
Assyrian captivity of Israel
Encyclopedia
Tiglath-Pileser III
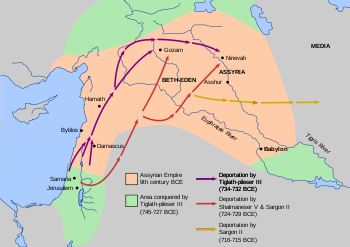
Tiglath-Pileser III was a prominent king of Assyria in the eighth century BC and is widely regarded as the founder of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Tiglath-Pileser III seized the Assyrian throne during a civil war and killed the royal family...
(Pul
Pul
Pul or PUL may refer to:* Pul, an abbreviation for the Assyrian King, Tiglath-Pileser III* Pul, one 1/100th of the Afghan afghani * PUL, an initialism for Polyurethane laminate...
) and Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V was king of Assyria from 727 to 722 BC. He first appears as governor of Zimirra in Phoenicia in the reign of his father, Tiglath-Pileser III....
. The later Assyrian rulers Sargon II
Sargon II
Sargon II was an Assyrian king. Sargon II became co-regent with Shalmaneser V in 722 BC, and became the sole ruler of the kingdom of Assyria in 722 BC after the death of Shalmaneser V. It is not clear whether he was the son of Tiglath-Pileser III or a usurper unrelated to the royal family...
and his son and successor, Sennacherib
Sennacherib
Sennacherib |Sîn]] has replaced brothers for me"; Aramaic: ) was the son of Sargon II, whom he succeeded on the throne of Assyria .-Rise to power:...
, were responsible for finishing the twenty year demise of Israel's northern ten tribe kingdom. Sennacherib also invaded some parts of the Southern Kingdom of Judah
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was a Jewish state established in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. It is often referred to as the "Southern Kingdom" to distinguish it from the northern Kingdom of Israel....
. He records forty-six fortified towns captured from Judah, and presumably carried away into Assyria. Jerusalem was besieged, but not taken. The tribes exiled by Assyria later became known as the Ten Lost Tribes
Ten Lost Tribes
The Ten Lost Tribes of Israel refers to those tribes of ancient Israel that formed the Kingdom of Israel and which disappeared from Biblical and all other historical accounts after the kingdom was destroyed in about 720 BC by ancient Assyria...
.
Biblical account
The captivities began in approximately 740 BC740s BC
-Events and trends:* 747 BC—February 26 – Nabonassar becomes king of Babylonia.* 747 BC—Meles becomes king of Lydia.* c. 747 BC—Third Intermediate Period of Egypt ends. Late Period of ancient Egypt starts. Nubian period starts in Ancient Egypt.* c...
, when the tribes of Reuben
Tribe of Reuben
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Reuben was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Reuben was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government...
, Gad
Tribe of Gad
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Gad was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Gad was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government existed,...
, and eastern half-tribe of Manasseh
Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh was one of the Tribes of Israel. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the House of Joseph....
were carried away by one of the first successful Assyrian invasions.
And the Elohim of Israel stirred up the spirit of Pul king of Assyria, and the spirit of Tilgathpilneser king of Assyria, and he carried them away, even the Reubenites, and the Gadites, and the half tribe of Manasseh, and brought them unto Halah, and Habor, and Hara, and to the river Gozan, unto this day.
In the days of Pekah king of Israel came Tiglathpileser king of Assyria, and took Ijon, and Abelbethmaachah, and Janoah, and Kedesh, and Hazor, and Gilead, and Galilee, all the land of Naphtali, and carried them captive to Assyria.
In 722 BC
720s BC
-Events and trends:*728 BC—Piye invades Egypt, conquering Memphis, and receives the submission of the rulers of the Nile Delta. He founds the Twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt.*727 BC—Babylonia makes itself independent of Assyria, upon the death of Tiglath-Pileser III....
, nearly twenty years after the initial deportations, the ruling city of the Northern Kingdom of Israel, Samaria, was finally taken by Sargon II
Sargon II
Sargon II was an Assyrian king. Sargon II became co-regent with Shalmaneser V in 722 BC, and became the sole ruler of the kingdom of Assyria in 722 BC after the death of Shalmaneser V. It is not clear whether he was the son of Tiglath-Pileser III or a usurper unrelated to the royal family...
after a three year siege started by Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V was king of Assyria from 727 to 722 BC. He first appears as governor of Zimirra in Phoenicia in the reign of his father, Tiglath-Pileser III....
.
Against him came up ShalmaneserShalmaneserShalmaneser is the name of several Assyrian kings:*Shalmaneser I *Shalmaneser II, King of Assyria from 1031 BC to 1019 BC*Shalmaneser III, king of Assyria *Shalmaneser IV, king of Assyria...
king of AssyriaAssyriaAssyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
; and Hoshea became his servant, and gave him presents.
And the king of Assyria found conspiracy in Hoshea: for he had sent messengers to So king of Egypt, and brought no present to the king of Assyria, as he had done year by year: therefore the king of Assyria shut him up, and bound him in prison.
Then the king of Assyria came up throughout all the land, and went up to Samaria, and besieged it three years.
In the ninth year of Hoshea the king of Assyria took SamariaSamariaSamaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
, and carried Israel away into Assyria, and placed them in Halah and in Habor by the river of Gozan, and in the cities of the Medes.
And the king of Assyria did carry away Israel unto Assyria and put them in Halah and in Habor by the river of Gozan, and in the cities of the Medes: because they obeyed not the voice of the their God, but transgressed his covenant, and all that Moses the servant of the commanded and would not hear them, nor do them.
