Apert syndrome
Encyclopedia
Apert syndrome is a form of acrocephalosyndactyly, a congenital disorder
characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch
, the precursor of the maxilla
and mandible. Disturbances in the development of the branchial arches in fetal development create lasting and widespread effects.
In 1906, Eugène Apert
, a French physician, described nine people sharing similar attributes and characteristics. Linguistically, "acro" is Greek for "peak", referring to the "peaked" head that is common in the syndrome. "Cephalo", also from Greek, is a combining form meaning "head". "Syndactyly
" refers to webbing of fingers and toes.
In embryology
, the hands and feet have selective cells that die, called selective cell death or apoptosis
, causing separation of the digits. In the case of acrocephalosyndactyly, selective cell death does not occur and skin, and rarely bone, between the fingers and toes fuses.
The cranial bones are affected as well, similar to Crouzon syndrome
and Pfeiffer syndrome
. Craniosynostosis
occurs when the fetal skull and facial bones fuse too soon in utero
, disrupting normal bone growth. Fusion of different sutures
leads to different patterns of growth on the skull. Examples include: trigonocephaly
(fusion of the metopic suture), brachycephaly
(fusion of the coronal suture
), dolichocephaly
(fusion of the sagittal suture
), plagiocephaly
(fusion of coronal and lambdoidal sutures unilaterally), and oxycephaly or turricephaly (fusion of coronal and lambdoid sutures).
The largest study shows an incidence of 1 per 65000 live births, with no preference for either sex.
or concave face may develop as a result of deficient growth in the mid-facial bones, leading to a conditir prognathism. Other features of acrocephalosyndactyly may include shallow bony orbits and broadly spaced eyes. Low-set ears are also a typical characteristic of branchial arch syndromes.
The hands in patients with Apert syndrome always show four common features :
The deformity of the space between the index finger and the thumb may be variable. Based on this first webspace, we can differentiate three different types of handdeformation:
. The offspring of a parent with Apert syndrome has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition. In 1995, A.O.M. Wilkie published a paper showing evidence that acrocephalosyndactyly is caused by a defect on the fibroblast growth factor receptor
2 gene
, on chromosome 10.
Apert syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder; approximately two-thirds of the cases are due to a C to G mutation at the position 755 in the FGFR2 gene, which causes a Ser to Trp change in the protein. This is a male-specific mutation hotspot: in a study of 57 cases, the mutation always occurred on the paternally derived allele. On the basis of the observed birth prevalence of the disease (1 in 70,000), the apparent rate of C to G mutations at this site is about .00005, which is 200 to 800 fold higher than the usual rate for mutations at CG dinucleotides. Moreover, the incidence rises sharply with the age of the father. Goriely et al. (2003) analyzed the allelic distribution of mutations in sperm samples from men of different ages and concluded that the simplest explanation for the data is that the C to G mutation gives the cell an advantage in the male germline.
It still isn’t very clear why people with Apert Syndrome both have craniosynostosis and syndactyly. There has been one study that suggests it has something to do with the expression of three isoforms of FGFR2, the gene with the point mutations that causes the syndrome in 98% of the patients.
KFGR, keratinocyte growth factor receptor, is an isoform active in the metaphysis
and interphalangeal joints. FGFR1 is an isoform active in the diaphysis
. FGFR2-Bek is active in the metaphysis, as well as the diaphysis but also in the interdigital mesenchyme
. The point mutation increases the ligand-dependent activation of FGFR2, and thus of its isoforms. This means that FGFR2 loses its specificity, causing binding of FGF’s that normally don’t bind to the receptor. Since FGF suppresses apoptosis
, the interdigital mesenchyme is maintained. FGF also increases replication and differentiation of osteoblasts, thus early fusion of several sutures of the skull. This may explain why both symptoms are always found in Apert Syndrome.
or monobloc midface distraction osteogenesis
which detaches the midface or the entire upper face, respectively, from the rest of the skull are performed in order to reposition it in the correct plane. These surgeries are performed by both plastic and oral and maxillofacial (OMS) surgeons, often in collaboration.
However, some guidelines can be given depending on the severity of the deformities.
In general it is initially recommended to release the first and fourth interdigital spaces thus releasing the border rays.
This makes it possible for the child to grasp things with its hand, a very important function for the child's development. Later the second and third interdigital spaces have to be released.
Because there are three handtypes in Apert, all with their own deformities, they all need a different approach regarding their treatment:
With growing of a child and respectively the hands, secondary revisions are needed to treat the contractures and to improve the aesthetics.
), a narrow palate, and crowding of the teeth.
