.gif)
Avanti (India)
Encyclopedia
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
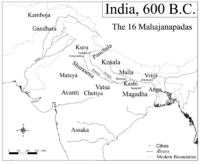
n janapada (realm), roughly corresponded to the present day Malwa region. According to the Buddhist text, the Anguttara Nikaya, Avanti was one of the solasa mahajanapadas
Mahajanapadas
Mahājanapadas , literally "great realms", were ancient Indian kingdoms or countries...
(sixteen great realms) of the 6th century BCE. The janapada was divided into two parts by the Vindhyas, the northern part had its capital at Ujjayini
Ujjain
Ujjain , is an ancient city of Malwa region in central India, on the eastern bank of the Kshipra River , today part of the state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the administrative centre of Ujjain District and Ujjain Division.In ancient times the city was called Ujjayini...
and the southern part had its centre at Mahishmati
Maheshwar
Maheshwar is a town in Khargone district of Madhya Pradesh state, in central India. It is located 13 km east of National Highway 3 and 91 km from Indore, the commercial capital of the state. The town lies on the north bank of the Narmada River.-Etymology:The name Maheshwar comes from...
.
The Avantis, the ancient people belonging to this realm were described as mahavala (very powerful) in the Udyoga Parva
Udyoga Parva
The Udyoga Parva is the fifth Parva of the Mahabharata, abounding with incidents appertaining to war and peace. It is the Book of the effort in preparations for war ....
(19.24) of the Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
. According to the Vishnu Purana
Vishnu Purana
The Vishnu Purana is a religious Hindu text and one of the eighteen Mahapuranas. It is considered one of the most important Puranas and has been given the name Puranaratna...
(II.3), the Bhagavata Purana
Bhagavata purana
The Bhāgavata Purāṇa is one of the "Maha" Puranic texts of Hindu literature, with its primary focus on bhakti to the incarnations of Vishnu, particularly Krishna...
(XII.I.36) and the Brahma Purana
Brahma Purana
The Brahma Purana is one of the major eighteen Mahapuranas, a genre of Hindu religious texts. The extant text comprises 246 chapters. It is divided into two parts, namely the Purvabhaga and the Uttarabhaga . The first part narrates the story behind the creation of the cosmos, details the life and...
(XIX.17), the Avantis were associated with the Malavas, the Saurashtra
Saurashtra
Saurashtra is a region of western India, located on the Arabian Sea coast of Gujarat state. It is a peninsula also called Kathiawar after the Kathi Darbar who ruled part of the region once. The Peninsula is shared with the Kachchh region which occupies the north, Saurashtra or Sorath forming the...
s, the Abhiras, the Suras, the Karusha
Karusha Kingdom
Karusha Kingdom was one among the many kingdoms ruled by Yadava kings in the central and western India.It lies to the south of Chedi. Karusha king Dantavaktra supported Chedi king Sishupala and was killed by Vasudeva Krishna...
s and the Arbudas and were described as dwelling along the Pariyatra (or Paripatra) mountains (a western branch of the Vindhyas).
The Haihayas of Mahishmati
According to the Puranic accounts, the HaihayasHaihayas
The Haihayas were an ancient confederacy of five ganas , who claimed their common ancestry from Yadu. According to the Harivamsha Purana...
were the earliest rulers of Avanti, who captured the region from the Nagas. Initially, they ruled from Mahishmati. Later the whole janapada was divided into two parts with the capitals at Mahishmati and Ujjayini. The Haihayas were a confederation of five clans, the Vitihotras, the Bhojas, the Avantis, the Tundikeras and the Sharyatas. Later, the Haihayas were better known by their dominant clan - the Vitihotras. Ripunjaya, the last Vitihotra ruler of Ujjayini was overthrown by his amatya (minister) Pulika, who placed his son, Pradyota on the throne.
The Mahagovindasuttanta of the Dighanikaya
Digha Nikaya
The Digha Nikaya is a Buddhist scripture, the first of the five nikayas, or collections, in the Sutta Pitaka, which is one of the "three baskets" that compose the Pali Tipitaka of Theravada Buddhism...
mentions about an Avanti king Vessabhu (Vishvabhu) and his capital Mahissati (Mahishmati). Probably he was a Vitihotra ruler.
Pradyota dynasty
Pradyota was contemporary to Gautama BuddhaGautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
. He was also known as Chandapradyota Mahasena. Pradyota captured the Vatsa
Vatsa
Vatsa was one of the solasa Mahajanapadas of Uttarapatha of ancient India mentioned in the Anguttara Nikaya....
king Udayana but later he married Pradyota’s daughter Vasavadatta. The Mahavagga described him as cruel and according to the Majjhima Nikaya, Ajatashatru
Ajatashatru
Ajatasatru was a king of the Magadha empire in north India. He was the son of King Bimbisara, the Great Monarch of Magadha. He was contemporary to Mahavira and Buddha. He took over the kingdom of Magadha from his father forcefully by imprisoning him...
