryon
Baryon
A baryon is a composite particle made up of three quarks . Baryons and mesons belong to the hadron family, which are the quark-based particles...
s, i.e. proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s and neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s and combinations of these, such as non-emitting ordinary atoms. Candidates for baryonic dark matter include non-luminous gas, Massive Astrophysical Compact Halo Objects
Massive compact halo object
Massive astrophysical compact halo object, or MACHO, is a general name for any kind of astronomical body that might explain the apparent presence of dark matter in galaxy halos. A MACHO is a body composed of normal baryonic matter, which emits little or no radiation and drifts through interstellar...
(MACHOs: condensed objects such as black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
s, neutron star
Neutron star
A neutron star is a type of stellar remnant that can result from the gravitational collapse of a massive star during a Type II, Type Ib or Type Ic supernova event. Such stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons, which are subatomic particles without electrical charge and with a slightly larger...
s, white dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
s, very faint star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, or non-luminous objects like planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s), and brown dwarf
Brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are sub-stellar objects which are too low in mass to sustain hydrogen-1 fusion reactions in their cores, which is characteristic of stars on the main sequence. Brown dwarfs have fully convective surfaces and interiors, with no chemical differentiation by depth...
s.
The total amount of baryonic dark matter can be inferred from Big Bang nucleosynthesis
Big Bang nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis refers to the production of nuclei other than those of H-1 during the early phases of the universe...
, and observations of the cosmic microwave background. Both indicate that the amount of baryonic dark matter is much smaller than the total amount of dark matter.
In the case of big bang nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process of creating new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons . It is thought that the primordial nucleons themselves were formed from the quark–gluon plasma from the Big Bang as it cooled below two trillion degrees...
, the problem is that large amounts of ordinary matter means a denser early universe, more efficient conversion of matter to helium-4
Helium-4
Helium-4 is a non-radioactive isotope of helium. It is by far the most abundant of the two naturally occurring isotopes of helium, making up about 99.99986% of the helium on earth. Its nucleus is the same as an alpha particle, consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Alpha decay of heavy...
and less unburned deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
that can remain. If one assumes that all of the dark matter in the universe consists of baryons, then there is far too much deuterium in the universe. This could be resolved if there were some means of generating deuterium, but large efforts in the 1970s failed to come up with plausible mechanisms for this to occur. For instance, MACHOs, which include, for example, brown dwarfs (balls of hydrogen and helium with masses
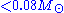 ), never begin nuclear fusion of hydrogen, but they do burn deuterium. Other possibilities that were examined include "Jupiters", which are similar to brown dwarf but have masses
), never begin nuclear fusion of hydrogen, but they do burn deuterium. Other possibilities that were examined include "Jupiters", which are similar to brown dwarf but have masses  and do not burn anything, and white dwarf
and do not burn anything, and white dwarfWhite dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
s.