Congenital disorder
A congenital disorder, or congenital disease, is a condition existing at birth and often before birth, or that develops during the first month of life , regardless of causation...
characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch
Branchial arch
In the development of vertebrate animals, the pharyngeal arches are anlage for a multitude of structures. In humans, they develop during the fourth week in utero as a series of mesodermal outpouchings on the left and right sides of the developing pharynx...
, the precursor of the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
and mandible. Disturbances in the development of the branchial arches in fetal development create lasting and widespread effects.
In 1906, Eugène Apert
Eugène Apert
Eugène Charles Apert was a French pediatrician who was born in Paris.He received his doctorate in 1897 and afterwards was associated with the Hôtel-Dieu and Hôpital Saint-Louis. From 1919 until 1934, he worked at the Hôpital des Enfants-Malades in Paris...
, a French physician, described nine people sharing similar attributes and characteristics. Linguistically, "acro" is Greek for "peak", referring to the "peaked" head that is common in the syndrome. "Cephalo", also from Greek, is a combining form meaning "head". "Syndactyly
Syndactyly
Syndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and kangaroo, but is an unusual condition in humans.-Classification:...
" refers to webbing of fingers and toes.
In embryology
Embryology
Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage...
, the hands and feet have selective cells that die, called selective cell death or apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
, causing separation of the digits. In the case of acrocephalosyndactyly, selective cell death does not occur and skin, and rarely bone, between the fingers and toes fuses.
The cranial bones are affected as well, similar to Crouzon syndrome
Crouzon syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is a genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible...
and Pfeiffer syndrome
Pfeiffer syndrome
Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull , which prevents further growth of the skull and affects the shape of the head and face...
. Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in an infant skull prematurely fuses by ossification, thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull...
occurs when the fetal skull and facial bones fuse too soon in utero
In utero
In utero is a Latin term literally meaning "in the womb". In biology, the phrase describes the state of an embryo or fetus. In legal contexts, the phrase is used to refer to unborn children. Under common law, unborn children are still considered to exist for property transfer purposes.-See also:*...
, disrupting normal bone growth. Fusion of different sutures
Suture (anatomical)
In anatomy, a suture is a fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements of an animal, with or without significant overlap of the elements....
leads to different patterns of growth on the skull. Examples include: trigonocephaly
Trigonocephaly
Trigonocephaly is a congenital condition of premature fusion of the metopic suture leading to a triangular shaped forehead. The merging of the two frontal bones leads to transverse growth restriction and parallel growth expansion...
(fusion of the metopic suture), brachycephaly
Brachycephaly
Brachycephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a type of cephalic disorder. This can result from premature fusion of the coronal sutures or from external deformation . The coronal suture is the fibrous joint that unites the frontal bone with the two parietal bones of the skull. The parietal...
(fusion of the coronal suture
Coronal suture
The coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the frontal and parietal bones of the skull. At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet.-Pathology:...
), dolichocephaly
Dolichocephaly
Dolichocephaly is another word for scaphocephaly, a condition where the head is longer than would be expected, relative to the width of the head.It can present in cases of Sensenbrenner syndrome, Sotos syndrome, as well as Marfan syndrome.-External links:...
(fusion of the sagittal suture
Sagittal suture
The sagittal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word Sagitta, meaning "arrow". The derivation of this term may be demonstrated by observing how the sagittal suture is notched posteriorly, like an arrow,...
), plagiocephaly
Plagiocephaly
Plagiocephaly is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion of the skull.-Causes:It is a common finding at birth and may be the result of a restrictive intrauterine environment. If there is premature union of skull bones, this is more properly called craniosynostosis...
(fusion of coronal and lambdoidal sutures unilaterally), and oxycephaly or turricephaly (fusion of coronal and lambdoid sutures).
The largest study shows an incidence of 1 per 65000 live births, with no preference for either sex.
Craniosynostosis
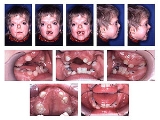
The cranial malformations are the most apparent effects of acrocephalosyndactyly. Craniosynostosis occurs, with brachiocephaly being the common pattern of growth. Another common characteristic is a high, prominent forehead with a flat posterior skull. Due to the premature closing of the coronal sutures, increased cranial pressure can develop, leading to mental deficiency. A flator concave face may develop as a result of deficient growth in the mid-facial bones, leading to a conditir prognathism. Other features of acrocephalosyndactyly may include shallow bony orbits and broadly spaced eyes. Low-set ears are also a typical characteristic of branchial arch syndromes.
