
Angle condition
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, the angle condition is a constraint that is satisfied by the locus of points in the s-plane on which closed-loop pole
s of a system reside. In combination with the magnitude condition
, these two mathematical expressions fully determine the root locus
.
Let the characteristic equation
of a system be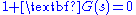 , where
, where 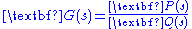 . Rewriting the equation in polar form is useful.
. Rewriting the equation in polar form is useful.
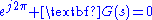
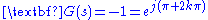 where
where
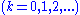 are the only solutions to this equation. Rewriting
are the only solutions to this equation. Rewriting 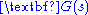 in factored form
in factored form
,
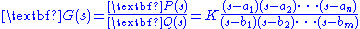 ,
,
and representing each factor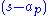 and
and 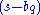 by their vector equivalents,
by their vector equivalents, 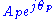 and
and 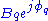 , respectively,
, respectively, 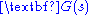 may be rewritten.
may be rewritten.
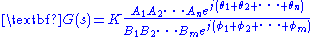
Simplifying the characteristic equation,
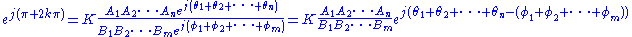 ,
,
from which we derive the angle condition:
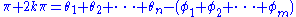
where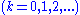 ,
,
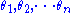 are the angles of poles 1 to n, and
are the angles of poles 1 to n, and
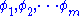 are the angles of zeros 1 to m.
are the angles of zeros 1 to m.
The magnitude condition
is derived similarly.
Closed-loop pole
Closed-loop poles are the positions of the poles of a closed-loop transfer function in the s-plane. The open-loop transfer function is equal to the product of all transfer function blocks in the forward path in the block diagram...
s of a system reside. In combination with the magnitude condition
Magnitude condition
The magnitude condition is a constraint that is satisfied by the locus of points in the s-plane on which closed-loop poles of a system reside. In combination with the angle condition, these two mathematical expressions fully determine the root locus....
, these two mathematical expressions fully determine the root locus
Root locus
Root locus analysis is a graphical method for examining how the roots of a system change with variation of a certain system parameter, commonly the gain of a feedback system. This is a technique used in the field of control systems developed by Walter R...
.
Let the characteristic equation
Characteristic equation
Characteristic equation may refer to:* Characteristic equation , used to solve linear differential equations* Characteristic equation, a characteristic polynomial equation in linear algebra used to find eigenvalues...
of a system be
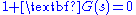 , where
, where 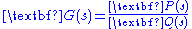 . Rewriting the equation in polar form is useful.
. Rewriting the equation in polar form is useful.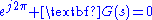
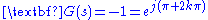 where
where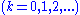 are the only solutions to this equation. Rewriting
are the only solutions to this equation. Rewriting 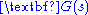 in factored form
in factored formFactorization
In mathematics, factorization or factoring is the decomposition of an object into a product of other objects, or factors, which when multiplied together give the original...
,
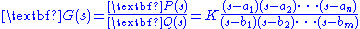 ,
,and representing each factor
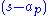 and
and 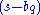 by their vector equivalents,
by their vector equivalents, 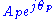 and
and 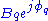 , respectively,
, respectively, 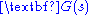 may be rewritten.
may be rewritten.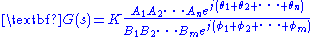
Simplifying the characteristic equation,
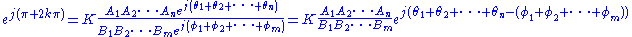 ,
,from which we derive the angle condition:
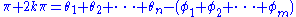
where
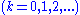 ,
,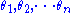 are the angles of poles 1 to n, and
are the angles of poles 1 to n, and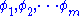 are the angles of zeros 1 to m.
are the angles of zeros 1 to m.The magnitude condition
Magnitude condition
The magnitude condition is a constraint that is satisfied by the locus of points in the s-plane on which closed-loop poles of a system reside. In combination with the angle condition, these two mathematical expressions fully determine the root locus....
is derived similarly.

