
Application Services Library
Encyclopedia
ASL is a methodology used in the IT industry.
The Application Services Library (ASL) is a public domain
standard
, which describes a standard for processes within Application Management (the discipline of producing and maintaining information systems and applications). The term "library" is used because the ASL standard is based on the descriptions of best practices from the industry.
This standard was developed in the late nineties in the Netherlands
, originally as the proprietary R2C model, which evolved into ASL in 2000. In 2001 it was donated by the IT Service Provider PinkRoccade to the ASL Foundation, now the ASL BiSL Foundation.
ASL is closely related to ITIL
, BiSL
and CMM
. It is described in several books and articles (most of them only available in Dutch
), as well as on the official website of the ASL BiSL Foundation.
The standard was developed because of the inability to structure the way of working within the Application Management departments by only using the ITIL framework, an older library embraced by the IT infrastructure departments for structuring their way of working. At the time of development, ITIL was very useful for infrastructure management but lacked specific guidance for application design, development, maintenance and support. Newer ITIL versions, particularly V3, have increasingly addressed the Application Development and Application Management domains. A reference to a white paper comparing ITIL V3 and ASL is included.
ASL was defined in order to fill this gap for Application Management. A similar development has led to the definition of the BiSL-standard for Information Management / Functional Management.
The goal of ASL is to assist in the professionalisation of Application Management.
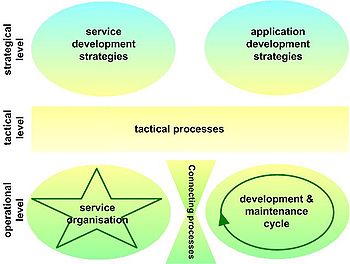 ASL contains six clusters of processes, three on the operational level, one on the tactical level and two on the strategic level.
ASL contains six clusters of processes, three on the operational level, one on the tactical level and two on the strategic level.
There are five processes within the cluster Service Organisation. The processes in the Service Organisation cluster support the daily use of the information systems. The processes in this cluster are:
These processes have as well been defined in the ITIL framework. The processes are similar, but are viewed from another point of view, therefore the activities in each of these processes may differ from the activities in an ITIL-environment.
Development and Maintenance
Within this cluster the majority of the work of Application Development is done. A major part of the work of Application Management deals with designing, programming and testing applications and information systems. Processes are
These processes are not described at all in the ITIL V1 framework, but do have their counterparts in BiSL, the model for Information management / Functional Management.
Connecting processes
The connecting processes aim at the synchronisation of the activities between Service Organisation/operations (using the applications) and development and maintenance (changing the applications). The two processes included are:
es
The processes in this cluster are used in the management of the activities within the clusters on the operational level. The processes are located on the tactical level, are used for steering the operational processes. The processes included are:
Applications live for longer than expected. Systems, functionality, concepts and structure of information systems remain stable over many years. This knowledge is rarely used. It is important that, while maintaining and enhancing systems, there is a clear view needed what the demands are in the future, and based on that, what and how the future of these applications should look like.
This view, the application management strategies, is created within the cluster application cycle management. The processes in this cluster are:
Organisation Cycle Management
Also the future of the Application Management organisation, with aspects as skills and capabilities, markets and customers, is very important. Creating the organisation management strategies for this is the aim of Organization Cycle Management. Processes in this cluster include:
The Application Services Library (ASL) is a public domain
Public domain
Works are in the public domain if the intellectual property rights have expired, if the intellectual property rights are forfeited, or if they are not covered by intellectual property rights at all...
standard
Standardization
Standardization is the process of developing and implementing technical standards.The goals of standardization can be to help with independence of single suppliers , compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality....
, which describes a standard for processes within Application Management (the discipline of producing and maintaining information systems and applications). The term "library" is used because the ASL standard is based on the descriptions of best practices from the industry.
This standard was developed in the late nineties in the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, originally as the proprietary R2C model, which evolved into ASL in 2000. In 2001 it was donated by the IT Service Provider PinkRoccade to the ASL Foundation, now the ASL BiSL Foundation.
ASL is closely related to ITIL
Information Technology Infrastructure Library
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library , is a set of good practices for IT service management that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. In its current form , ITIL is published in a series of five core publications, each of which covers an ITSM lifecycle stage...
, BiSL
Business Information Services Library
Business Information Services Library , previously known as Business Information Service Management Library, is a framework used for functional management and information management....
and CMM
Capability Maturity Model
The Capability Maturity Model is a development model that was created after study of data collected from organizations that contracted with the U.S. Department of Defense, who funded the research. This model became the foundation from which CMU created the Software Engineering Institute...
