
Associated Universities, Inc
Encyclopedia
Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI) is a research management corporation that builds and operates facilities for the research community. AUI is a not-for-profit
501(c)(3) corporation, headquartered in Washington, DC. The President and Chief Executive Officer is Ethan J. Schreier. AUI’s major current operating unit is the National Radio Astronomy Observatory
(NRAO), which it operates under a Cooperative Agreement with the National Science Foundation.
, Cornell University
, Harvard University
, Johns Hopkins University
, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
, University of Pennsylvania
, Princeton University
, University of Rochester
, and Yale University
.
AUI was granted an absolute charter by the Board of Regents of the State University of New York Education Department, which called for AUI to "acquire, plan, construct and operate laboratories and other facilities" that would unite the resources of universities, other research organizations and the Federal Government. It was envisioned that AUI would create facilities and laboratories so large, complex, and costly as to be outside the scope of a single university. These facilities were to be made available on a competitive basis to all qualified scientists without regard to affiliation, as well as to resident scientific staff.
Over the years, AUI took on a broad national character with a diversified Board of Trustees from universities and other institutions across the country. The nine founding universities are still represented, although ties to their administrations are not of a formal nature.
From 1947 until 1998, AUI was responsible for building and then managing the Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory
(BNL), a multi-disciplinary science research center located on Long Island, New York. In that period, AUI/BNL were responsible for the design, development, construction, and operation of numerous major facilities, the most recent being the National Synchrotron Light Source
and the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
. During AUI’s management at Brookhaven, six Nobel prizes were awarded for research conducted wholly or partially at BNL. Four of those prizes were awarded to scientists at the laboratory, in 1957, 1976, 1980 and 1988.
In 1955, AUI proposed the establishment of a national radio observatory and has managed the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) for NSF since its creation in 1956.
In 2002, AUI was named by NSF as the North American Executive for the international Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
In 2008, AUI, together with the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), created the Virtual Astronomical Observatory LLC, to manage the Virtual Astronomical Observatory for NSF and NASA.
. NRAO designs, builds, and operates high sensitivity radio telescope
s for use by scientists around the world.
NRAO telescopes are open to all astronomers regardless of institutional or national affiliation. Observing time on NRAO telescopes is available on a competitive basis to qualified scientists after evaluation of research proposals on the basis of scientific merit, the capability of the instruments to do the work, and the availability of the telescope during the requested time. NRAO also provides both formal and informal programs in education and public outreach for teachers, students, the general public, and the media. NRAO’s facilities are discussed below.
(ALMA), the world’s most advanced millimeter/submillimeter observatory, is under construction on the Chajnantor plateau of the Chilean Andes near San Pedro de Atacama, 5000 m above sea level. ALMA is being built by an international partnership comprising North America, Europe and East Asia, in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. AUI is the North American Executive for ALMA.
ALMA will be an international astronomy facility, a single research instrument composed of up to 80 high-precision antennas which will enable transformational research into the physics of the cold Universe, regions that are optically dark but shine brightly in the millimeter portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Providing astronomers with a new window on celestial origins, ALMA will probe the first stars and galaxies and directly image the formation of planets.
ALMA is funded in East Asia by the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan, in Europe by the European Organization for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) and in North America by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC). ALMA construction and operations are led on behalf of East Asia by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), on behalf of Europe by ESO and on behalf of North America by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), which is managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI).

is the world's largest fully steerable radio telescope. The 100-meter Green Bank Telescope (GBT) is located in a radio quiet zone in Green Bank, West Virginia.
 The Very Large Array
The Very Large Array
(VLA), an array of 27 25-meter antennas, is located on the Plains of San Agustin about 50 miles west of Socorro, New Mexico. Dedicated in 1980, it is an exceedingly powerful scientific instrument that has transformed many areas of astronomy, and has been used by more astronomers and has produced more scientific papers than any other radio telescope in the world. Even after more than a quarter of a century, the VLA exceeds all other radio astronomy facilities with its combination of sensitivity, flexibility, speed, and overall imaging quality. The VLA is currently being rebuilt as a new observatory, the Expanded Very Large Array (EVLA). The EVLA will provide a radio telescope of unprecedented sensitivity, resolution, and imaging capability, by modernizing and extending the existing Very Large Array. When completed, the EVLA will have sensitivity improvements of an order of magnitude, with frequency between 1.0 and 50 GHz, with up to 8 GHz bandwidth per polarization. The modifications are well over 50% complete, and early science with the VLA is expected in 2010.
