
Autocorrelator
Encyclopedia
A real time interferometric
autocorrelator is an electronic tool used to examine the autocorrelation
of, among other things, optical beam intensity and spectral components through examination of variable beam path differences. See Optical autocorrelation
.
autocorrelator, the input beam is split into a fixed path beam and a variable path beam using a standard beamsplitter. The fixed path beam travels a known and constant distance, whereas the variable path beam has its path length changed via rotating mirrors or other path changing mechanisms. At the end of the two paths, the beams are ideally parallel, but slightly separated, and using a correctly positioned lens, the two beams are crossed inside a second harmonic generating (SHG)
crystal. The autocorrelation term of the output is then passed into a photomultiplying tube (PMT)
and measured.
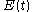 , the constant fixed path distance as
, the constant fixed path distance as 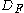 , and the variable path distance as a function of time
, and the variable path distance as a function of time 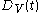 , the input to the SHG can be viewed as
, the input to the SHG can be viewed as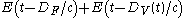
This comes from being the speed of light and
being the speed of light and 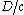 being the time for the beam to travel the given path. In general, SHG produces output proportional to the square of the input, which in this case is
being the time for the beam to travel the given path. In general, SHG produces output proportional to the square of the input, which in this case is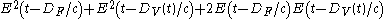
The first two terms are based only on the fixed and variable paths respectively, but the third term is based on the difference between them, as is evident in
The PMT used is assumed to be much slower than the envelope function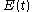 , so it effectively integrates the incoming signal
, so it effectively integrates the incoming signal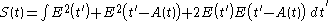
Since both the fixed path and variable path terms are not dependent on each other, they would constitute a background "noise" in examination of the autocorrelation term and would ideally be removed first. This can be accomplished by examining the momentum vectors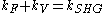
If the fixed and variable momentum vectors are assumed to be of approximately equal magnitude, the second harmonic momentum vector will fall geometrically between them. Assuming enough space is given in the component setup, the PMT could be fitted with a slit to decrease the effect the divergent fixed and variable beams have on the autocorrelation measurement, without losing much of the autocorrelation term.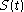 can then be assumed to be nearly equal to
can then be assumed to be nearly equal to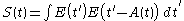
which gives the autocorrelation as a function of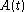 , the difference in path lengths.
, the difference in path lengths.
Interferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
autocorrelator is an electronic tool used to examine the autocorrelation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
of, among other things, optical beam intensity and spectral components through examination of variable beam path differences. See Optical autocorrelation
Optical autocorrelation
In optics, various autocorrelation functions can be experimentally realized. The field autocorrelation may be used to calculate the spectrum of a source of light, while the intensity autocorrelation and the interferometric autocorrelation are commonly used to estimate the duration of ultrashort...
.
Description
In an interferometricInterferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
autocorrelator, the input beam is split into a fixed path beam and a variable path beam using a standard beamsplitter. The fixed path beam travels a known and constant distance, whereas the variable path beam has its path length changed via rotating mirrors or other path changing mechanisms. At the end of the two paths, the beams are ideally parallel, but slightly separated, and using a correctly positioned lens, the two beams are crossed inside a second harmonic generating (SHG)
Second harmonic generation
An optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device, in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency...
crystal. The autocorrelation term of the output is then passed into a photomultiplying tube (PMT)
Photomultiplier
Photomultiplier tubes , members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically phototubes, are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum...
and measured.
Details
Considering the input beam as a single pulse with envelope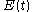 , the constant fixed path distance as
, the constant fixed path distance as 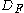 , and the variable path distance as a function of time
, and the variable path distance as a function of time 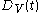 , the input to the SHG can be viewed as
, the input to the SHG can be viewed as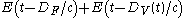
This comes from
 being the speed of light and
being the speed of light and 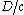 being the time for the beam to travel the given path. In general, SHG produces output proportional to the square of the input, which in this case is
being the time for the beam to travel the given path. In general, SHG produces output proportional to the square of the input, which in this case is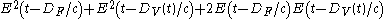
The first two terms are based only on the fixed and variable paths respectively, but the third term is based on the difference between them, as is evident in

The PMT used is assumed to be much slower than the envelope function
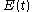 , so it effectively integrates the incoming signal
, so it effectively integrates the incoming signal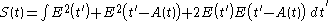
Since both the fixed path and variable path terms are not dependent on each other, they would constitute a background "noise" in examination of the autocorrelation term and would ideally be removed first. This can be accomplished by examining the momentum vectors
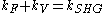
If the fixed and variable momentum vectors are assumed to be of approximately equal magnitude, the second harmonic momentum vector will fall geometrically between them. Assuming enough space is given in the component setup, the PMT could be fitted with a slit to decrease the effect the divergent fixed and variable beams have on the autocorrelation measurement, without losing much of the autocorrelation term.
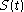 can then be assumed to be nearly equal to
can then be assumed to be nearly equal to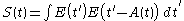
which gives the autocorrelation as a function of
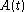 , the difference in path lengths.
, the difference in path lengths.Technical specifications
- Calibration Factor -- the factor to convert real-time to pulse delay time when viewing the output of the autocorrelator. One example of this would be 30 ps/ms in the Coherent Model FR-103 scanning autocorrelator, which suggests that a 30 ps pulse autocorrelation width would produce a 1 ms FWHM trace when viewed on an oscilloscope.
- Time Resolution -- related to the time constant of the PMT, an estimate can be made by multiplying the time constant with the calibration factor.
See also
- Autocorrelation techniqueAutocorrelation techniqueThe autocorrelation technique is a method for estimating the dominating frequency in a complex signal, as well as its variance. Specifically, it calculates the first two moments of the power spectrum, namely the mean and variance...
- :Category:Nonlinear optics
- :Category:Nonlinear optical materials
- Optical autocorrelationOptical autocorrelationIn optics, various autocorrelation functions can be experimentally realized. The field autocorrelation may be used to calculate the spectrum of a source of light, while the intensity autocorrelation and the interferometric autocorrelation are commonly used to estimate the duration of ultrashort...