. It is described in several books and articles (most of them only available in Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
), as well as on the official website of the ASL BiSL Foundation.
The standard was developed because of the inability to structure the way of working within the Application Management departments by only using the ITIL framework, an older library embraced by the IT infrastructure departments for structuring their way of working. At the time of development, ITIL was very useful for infrastructure management but lacked specific guidance for application design, development, maintenance and support. Newer ITIL versions, particularly V3, have increasingly addressed the Application Development and Application Management domains. A reference to a white paper comparing ITIL V3 and ASL is included.
ASL was defined in order to fill this gap for Application Management. A similar development has led to the definition of the BiSL-standard for Information Management / Functional Management.
Purpose
The ASL is intended to support Application Management by providing tools. Two main categories of aids are defined:- Descriptions of the processes for Application Management. Plus the use of best-practises
- Standard terminology, avoiding the pitfall of talking about different topics while using the same words.
The goal of ASL is to assist in the professionalisation of Application Management.
Structure of ASL

Operational level
Service organisationThere are five processes within the cluster Service Organisation. The processes in the Service Organisation cluster support the daily use of the information systems. The processes in this cluster are:
- incident managementIncident managementIncident Management refers to the activities of an organization to identify, analyze and correct hazards. For instance, a fire in a factory would be a risk that realized, or an incident that happened...
- continuity management
- capacity managementCapacity managementCapacity Management is a process used to manage information technology . Its primary goal is to ensure that IT capacity meets current and future business requirements in a cost-effective manner. One common interpretation of Capacity Management is described in the ITIL framework...
- availability management
- configuration managementConfiguration managementConfiguration management is a field of management that focuses on establishing and maintaining consistency of a system or product's performance and its functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life.For information assurance, CM...
These processes have as well been defined in the ITIL framework. The processes are similar, but are viewed from another point of view, therefore the activities in each of these processes may differ from the activities in an ITIL-environment.
Development and Maintenance
Within this cluster the majority of the work of Application Development is done. A major part of the work of Application Management deals with designing, programming and testing applications and information systems. Processes are
- impact analysis
- designDesignDesign as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
- realization
- testingSoftware testingSoftware testing is an investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about the quality of the product or service under test. Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to appreciate and understand the risks of software...
- implementationImplementationImplementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy.-Computer Science:...
These processes are not described at all in the ITIL V1 framework, but do have their counterparts in BiSL, the model for Information management / Functional Management.
Connecting processes
The connecting processes aim at the synchronisation of the activities between Service Organisation/operations (using the applications) and development and maintenance (changing the applications). The two processes included are:
- change managementChange managementChange management is a structured approach to shifting/transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state. It is an organizational process aimed at helping employees to accept and embrace changes in their current business environment....
- release managementRelease managementThe release management process is a relatively new but rapidly growing discipline within software engineering of managing software releases....
.
Tactical level
Management processManagement process
Management process is a process of planning and controlling the performance or execution of any type of activity, such as:* a project or...
es
The processes in this cluster are used in the management of the activities within the clusters on the operational level. The processes are located on the tactical level, are used for steering the operational processes. The processes included are:
- quality managementQuality managementThe term Quality management has a specific meaning within many business sectors. This specific definition, which does not aim to assure 'good quality' by the more general definition , can be considered to have four main components: quality planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality...
- service level management
- cost management
- planningPlanningPlanning in organizations and public policy is both the organizational process of creating and maintaining a plan; and the psychological process of thinking about the activities required to create a desired goal on some scale. As such, it is a fundamental property of intelligent behavior...
& control.
Strategic level
Application Cycle ManagementApplications live for longer than expected. Systems, functionality, concepts and structure of information systems remain stable over many years. This knowledge is rarely used. It is important that, while maintaining and enhancing systems, there is a clear view needed what the demands are in the future, and based on that, what and how the future of these applications should look like.
This view, the application management strategies, is created within the cluster application cycle management. The processes in this cluster are:
- life cycle management
- information portfolio managementIT portfolio managementIT portfolio management is the application of systematic management to large classes of items managed by enterprise Information Technology capabilities. Examples of IT portfolios would be planned initiatives, projects, and ongoing IT services...
- customer organisation strategy
- customer environment strategy
- ICT development strategy.
Organisation Cycle Management
Also the future of the Application Management organisation, with aspects as skills and capabilities, markets and customers, is very important. Creating the organisation management strategies for this is the aim of Organization Cycle Management. Processes in this cluster include:
- account definition
- market definition
- skills definition
- technology definition
- service delivery definition