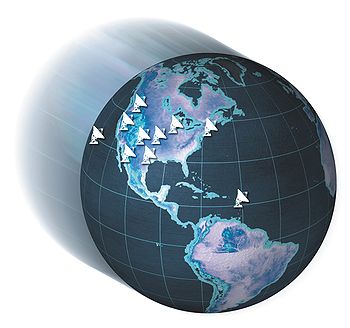
(VLBA) is a continent-wide radio telescope system offering the greatest resolving power of any astronomical instrument operational today. It is a system of ten identical 25-meter radio-telescope antennas, spread from St. Croix in the U.S. Virgin Islands, across the continental United States, to Mauna Kea, Hawaii, working together as a single instrument.
Non-profit organization
Nonprofit organization is neither a legal nor technical definition but generally refers to an organization that uses surplus revenues to achieve its goals, rather than distributing them as profit or dividends...
501(c)(3) corporation, headquartered in Washington, DC. The President and Chief Executive Officer is Ethan J. Schreier. AUI’s major current operating unit is the National Radio Astronomy Observatory
National Radio Astronomy Observatory
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a Federally Funded Research and Development Center of the United States National Science Foundation operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc for the purpose of radio astronomy...
(NRAO), which it operates under a Cooperative Agreement with the National Science Foundation.
History
AUI was established in 1946 as an educational institution dedicated to research, development, and education in the physical, biological and engineering sciences. Nine northeastern universities joined in sponsoring AUI in 1946: Columbia UniversityColumbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the...
, Cornell University
Cornell University
Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions...
, Harvard University
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
, Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University, commonly referred to as Johns Hopkins, JHU, or simply Hopkins, is a private research university based in Baltimore, Maryland, United States...
, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research.Founded in 1861 in...
, University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania is a private, Ivy League university located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Penn is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States,Penn is the fourth-oldest using the founding dates claimed by each institution...
, Princeton University
Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university located in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. The school is one of the eight universities of the Ivy League, and is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution....
, University of Rochester
University of Rochester
The University of Rochester is a private, nonsectarian, research university in Rochester, New York, United States. The university grants undergraduate and graduate degrees, including doctoral and professional degrees. The university has six schools and various interdisciplinary programs.The...
, and Yale University
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
.
AUI was granted an absolute charter by the Board of Regents of the State University of New York Education Department, which called for AUI to "acquire, plan, construct and operate laboratories and other facilities" that would unite the resources of universities, other research organizations and the Federal Government. It was envisioned that AUI would create facilities and laboratories so large, complex, and costly as to be outside the scope of a single university. These facilities were to be made available on a competitive basis to all qualified scientists without regard to affiliation, as well as to resident scientific staff.
Over the years, AUI took on a broad national character with a diversified Board of Trustees from universities and other institutions across the country. The nine founding universities are still represented, although ties to their administrations are not of a formal nature.
From 1947 until 1998, AUI was responsible for building and then managing the Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory , is a United States national laboratory located in Upton, New York on Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base...
(BNL), a multi-disciplinary science research center located on Long Island, New York. In that period, AUI/BNL were responsible for the design, development, construction, and operation of numerous major facilities, the most recent being the National Synchrotron Light Source
National Synchrotron Light Source
The National Synchrotron Light Source at Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton, New York is a national user research facility funded by the U.S. Department of Energy...
and the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider is one of two existing heavy-ion colliders, and the only spin-polarized proton collider in the world. It is located at Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton, New York and operated by an international team of researchers...
. During AUI’s management at Brookhaven, six Nobel prizes were awarded for research conducted wholly or partially at BNL. Four of those prizes were awarded to scientists at the laboratory, in 1957, 1976, 1980 and 1988.
In 1955, AUI proposed the establishment of a national radio observatory and has managed the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) for NSF since its creation in 1956.
In 2002, AUI was named by NSF as the North American Executive for the international Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
In 2008, AUI, together with the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), created the Virtual Astronomical Observatory LLC, to manage the Virtual Astronomical Observatory for NSF and NASA.
