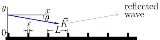
Ridged mirror
Encyclopedia
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror (or ridged atomic mirror, or Fresnel diffraction mirror) is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles (atoms) coming at the grazing
incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this surface has narrow ridges.
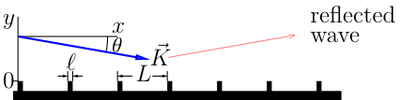 Various estimates for the efficiency of quantum reflection
Various estimates for the efficiency of quantum reflection
of waves from ridged mirror were discussed in the literature. All the estimates explicitly use the de Broglie theory about wave properties of reflected atoms.
from the surface, reducing the effective constant of the van der Waals
of the van der Waals
attraction of atoms to the surface. Such interpretation leads to the estimate of the reflectivity
where is width of the ridges,
is width of the ridges, 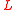 is distance between ridges,
is distance between ridges,  is grazing angle, and
is grazing angle, and  is wavenumber and
is wavenumber and 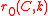 is coefficient of reflection of atoms with wavenumber
is coefficient of reflection of atoms with wavenumber  from a flat surface at the normal incidence. Such estimate predicts the enhancement of the reflectivity at the increase of period
from a flat surface at the normal incidence. Such estimate predicts the enhancement of the reflectivity at the increase of period 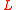 ; this estimate is valid at
; this estimate is valid at 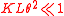 . See quantum reflection
. See quantum reflection
for the approximation (fit) of the function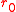 .
.
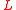 , the ridges just blocks the part of the wavefront. Then, it can be interpreted in terms of the Fresnel diffraction
, the ridges just blocks the part of the wavefront. Then, it can be interpreted in terms of the Fresnel diffraction
of the de Broglie wave, or the Zeno effect; such interpretation leads to the estimate the reflectivity
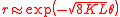 ,
,
where the grazing angle is supposed to be small. This estimate predicts enhancement of the reflectivity at the reduction of period
is supposed to be small. This estimate predicts enhancement of the reflectivity at the reduction of period 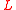 . This estimate requires that
. This estimate requires that 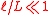 .
.
 of the ridges and the period,
of the ridges and the period, 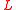 . The width of the ridges cannot be smaller than the size of atom; this sets the limit of performance of the ridged mirrors.
. The width of the ridges cannot be smaller than the size of atom; this sets the limit of performance of the ridged mirrors.
In Shimizu's and Fujita's work, atom holography is achieved via electrodes implanted into SiN4 film over an atomic mirror, or maybe as the atomic mirror itself.
Ridged mirrors can also reflect visible light; however, for light waves, the performance is not better than that of a flat surface. An ellipsoidal ridged mirror is proposed as the focusing element for an atomic optical system with submicrometre resolution (atomic nanoscope
).
Grazing
Grazing generally describes a type of feeding, in which a herbivore feeds on plants , and also on other multicellular autotrophs...
incidence angle, characterised in the following: in order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this surface has narrow ridges.
Reflectivity of ridged atomic mirrors

Quantum reflection
Quantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
of waves from ridged mirror were discussed in the literature. All the estimates explicitly use the de Broglie theory about wave properties of reflected atoms.
Scaling of the van der Waals force
The ridges enhance the quantum reflectionQuantum reflection
Quantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
from the surface, reducing the effective constant
 of the van der Waals
of the van der WaalsVan der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
attraction of atoms to the surface. Such interpretation leads to the estimate of the reflectivity
-
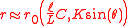 ,
,
where
 is width of the ridges,
is width of the ridges, 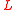 is distance between ridges,
is distance between ridges,  is grazing angle, and
is grazing angle, and  is wavenumber and
is wavenumber and 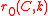 is coefficient of reflection of atoms with wavenumber
is coefficient of reflection of atoms with wavenumber  from a flat surface at the normal incidence. Such estimate predicts the enhancement of the reflectivity at the increase of period
from a flat surface at the normal incidence. Such estimate predicts the enhancement of the reflectivity at the increase of period 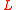 ; this estimate is valid at
; this estimate is valid at 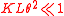 . See quantum reflection
. See quantum reflectionQuantum reflection
Quantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
for the approximation (fit) of the function
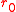 .
.Interpretation as Zeno effect
For narrow ridges with large period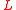 , the ridges just blocks the part of the wavefront. Then, it can be interpreted in terms of the Fresnel diffraction
, the ridges just blocks the part of the wavefront. Then, it can be interpreted in terms of the Fresnel diffractionFresnel diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction, is an approximation of Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field....
of the de Broglie wave, or the Zeno effect; such interpretation leads to the estimate the reflectivity
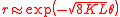 ,
,where the grazing angle
 is supposed to be small. This estimate predicts enhancement of the reflectivity at the reduction of period
is supposed to be small. This estimate predicts enhancement of the reflectivity at the reduction of period 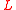 . This estimate requires that
. This estimate requires that 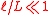 .
.Fundamental limit
For efficient ridged mirrors, both estimates above should predict high reflectivity. This implies reduction of both, width, of the ridges and the period,
of the ridges and the period, 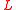 . The width of the ridges cannot be smaller than the size of atom; this sets the limit of performance of the ridged mirrors.
. The width of the ridges cannot be smaller than the size of atom; this sets the limit of performance of the ridged mirrors.Applications of ridged mirrors
Ridged mirrors are not yet commercialized, although certain achievements can be mentioned. The reflectivity of a ridged atomic mirror can be orders of magnitude better than that of a flat surface. The use of a ridged mirror as an atomic hologram has been demonstrated.In Shimizu's and Fujita's work, atom holography is achieved via electrodes implanted into SiN4 film over an atomic mirror, or maybe as the atomic mirror itself.
Ridged mirrors can also reflect visible light; however, for light waves, the performance is not better than that of a flat surface. An ellipsoidal ridged mirror is proposed as the focusing element for an atomic optical system with submicrometre resolution (atomic nanoscope
Atomic nanoscope
The atomic de Broglie microscope is an imaging system which is expected to provide resolution at the nanometer scale....
).
See also
- Atomic mirror
- Quantum reflectionQuantum reflectionQuantum reflection is a physical phenomenon involving the reflection of a matter wave from an attractive potential. In classical physics, such a phenomenon is not possible; for instance when one magnet is pulled toward another, you do not expect one of the magnets to suddenly Quantum reflection is...
- Atomic nanoscopeAtomic nanoscopeThe atomic de Broglie microscope is an imaging system which is expected to provide resolution at the nanometer scale....
- Zeno effect
- Matter wave

