
Autocorrelation technique
Encyclopedia
The autocorrelation technique is a method for estimating the dominating frequency in a complex
signal, as well as its variance. Specifically, it calculates the first two moments of the power spectrum, namely the mean and variance. It is also known as the pulse-pair algorithm in radar
theory.
The algorithm is both computationally faster and significantly more accurate compared to the Fourier transform
, since the resolution is not limited by the number of samples used.
of lag 1 can be expressed using the inverse Fourier transform of the power spectrum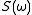 :
: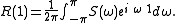
If we model the power spectrum as a single frequency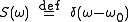 , this becomes:
, this becomes: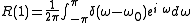
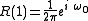
where it is apparent that the phase of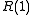 equals the signal frequency.
equals the signal frequency.
with lag one, evaluated over a signal consisting of N samples: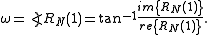
The spectral variance is calculated as follows: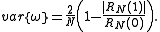
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
signal, as well as its variance. Specifically, it calculates the first two moments of the power spectrum, namely the mean and variance. It is also known as the pulse-pair algorithm in radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
theory.
The algorithm is both computationally faster and significantly more accurate compared to the Fourier transform
Discrete Fourier transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform is a specific kind of discrete transform, used in Fourier analysis. It transforms one function into another, which is called the frequency domain representation, or simply the DFT, of the original function...
, since the resolution is not limited by the number of samples used.
Derivation
The autocorrelationAutocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
of lag 1 can be expressed using the inverse Fourier transform of the power spectrum
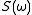 :
: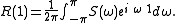
If we model the power spectrum as a single frequency
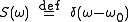 , this becomes:
, this becomes: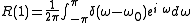
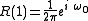
where it is apparent that the phase of
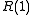 equals the signal frequency.
equals the signal frequency.Implementation
The mean frequency is calculated based on the autocorrelationAutocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
with lag one, evaluated over a signal consisting of N samples:
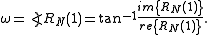
The spectral variance is calculated as follows:
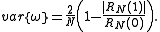
Applications
- Estimation of blood velocity and turbulence in color flow imaging used in medical ultrasonographyMedical ultrasonographyDiagnostic sonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions...
. - Estimation of target velocity in pulse-doppler radarPulse-doppler radarPulse-Doppler is a 4D radar system capable of detecting both target 3D location as well as measuring radial velocity . It uses the Doppler effect to avoid overloading computers and operators as well as to reduce power consumption...
External links
- A covariance approach to spectral moment estimation, Miller et al., IEEE Transactions on Information Theory.
- Doppler Radar Meteorological Observations Doppler Radar Theory. Autocorrelation technique described on p.2-11
- Real-Time Two-Dimensional Blood Flow Imaging Using an Autocorrelation Technique, by Chihiro Kasai, Koroku Namekawa, Akira Koyano, and Ryozo Omoto, IEEE Transactions on sonics and ultrasonics, May 1985