National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO)
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), headquartered in Charlottesville, VA, is a Federally Funded Research and Development Center(FFRDC) operated by Associated Universities, Inc. under cooperative agreement with the United States National Science FoundationNational Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
. NRAO designs, builds, and operates high sensitivity radio telescope
Radio telescope
A radio telescope is a form of directional radio antenna used in radio astronomy. The same types of antennas are also used in tracking and collecting data from satellites and space probes...
s for use by scientists around the world.
NRAO telescopes are open to all astronomers regardless of institutional or national affiliation. Observing time on NRAO telescopes is available on a competitive basis to qualified scientists after evaluation of research proposals on the basis of scientific merit, the capability of the instruments to do the work, and the availability of the telescope during the requested time. NRAO also provides both formal and informal programs in education and public outreach for teachers, students, the general public, and the media. NRAO’s facilities are discussed below.
Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA)
The Atacama Large Millimeter ArrayAtacama Large Millimeter Array
The Atacama Large Millimeter/sub-millimeter Array is an array of radio telescopes in the Atacama desert of northern Chile. Since a high and dry site is crucial to millimeter wavelength operations, the array is being constructed on the Chajnantor plateau at 5000 metres altitude...
(ALMA), the world’s most advanced millimeter/submillimeter observatory, is under construction on the Chajnantor plateau of the Chilean Andes near San Pedro de Atacama, 5000 m above sea level. ALMA is being built by an international partnership comprising North America, Europe and East Asia, in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. AUI is the North American Executive for ALMA.
ALMA will be an international astronomy facility, a single research instrument composed of up to 80 high-precision antennas which will enable transformational research into the physics of the cold Universe, regions that are optically dark but shine brightly in the millimeter portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Providing astronomers with a new window on celestial origins, ALMA will probe the first stars and galaxies and directly image the formation of planets.
ALMA is funded in East Asia by the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan, in Europe by the European Organization for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) and in North America by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC). ALMA construction and operations are led on behalf of East Asia by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), on behalf of Europe by ESO and on behalf of North America by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), which is managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI).

Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope (GBT)
The Robert C. Byrd Green Bank TelescopeGreen Bank Telescope
The Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope is the world's largest fully steerable radio telescope and the world's largest land-based movable structure. It is part of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory site at Green Bank, West Virginia, USA. The telescope honors the name of the late Senator...
is the world's largest fully steerable radio telescope. The 100-meter Green Bank Telescope (GBT) is located in a radio quiet zone in Green Bank, West Virginia.
Very Large Array (VLA)/ Expanded Very Large Array

Very Large Array
The Very Large Array is a radio astronomy observatory located on the Plains of San Agustin, between the towns of Magdalena and Datil, some fifty miles west of Socorro, New Mexico, USA...
(VLA), an array of 27 25-meter antennas, is located on the Plains of San Agustin about 50 miles west of Socorro, New Mexico. Dedicated in 1980, it is an exceedingly powerful scientific instrument that has transformed many areas of astronomy, and has been used by more astronomers and has produced more scientific papers than any other radio telescope in the world. Even after more than a quarter of a century, the VLA exceeds all other radio astronomy facilities with its combination of sensitivity, flexibility, speed, and overall imaging quality. The VLA is currently being rebuilt as a new observatory, the Expanded Very Large Array (EVLA). The EVLA will provide a radio telescope of unprecedented sensitivity, resolution, and imaging capability, by modernizing and extending the existing Very Large Array. When completed, the EVLA will have sensitivity improvements of an order of magnitude, with frequency between 1.0 and 50 GHz, with up to 8 GHz bandwidth per polarization. The modifications are well over 50% complete, and early science with the VLA is expected in 2010.

Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA)
The Very Long Baseline ArrayVery Long Baseline Array
The Very Long Baseline Array is a system of ten radio telescopes controlled remotely from the Array Operations Center in Socorro, New Mexico by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory. The array works together as the world's largest dedicated, full-time astronomical instrument using the...
(VLBA) is a continent-wide radio telescope system offering the greatest resolving power of any astronomical instrument operational today. It is a system of ten identical 25-meter radio-telescope antennas, spread from St. Croix in the U.S. Virgin Islands, across the continental United States, to Mauna Kea, Hawaii, working together as a single instrument.

