
Aminal
Encyclopedia
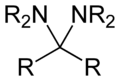
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
or type of chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
that has two amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
groups attached to the same carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom: -C(NR2)(NR2)-. Again R can be hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
or an alkyl group.
The aminal and the hemiaminal groups are the cousins of hemiacetal
Hemiacetal
Hemiacetals and hemiketals are compounds that are derived from aldehydes and ketones respectively. The Greek word hèmi means half...
s and acetal
Acetal
An acetal is a molecule with two single-bonded oxygen atoms attached to the same carbon atom.Traditional usages distinguish ketals from acetals...
s with nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
replaced by oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. Aminals are encountered in for instance the Fischer indole synthesis
Fischer indole synthesis
The Fischer indole synthesis isa chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Hermann Emil Fischer. Today antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often...
.
Hemiaminal ethers

Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
s are also sometimes called aminals although it is discouraged by the IUPAC. They have the following structure: R‴-C(NR'2)(OR")-R⁗. The glycosylamine
Glycosylamine
Glycosylamine is a class of biochemical compounds consisting of an amine with a β-N-glycosidic bond to a carbohydrate, thus forming a cyclic hemiaminal ether bond .Examples include nucleosides such as adenosine....
s are examples of cyclic hemiaminal ethers.