, the king of Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
fortified Rajagriha to protect it from an invasion led by Pradyota. He also waged war on Pushkarasarin, king of Takshashila
Taxila
Taxila is a Tehsil in the Rawalpindi District of Punjab province of Pakistan. It is an important archaeological site.Taxila is situated about northwest of Islamabad Capital Territory and Rawalpindi in Panjab; just off the Grand Trunk Road...
Pradyota’s chief queen Gopalamata (mother of prince Gopala) was a disciple of Buddhist monk Mahakatyayana and constructed a stupa
Stupa
A stupa is a mound-like structure containing Buddhist relics, typically the remains of Buddha, used by Buddhists as a place of worship....
in Ujjayini.
Prodyota had two sons, Gopala and Palaka. He was succeeded by Palaka. According to Jaina accounts Palaka ascended to the throne on the day of passing away of Mahavira
Mahavira
Mahāvīra is the name most commonly used to refer to the Indian sage Vardhamāna who established what are today considered to be the central tenets of Jainism. According to Jain tradition, he was the 24th and the last Tirthankara. In Tamil, he is referred to as Arukaṉ or Arukadevan...
. According to the Kathasaritsagara
Kathasaritsagara
Kathasaritsagara is a famous 11th-century collection of Indian legends, fairy tales and folk tales as retold by a Saivite Brahmin named Somadeva....
and the Avashyaka Kathanaka, the kingdom of Vatsa
Vatsa
Vatsa was one of the solasa Mahajanapadas of Uttarapatha of ancient India mentioned in the Anguttara Nikaya....
was already a part of Avanti during the reign of Palaka and a prince of the royal family was the governor of Kaushambi. In the Mricchakatika, Palaka was described as a tyrant who was overthrown by a popular revolt. This revolt placed Aryaka on the throne of Ujjayini. The Puranas place Nadivardhana or Vartivardhana after Aryaka. But these names are probably corruptions of Avantivardhana, the name of the son of Palaka according to the Kathasaritsagara or the son of Gopala according to the Nepali Brihatkatha. He was defeated by Shishunaga
Shishunaga
Shishunaga was the founder of the Shishunaga dynasty of the Magadha Empire in the present day northern India. Initially, he was an amatya of the Magadha empire under the Haryanka dynasty. He was placed on the throne by the people who revolted against the Haryanka dynasty rule...
, the king of Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
.
Avanti under Magadhan rule
Avanti was a part of the Magadha empire during the rule of the ShaishunagaShishunaga dynasty
The Shishunaga dynasty was the third ruling dynasty of Magadha, a kingdom in ancient India. But according to the Puranas, this dynasty is the second ruling dynasty of Magadha, which succeeded the Barhadratha dynasty....
and the Nanda
Nanda Dynasty
The Nanda Empire originated from the region of Magadha in Ancient India during the 5th and 4th centuries BC. At its greatest extent, the Nanda Empire extended from Bengal in the east, to Punjab in the west and as far south as the Vindhya Range...
dynasties. During the Mauryan dynasty rule, Avanti became the or the western province of the empire, with its capital at Ujjayini. The Junagarh Rock inscription of Rudradaman I
Rudradaman I
Rudradaman I was a Saka ruler from the Western Kshatrapas dynasty. He was the grandson of the celebrated Sah king Chastana. Rudradaman I was instrumental in the decline of the Satavahana Empire.- Mahakshatrapa :...
(150 CE) mentions Pushyagupta as the governor of the western province during the reign of Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya , was the founder of the Maurya Empire. Chandragupta succeeded in conquering most of the Indian subcontinent. Chandragupta is considered the first unifier of India and its first genuine emperor...
. During the reign of the next ruler Bindusara
Bindusara
Bindusara was the second Mauryan emperor after Chandragupta Maurya. During his reign, the empire expanded southwards. He had two well-known sons, Susima and Ashoka, who were the viceroys of Taxila and Ujjain...
, prince Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
was the provincial governor. After the fall of the Mauryas, at the time of Pusyamitra Sunga
Pusyamitra Sunga
Pusyamitra Sunga was the founder and first King of the Sunga Dynasty in Northern India.Pusyamitra Sunga was originally a Senapati of the Mauryan empire. In 185 BCE he assassinated the last Mauryan Emperor during an army review, and proclaimed himself King...
, his son Agnimitra
Agnimitra
Agnimitra was the second King of the Sunga Dynasty of northern India. He succeeded his father, Pusyamitra Sunga, in 149 BCE...
was the Magadhan viceroy at Vidisha
Vidisha
Vidisha is a city in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India, located near the state capital Bhopal. Vidishā is the administrative headquarters of Vidisha District. The city was also known as Bhilsa during the medieval period.-Geography:...
, but he ruled independent of Magadha for all practical purposes.

