.gif)
Atomic mirror (physics)
Encyclopedia
In physics
, an atomic mirror is a device which reflects
neutral atoms in the similar way as the conventional mirror reflects visible light. Atomic mirrors can be made of electric field
s or magnetic field
s, electromagnetic waves or just silicon wafer; in the last case, atoms are reflected by the attracting tails of the van der Waals attraction (see quantum reflection
). Such reflection is efficient when the normal component of the wavenumber of the atoms is small or comparable to the effective depth of the attraction potential (roughly, the distance at which the potential becomes comparable to the kinetic energy of the atom). To reduce the normal component, most atomic mirrors are blazed at the grazing incidence.
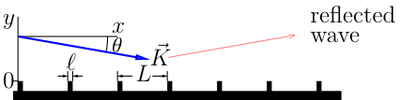 At grazing incidence, the efficiency of the quantum reflection
At grazing incidence, the efficiency of the quantum reflection
can be enhanced by a surface covered with ridges (ridged mirror
).
The set of narrow ridges reduces the van der Waals
attraction of atoms to the surfaces and enhances the reflection. Each ridge blocks part of the wavefront, causing Fresnel diffraction
.
Such a mirror can be interpreted in terms of the Zeno effect. We may assume that the atom is "absorbed" or "measured" at the ridges. Frequent measuring (narrowly-spaced ridges) suppresses the transition of the particle to the half-space with absorbers, causing specular reflection
. At large separation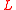 between thin ridges, the reflectivity of the ridged mirror
between thin ridges, the reflectivity of the ridged mirror
is determined by dimensionless momentum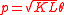 , and does not depend on the origin of the wave; therefore, it is suitable for reflection of atoms.
, and does not depend on the origin of the wave; therefore, it is suitable for reflection of atoms.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, an atomic mirror is a device which reflects
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
neutral atoms in the similar way as the conventional mirror reflects visible light. Atomic mirrors can be made of electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
s or magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s, electromagnetic waves or just silicon wafer; in the last case, atoms are reflected by the attracting tails of the van der Waals attraction (see quantum reflection
Quantum reflection
Quantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
). Such reflection is efficient when the normal component of the wavenumber of the atoms is small or comparable to the effective depth of the attraction potential (roughly, the distance at which the potential becomes comparable to the kinetic energy of the atom). To reduce the normal component, most atomic mirrors are blazed at the grazing incidence.

Quantum reflection
Quantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
can be enhanced by a surface covered with ridges (ridged mirror
Ridged mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles coming at the grazing incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this...
).
The set of narrow ridges reduces the van der Waals
Van der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
attraction of atoms to the surfaces and enhances the reflection. Each ridge blocks part of the wavefront, causing Fresnel diffraction
Fresnel diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction, is an approximation of Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field....
.
Such a mirror can be interpreted in terms of the Zeno effect. We may assume that the atom is "absorbed" or "measured" at the ridges. Frequent measuring (narrowly-spaced ridges) suppresses the transition of the particle to the half-space with absorbers, causing specular reflection
Specular reflection
Specular reflection is the mirror-like reflection of light from a surface, in which light from a single incoming direction is reflected into a single outgoing direction...
. At large separation
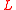 between thin ridges, the reflectivity of the ridged mirror
between thin ridges, the reflectivity of the ridged mirrorRidged mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles coming at the grazing incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this...
is determined by dimensionless momentum
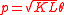 , and does not depend on the origin of the wave; therefore, it is suitable for reflection of atoms.
, and does not depend on the origin of the wave; therefore, it is suitable for reflection of atoms.Applications
- Atomic interferometryInterferometryInterferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
- Atom holography (see also atom laserAtom laserAn atom laser is a coherent state of propagating atoms. They are created out of a Bose–Einstein condensate of atoms that are output coupled using various techniques. Much like an optical laser, an atom laser is a coherent beam that behaves like a wave. There has been some argument that the term...
) This was demonstrated by Shimizu and Fujita in 2002. - Atomic nanoscopeAtomic nanoscopeThe atomic de Broglie microscope is an imaging system which is expected to provide resolution at the nanometer scale....
See also
- Quantum reflectionQuantum reflectionQuantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
- Ridged mirrorRidged mirrorIn atomic physics, a ridged mirror is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles coming at the grazing incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this...
- Zeno effect
- Atomic nanoscopeAtomic nanoscopeThe atomic de Broglie microscope is an imaging system which is expected to provide resolution at the nanometer scale....
- Atom laserAtom laserAn atom laser is a coherent state of propagating atoms. They are created out of a Bose–Einstein condensate of atoms that are output coupled using various techniques. Much like an optical laser, an atom laser is a coherent beam that behaves like a wave. There has been some argument that the term...

