
Annular velocity
Encyclopedia
Annular Velocityhttp://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Display.cfm?Term=annular%20velocity is the speed of a fluid's movement in a column called an annulus
in wells being drilled with circulating drilling fluid. It is commonly measured in feet per minute (ft/min) or meters per minute (m/min). Annular velocity is often abbreviated as AV, though this is not exclusively so, as AV also refers to apparent viscosity
which is calculated from rheometer
readings from tests that the mud engineer
performs.
applications in the oil exploration industry. There may be other applications in other fields of study such as fluid mechanics
(the study of the movement of fluid) or fluid dynamics
(the study of the flow of fluid).
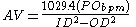
Or
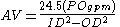
Where:
solids (drill cuttings
) from the wellbore. By maintaining the annular velocity at certain rates (speeds) in conjunction with the rheological properties of the drilling fluid
, the wellbore is kept clean of the drill cuttings
to prevent them from settling back down to the bottom and causing drilling problems.
Annular drilling is an efficient process that can cut in metals like steel and stainless steel holes with diameters ranging from 7/16" to 5".
The other major variable is the rheology
of the drilling fluid. Rheology
is sometimes thought of as viscosity
to the uninitiated, though improperly. Viscosity
(sometimes thought of as its thickness) is a very basic measurement of the fluids resistance to change in movement or flow. The viscosity
of a fluid can be measured with a Marsh Funnel
. Rheology
is the study of viscosity
and requires more precise and complicated procedures and equipment
for its determination. For drilling fluid applications a rheometer
is used.
Annulus (oil well)
The annulus of an oil well refers to any void between any piping, tubing or casing and the piping, tubing, or casing immediately surrounding it. It is named after the corresponding geometric concept...
in wells being drilled with circulating drilling fluid. It is commonly measured in feet per minute (ft/min) or meters per minute (m/min). Annular velocity is often abbreviated as AV, though this is not exclusively so, as AV also refers to apparent viscosity
Apparent viscosity
Apparent viscosity is a rheological property calculated from rheometer readings performed by a Mud engineer on drilling fluid. It is normally abbreviated as AV. It is expressed in cP . Centipoise is the amount of force required to move one layer of fluid in relation to another...
which is calculated from rheometer
Rheometer
A rheometer is a laboratory device used to measure the way in which a liquid, suspension or slurry flows in response to applied forces. It is used for those fluids which cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case...
readings from tests that the mud engineer
Mud engineer
A mud engineer works on an oil well or gas well drilling rig, and is responsible ensuring the properties of the drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, are within designed specifications.-Use of mud:Mud is a vital part of drilling operations...
performs.
Scope
For this article, annular velocity is described, as used in drilling fluidDrilling fluid
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid is a fluid used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Often used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. Liquid drilling fluid...
applications in the oil exploration industry. There may be other applications in other fields of study such as fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the study of fluids and the forces on them. Fluid mechanics can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; fluid kinematics, the study of fluids in motion; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion...
(the study of the movement of fluid) or fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
(the study of the flow of fluid).
Determination
The annular velocity can be calculated using one of the following formulæ.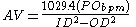
Or
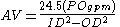
Where:
- AV = annular velocity
- PObpm = pump output in bpm (barrels per minute) 1 barrel = 42 gallons
- POgpm = pump output in gpm (gallons per minute) 1 gallon = 0.0238095238 barrels
- ID2 = inside diameter of the wellbore or casing, squared
- OD2 = outside diameter of the drill pipe or tubing, squared
- 1029.4 = A conversion factor constant used to calculate the volume between the outside of a tube within the inside of another tube, using barrels.
- 24.5 = A conversion factor constant used to calculate the volume between the outside of a tube within the inside of another tube, using gallons.
- Pump Output = Refers to the measurement of the quantity of a fluid (to put that fluid in motion).
Application
The annular velocity is one of two major variables in the process of cleaningsolids (drill cuttings
Drill cuttings
Drill cuttings are the broken bits of solid material removed from a borehole drilled by rotary, percussion, or auger methods. Boreholes drilled in this way include oil or gas wells, water wells, and holes drilled for geotechnical investigations or mineral exploration.The drill cuttings are commonly...
) from the wellbore. By maintaining the annular velocity at certain rates (speeds) in conjunction with the rheological properties of the drilling fluid
Drilling fluid
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid is a fluid used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Often used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. Liquid drilling fluid...
, the wellbore is kept clean of the drill cuttings
Drill cuttings
Drill cuttings are the broken bits of solid material removed from a borehole drilled by rotary, percussion, or auger methods. Boreholes drilled in this way include oil or gas wells, water wells, and holes drilled for geotechnical investigations or mineral exploration.The drill cuttings are commonly...
to prevent them from settling back down to the bottom and causing drilling problems.
Annular drilling is an efficient process that can cut in metals like steel and stainless steel holes with diameters ranging from 7/16" to 5".
The other major variable is the rheology
Rheology
Rheology is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in the liquid state, but also as 'soft solids' or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force....
of the drilling fluid. Rheology
Rheology
Rheology is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in the liquid state, but also as 'soft solids' or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force....
is sometimes thought of as viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
to the uninitiated, though improperly. Viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
(sometimes thought of as its thickness) is a very basic measurement of the fluids resistance to change in movement or flow. The viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
of a fluid can be measured with a Marsh Funnel
Marsh funnel
The Marsh funnel viscometer is a simple device for measuring viscosity from the time it takes a known volume of liquid to flow from the base of a cone through a short tube...
. Rheology
Rheology
Rheology is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in the liquid state, but also as 'soft solids' or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force....
is the study of viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
and requires more precise and complicated procedures and equipment
Rheometer
A rheometer is a laboratory device used to measure the way in which a liquid, suspension or slurry flows in response to applied forces. It is used for those fluids which cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case...
for its determination. For drilling fluid applications a rheometer
Rheometer
A rheometer is a laboratory device used to measure the way in which a liquid, suspension or slurry flows in response to applied forces. It is used for those fluids which cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case...
is used.
See also
- Fluid DynamicsFluid dynamicsIn physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
- Drilling fluidDrilling fluidIn geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid is a fluid used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Often used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. Liquid drilling fluid...
- RheologyRheologyRheology is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in the liquid state, but also as 'soft solids' or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force....
- Mud EngineerMud engineerA mud engineer works on an oil well or gas well drilling rig, and is responsible ensuring the properties of the drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, are within designed specifications.-Use of mud:Mud is a vital part of drilling operations...
- Petroleum EngineeringPetroleum engineeringPetroleum engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the activities related to the production of hydrocarbons, which can be either crude oil or natural gas. Subsurface activities are deemed to fall within the upstream sector of the oil and gas industry, which are the activities of...
- Drilling rigDrilling rigA drilling rig is a machine which creates holes or shafts in the ground. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person...
- Oilfield
- Oil wellOil wellAn oil well is a general term for any boring through the earth's surface that is designed to find and acquire petroleum oil hydrocarbons. Usually some natural gas is produced along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce mainly or only gas may be termed a gas well.-History:The earliest...
- Oil field acronymsOil field acronymsThe oil and gas industry uses many acronyms and abbreviations. Obviously, this list is not anywhere near exhaustive or definitive.It is an amalgam of user contributions. It is contextual and is meant for indicative purposes only...
- List of oilfield service companies
- List of oil fields
- Natural gas fieldNatural gas fieldOil and natural gas are produced by the same geological process according fossil fuel suggestion: anaerobic decay of organic matter deep under the Earth's surface. As a consequence, oil and natural gas are often found together...