The term "cities of the Medes" mentioned above may be a corruption from an original text "Mountains of Media
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
".
Assyrian Cuneiform
Assyrian cuneiform mention 27,290 captives were taken from Samaria, the capital of the Northern Kingdom of Israel, by the hand of Sargon IISargon II
Sargon II was an Assyrian king. Sargon II became co-regent with Shalmaneser V in 722 BC, and became the sole ruler of the kingdom of Assyria in 722 BC after the death of Shalmaneser V. It is not clear whether he was the son of Tiglath-Pileser III or a usurper unrelated to the royal family...
.
Sargon records his first campaign on the walls of the royal palace at Dur-Sarraku (Khorsabad):
In my first year of reign *** the people of Samaria *** to the number of 27,290 ... I carried away.
Fifty chariots for my royal equipment I selected. The city I rebuilt. I made it greater than it was before.
People of the lands I had conquered I settled therein. My official (Tartan) I placed over them as governor. (L.ii.4.)
The description of the final defeat of the Northern Kingdom of Israel above appears to be a minor event in Sargon's legacy. Some historians attribute the ease of Israel's defeat to the previous two decades of invasions, defeats, and deportations.
Some estimates assume a captivity numbering in the hundreds of thousands, minus those who died in defense of the kingdom and minus those who fled voluntarily before and during the invasions.
However, it has also been suggested that the numbers deported by the Assyrians were rather limited and the bulk of the population remained in situ. There is also evidence that significant numbers fled south to the kingdom of Judah
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was a Jewish state established in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. It is often referred to as the "Southern Kingdom" to distinguish it from the northern Kingdom of Israel....
.
No Historical Return
Unlike the Kingdom of JudahKingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was a Jewish state established in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. It is often referred to as the "Southern Kingdom" to distinguish it from the northern Kingdom of Israel....
, which was able to return from its Babylonian Captivity
Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity was the period in Jewish history during which the Jews of the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon—conventionally 587–538 BCE....
, the ten tribes of the Northern Kingdom never had a foreign edict granting permission to return and rebuild their homeland. Many centuries later, rabbis of the restored Kingdom of Judah were still debating the return of the lost ten tribes. However, Assyria had been conquered by Babylon, and Babylon had been conquered by the Medo-Persians; the same edict that freed Judah also freed representatives of the tribes of Israel. Members of various northern tribes were in the restored nation in 536 BC . Because of this, many people do not see any support for "Ten Lost Tribes," nor a future (or present-day) restoration of Israel .
Rumors of New Names
Two centuries after their exile, there have been theories that they were temporarily conquered again under different names at the hands of a different empire, Persia. This is the mid-19th century interpretation of the Behistun InscriptionBehistun Inscription
The Behistun Inscription The Behistun Inscription The Behistun Inscription (also Bistun or Bisutun, Modern Persian: بیستون The Behistun Inscription (also Bistun or Bisutun, Modern Persian: بیستون...
, King Darius's record of his conquered, by the famous transcriber and translator of the inscription George Rawlinson
George Rawlinson
Canon George Rawlinson was a 19th century English scholar, historian, and Christian theologian. He was born at Chadlington, Oxfordshire, and was the younger brother of Sir Henry Rawlinson....
:
“We have reasonable grounds for regarding the Gimirri, or CimmeriansCimmeriansThe Cimmerians or Kimmerians were ancient equestrian nomads of Indo-European origin.According to the Greek historian Herodotus, of the 5th century BC, the Cimmerians inhabited the region north of the Caucasus and the Black Sea during the 8th and 7th centuries BC, in what is now Ukraine and Russia...
, who first appeared on the confines of AssyriaAssyriaAssyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
and MediaMedesThe MedesThe Medes...
in the seventh century B.C., and the Sacae of the Behistun Rock, nearly two centuries later, as identical with the Beth-Khumree of Samaria, or the Ten Tribes of the House of IsraelHouse of IsraelThe House of Israel is a Jewish community in Ghana. This ethnic group claim to be one of the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel.-History of Jews in Ghana:...
.”
Further reading
- Keller, Werner. The Bible as History ISBN 0-281-04544-5
- Book of IsaiahBook of IsaiahThe Book of Isaiah is the first of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, preceding the books of Ezekiel, Jeremiah and the Book of the Twelve...
, , , , , , , , ,
See also
- AssyriaAssyriaAssyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
- Babylonian CaptivityBabylonian captivityThe Babylonian captivity was the period in Jewish history during which the Jews of the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon—conventionally 587–538 BCE....
- Kingdom of Israel
- History of ancient Israel and JudahHistory of ancient Israel and JudahIsrael and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of ancient Palestine. The earliest known reference to the name Israel in archaeological records is in the Merneptah stele, an Egyptian record of c. 1209 BCE. By the 9th century BCE the Kingdom of Israel had emerged as an important local power before...
- HosheaHosheaSee also Hosea, who has the same name in Biblical Hebrew.Hoshea was the last king of the Israelite Kingdom of Israel and son of Elah . William F. Albright dated reign to 732 – 721 BC, while E. R. Thiele offered the dates 732 – 723 BC.Assyrian records basically confirm the Biblical...
- Lost Tribes of Israel
- IsraeliteIsraeliteAccording to the Bible the Israelites were a Hebrew-speaking people of the Ancient Near East who inhabited the Land of Canaan during the monarchic period .The word "Israelite" derives from the Biblical Hebrew ישראל...
- Stick of Joseph