Syndactyly
All acrocephalosyndactyly syndromes show some level of limb anomalies so it can be hard to tell them apart. However, the typical hand deformities in patients with Apert Syndrome distinguish it from the other syndromes.The hands in patients with Apert syndrome always show four common features :
- a short thumb with radial deviation
- complex syndactylySyndactylySyndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and kangaroo, but is an unusual condition in humans.-Classification:...
of the index, long and ring finger - symbrachyphalangism
- simple syndactyly of the fourth webspace
The deformity of the space between the index finger and the thumb may be variable. Based on this first webspace, we can differentiate three different types of handdeformation:
- Type I: Also called a "spade hand". The most common and least severe type of deformation. The thumb shows radial deviation and clinodactylyClinodactyly-References:...
but is separated from the index finger. The index, long and ring finger are fused together in the distal interphalangeal joints and form a flat palm. During the embryonic stage the fusion has no effect on the longitudinal growth of these fingers so they have a normal length. In the fourth webspace we always see a simple syndactyly, either complete or incomplete. - Type II: Also called a "spoon" or "mitten" hand. This is a more serious anomaly since the thumb is fused to the index finger by simple complete or incomplete syndactyly. Only the distal phalanx of the thumb is not joined in the osseous union with the index finger and has a separate nail. Because the fusion of the digits is at the level of the distal interphalangeal joints, a concave palm is formed. Most of the time complete syndactyly of the fourth webspace.
- Type III: Also called the "hoof" or "rosebud" hand. This is the most uncommon but also most severe form of hand deformity in Apert syndrome. There is a solid osseous or cartilaginous fusion of all digits with one long, conjoined nail. The thumb is turned inwards and often it is impossible to tell the fingers apart. Usually proper imaging of the hand is very difficult, due to overlap of bones, but physical examination alone is not enough to measure the severity of deformation
Type I ("spade") Type II ("mitten") Type III ("rosebud") First webspace Simple Syndactyly Simple Syndactyly Complex Syndactyly Middle three fingers Side-to-side fusion with flat palm Fusion of fingertops forming a concave palm Tight fusion of all digits with one conjoined nail Fourth webspace Simple and incomplete syndactyly Simple and complete syndactyly Simple and complete syndactyly
Causes
Acrocephalosyndactyly may be an autosomal dominant disorder. Males and females are affected equally; however research is yet to determine an exact cause. Nonetheless, almost all cases are sporadic, signifying fresh mutations or environmental insult to the genomeGenome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
. The offspring of a parent with Apert syndrome has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition. In 1995, A.O.M. Wilkie published a paper showing evidence that acrocephalosyndactyly is caused by a defect on the fibroblast growth factor receptor
Fibroblast growth factor receptor
The fibroblast growth factor receptors are, as their name implies, receptors that bind to members of the fibroblast growth factor family of proteins. Some of these receptors are involved in pathological conditions...
2 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
, on chromosome 10.
Apert syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder; approximately two-thirds of the cases are due to a C to G mutation at the position 755 in the FGFR2 gene, which causes a Ser to Trp change in the protein. This is a male-specific mutation hotspot: in a study of 57 cases, the mutation always occurred on the paternally derived allele. On the basis of the observed birth prevalence of the disease (1 in 70,000), the apparent rate of C to G mutations at this site is about .00005, which is 200 to 800 fold higher than the usual rate for mutations at CG dinucleotides. Moreover, the incidence rises sharply with the age of the father. Goriely et al. (2003) analyzed the allelic distribution of mutations in sperm samples from men of different ages and concluded that the simplest explanation for the data is that the C to G mutation gives the cell an advantage in the male germline.
It still isn’t very clear why people with Apert Syndrome both have craniosynostosis and syndactyly. There has been one study that suggests it has something to do with the expression of three isoforms of FGFR2, the gene with the point mutations that causes the syndrome in 98% of the patients.
KFGR, keratinocyte growth factor receptor, is an isoform active in the metaphysis
Metaphysis
The metaphysis is the wider portion of a long bone adjacent to the epiphyseal plate. It is this part of the bone that grows during childhood; as it grows, it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses...
and interphalangeal joints. FGFR1 is an isoform active in the diaphysis
Diaphysis
The diaphysis is the main or mid section of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue ....
. FGFR2-Bek is active in the metaphysis, as well as the diaphysis but also in the interdigital mesenchyme
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme, or mesenchymal connective tissue, is a type of undifferentiated loose connective tissue that is derived mostly from mesoderm, although some are derived from other germ layers; e.g. some mesenchyme is derived from neural crest cells and thus originates from the ectoderm...
