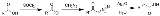
Arndt-Eistert synthesis
Overview
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s designed to convert a carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
to a higher carboxylic acid homologue (i.e. contains one additional carbon atom) and is considered a homologation
Homologation reaction
A homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A Homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the...
process. Named for the German chemists Fritz Arndt
Fritz Arndt
Fritz Arndt was a German chemist and together with Bernd Eistert he disoverered the Arndt-Eistert synthesis.- Life :Fritz Arndt was born on 6 July 1885, in Hamburg but started his chemistry studies at the University of Geneva followed by a the University of Bern and receiving his PhD from the...
(1885–1969) and Bernd Eistert
Bernd Eistert
Bernd Eistert was a German chemist. Together with Fritz Arndt he discovered the Arndt-Eistert synthesis.-Life:...
(1902–1978), Arndt-Eistert synthesis is a popular method of producing β-amino acids from α-amino acids. Acid chlorides react with diazomethane
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2. It is the simplest of diazo compounds. In the pure form at room temperature, it is a extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas, thus it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether...
to give diazoketones.

