
Barberpole illusion
Encyclopedia
The barberpole illusion is a visual illusion that reveals biases in the processing of visual motion
in the human brain. This visual illusion occurs when a diagonally-striped pole is rotated around its vertical axis (horizontally), it appears as though the stripes are moving in the direction of its vertical axis (downwards in the case of the animation to the right). rather than around it.
is commonly found outside barber shops
.
In 1929, psychologist
J. P. Guilford
noted the paradoxical motion inherent in the perceived motion of stripes on a rotating barber pole. The barber pole turns in place on its vertical axis, but the stripes appear to move upwards rather than turning with the pole.
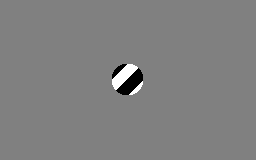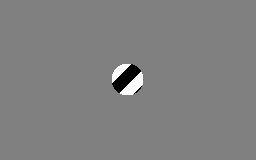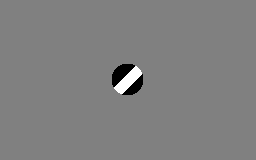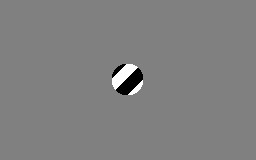 This illusion occurs because a bar or contour within a frame of reference provides ambiguous information about its "real" direction of movement. The actual motion of the line has many possibilities. The shape of the aperture thus tends to determine the perceived direction of motion for an otherwise identically moving contour. A vertically elongated aperture makes vertical motion dominant whereas a horizontally elongated aperture makes horizontal motion dominant. In the case of a circular or square aperture, the perceived direction of movement is usually orthogonal to the orientation of the stripes (diagonal, in this case). The perceived direction of movement relates to the termination of the line's end points within the inside border of the occluder. The vertical aperture, for instance, has longer edges at the vertical orientation, creating a larger number of terminators unambiguously moving vertically. This stronger motion signal forces us to perceive vertical motion. Functionally, this mechanism has evolved
This illusion occurs because a bar or contour within a frame of reference provides ambiguous information about its "real" direction of movement. The actual motion of the line has many possibilities. The shape of the aperture thus tends to determine the perceived direction of motion for an otherwise identically moving contour. A vertically elongated aperture makes vertical motion dominant whereas a horizontally elongated aperture makes horizontal motion dominant. In the case of a circular or square aperture, the perceived direction of movement is usually orthogonal to the orientation of the stripes (diagonal, in this case). The perceived direction of movement relates to the termination of the line's end points within the inside border of the occluder. The vertical aperture, for instance, has longer edges at the vertical orientation, creating a larger number of terminators unambiguously moving vertically. This stronger motion signal forces us to perceive vertical motion. Functionally, this mechanism has evolved
to ensure that we perceive a moving pattern as a rigid surface moving in one direction.
Individual motion-sensitive neurons in the visual system
have only limited information, as they see only a small portion of the visual field (a situation referred to as the "aperture problem"). In the absence of additional information the visual system prefers the slowest possible motion: i.e., motion orthogonal to the moving line. Neurons have been identified in the visual cortex
of ferrets, the activity of which may correspond to the perception of patterns such as barber poles.
Motion perception
Motion perception is the process of inferring the speed and direction of elements in a scene based on visual, vestibular and proprioceptive inputs...
in the human brain. This visual illusion occurs when a diagonally-striped pole is rotated around its vertical axis (horizontally), it appears as though the stripes are moving in the direction of its vertical axis (downwards in the case of the animation to the right). rather than around it.
History
The barber's poleBarber's pole
A barber's pole is a type of sign used by barbers to signify the place or shop where they perform their craft. The trade sign is, by a tradition dating back to the Middle Ages, a staff or pole with a helix of colored stripes...
is commonly found outside barber shops
Barber
A barber is someone whose occupation is to cut any type of hair, and to shave or trim the beards of men. The place of work of a barber is generally called a barbershop....
.
In 1929, psychologist
Psychologist
Psychologist is a professional or academic title used by individuals who are either:* Clinical professionals who work with patients in a variety of therapeutic contexts .* Scientists conducting psychological research or teaching psychology in a college...
J. P. Guilford
J. P. Guilford
Joy Paul Guilford was a US psychologist, best remembered for his psychometric study of human intelligence, including the important distinction between convergent and divergent production....
noted the paradoxical motion inherent in the perceived motion of stripes on a rotating barber pole. The barber pole turns in place on its vertical axis, but the stripes appear to move upwards rather than turning with the pole.
Explanation

Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
to ensure that we perceive a moving pattern as a rigid surface moving in one direction.
Individual motion-sensitive neurons in the visual system
Visual system
The visual system is the part of the central nervous system which enables organisms to process visual detail, as well as enabling several non-image forming photoresponse functions. It interprets information from visible light to build a representation of the surrounding world...
have only limited information, as they see only a small portion of the visual field (a situation referred to as the "aperture problem"). In the absence of additional information the visual system prefers the slowest possible motion: i.e., motion orthogonal to the moving line. Neurons have been identified in the visual cortex
Visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the part of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe, in the back of the brain....
of ferrets, the activity of which may correspond to the perception of patterns such as barber poles.
Auditory analogue
A similar effect occurs in the Shepard's tone, which is an auditory illusion.See also
- Auditory illusionAuditory illusionAn auditory illusion is an illusion of hearing, the aural equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the stimulus, or "impossible" sounds...
- Barber's poleBarber's poleA barber's pole is a type of sign used by barbers to signify the place or shop where they perform their craft. The trade sign is, by a tradition dating back to the Middle Ages, a staff or pole with a helix of colored stripes...
for the modern device exploiting this illusion - Motion perceptionMotion perceptionMotion perception is the process of inferring the speed and direction of elements in a scene based on visual, vestibular and proprioceptive inputs...
- Shepard toneShepard toneA Shepard tone, named after Roger Shepard, is a sound consisting of a superposition of sine waves separated by octaves. When played with the base pitch of the tone moving upward or downward, it is referred to as the Shepard scale. This creates the auditory illusion of a tone that continually...