. The point mutation increases the ligand-dependent activation of FGFR2, and thus of its isoforms. This means that FGFR2 loses its specificity, causing binding of FGF’s that normally don’t bind to the receptor. Since FGF suppresses apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
, the interdigital mesenchyme is maintained. FGF also increases replication and differentiation of osteoblasts, thus early fusion of several sutures of the skull. This may explain why both symptoms are always found in Apert Syndrome.
Craniosynostosis
Surgery is needed to prevent the closing of the coronal sutures from damaging brain development. In particular, the LeFort IIILefort III
The Le Fort III Osteotomy is used to correct generalised growth failure of the midface involving the upper jaw nose and cheek bones . The surgical approach and post operative management is similar as for the Le Fort II procedure....
or monobloc midface distraction osteogenesis
Distraction osteogenesis
Distraction osteogenesis, also called callus distraction, callotasis and osteodistraction is a surgical process used to reconstruct skeletal deformities and lengthen the long bones of the body...
which detaches the midface or the entire upper face, respectively, from the rest of the skull are performed in order to reposition it in the correct plane. These surgeries are performed by both plastic and oral and maxillofacial (OMS) surgeons, often in collaboration.
Syndactyly
There is no standard treatment for the hand malformations in Apert due to the differences and severity in clinical manifestations in different patients. Every patient should therefore be individually approached and treated, aiming at an adequate balance between hand functionality and aesthetics.However, some guidelines can be given depending on the severity of the deformities.
In general it is initially recommended to release the first and fourth interdigital spaces thus releasing the border rays.
This makes it possible for the child to grasp things with its hand, a very important function for the child's development. Later the second and third interdigital spaces have to be released.
Because there are three handtypes in Apert, all with their own deformities, they all need a different approach regarding their treatment:
- Type I hand usually only needs the interdigital web space release. First web release is rarely needed but often its deepening is necessary. Thumb clynodactyly correction will be needed.
- In type II hands it is recommended to release the first and fifth rays in the beginning, then the second and the third interdigital web spaces have to be freed. The clynodactyly of the thumb has to be corrected as well. The lengthening of the thumb phalanx may be needed thus increasing the first web space. In both type I and type II, the recurrent syndactyly of the second web space will occur because of a pseudoepiphysis at the base of the index metacarpal. This should be corrected by later revisions.
- Type III hands are the most challenging to treat because of their complexity. First of all, it is advised to release the first and fourth webspace thus converting it to type I hand. The treatment of macerations and nail bed infections should also be done in the beginning. For increasing of the first web space, lengthening of the thumb can be done. It is suggested that in severe cases an amputation of the index finger should be considered. However, before making this decision it is important to weigh the potential improvement to be achieved against the possible psychological problems of the child later due to the aesthetics of the hand. Later the second and/or third interdigital web space should be released.
With growing of a child and respectively the hands, secondary revisions are needed to treat the contractures and to improve the aesthetics.
Dental significance
Common relevant features of acrocephalosyndactyly are a high-arched palate, pseudomandibular prognathism (appearing as mandibular prognathismPrognathism
Prognathism is a term used to describe the positional relationship of the mandible and/or maxilla to the skeletal base where either of the jaws protrudes beyond a predetermined imaginary line in the coronal plane of the skull. In general dentistry, oral and maxillofacial surgery and orthodontics...
), a narrow palate, and crowding of the teeth.
See also
- Crouzon syndromeCrouzon syndromeCrouzon syndrome is a genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible...
- Pfeiffer syndromePfeiffer syndromePfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull , which prevents further growth of the skull and affects the shape of the head and face...
- Hearing loss with craniofacial syndromesHearing loss with craniofacial syndromesHearing loss with craniofacial syndromes is a common occurrence. Many of these multianomaly disorders involve structural malformations of the outer or middle ear, making a significant hearing loss highly likely.- Treacher Collins syndrome :...
- Saethre-Chotzen syndromeSaethre-Chotzen syndromeSaethre-Chotzen syndrome , also known as acrocephalosyndactyly type 3 and Chotzen syndrome, is a very rare autosomal dominant congenital disorder characterized by acrocephalosyndactyly, craniosynostosis...
External links
- Information from Teeter's Page at www.apert.org
- Apert Syndrome information from Seattle Children's Hospital Craniofacial Center
- cleftAdvocate – Non-profit support organization for all craniofacial conditions; on-line and in-person family support, insurance and advocacy assistance, and more.
- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on FGFR-Related Craniosynostosis Syndromes
- The National Craniofacial Association
- A resource for information and support
- Short explanation

