Almucantar
Encyclopedia
An Almucantar, also spelled almucantarat or almacantara, is a circle
on the celestial sphere
parallel to the horizon
. Two star
s that lie the same almucantar have the same altitude.
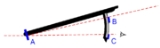
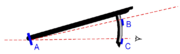 An almucantar staff is an instrument chiefly used to determine the time of sunrise
An almucantar staff is an instrument chiefly used to determine the time of sunrise
and sunset
, in order to find the amplitude and consequently the variations of the compass
. Usually made of pear
tree or boxwood, with an arch of 15° to 30°, it is an example of a backstaff
.
The sun casts that shadow of a vane (B in the image at the right) on a horizon vane (A). The horizon vane has a slit or hole to allow the observer to see the horizon in the distance. The observer aligns the horizon and shadow so they show at the same point on the horizon vane and sets the sighting vane (C) to align his line of sight with the horizon. The altitude of the sun is the angle between the shadow vane and the sighting vane.
of aerosols. Measurements are carried out rapidly at several angle at both sides of the Sun using a spectroradiometer
or a photometer
. There are several models to obtain aerosol properties from the solar almucantar. The most relevant were developed by Oleg Dubovik and used in the NASA AERONET
network and by Teruyuki Nakajima (named SKYRAD.PACK).
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
on the celestial sphere
Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the Earth and rotating upon the same axis. All objects in the sky can be thought of as projected upon the celestial sphere. Projected upward from Earth's equator and poles are the...
parallel to the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
. Two star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s that lie the same almucantar have the same altitude.
Almucantar staff

Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
and sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
, in order to find the amplitude and consequently the variations of the compass
Compass
A compass is a navigational instrument that shows directions in a frame of reference that is stationary relative to the surface of the earth. The frame of reference defines the four cardinal directions – north, south, east, and west. Intermediate directions are also defined...
. Usually made of pear
Pear
The pear is any of several tree species of genus Pyrus and also the name of the pomaceous fruit of these trees. Several species of pear are valued by humans for their edible fruit, but the fruit of other species is small, hard, and astringent....
tree or boxwood, with an arch of 15° to 30°, it is an example of a backstaff
Backstaff
The backstaff or back-quadrant is a navigational instrument that was used to measure the altitude of a celestial body, in particular the sun or moon...
.
The sun casts that shadow of a vane (B in the image at the right) on a horizon vane (A). The horizon vane has a slit or hole to allow the observer to see the horizon in the distance. The observer aligns the horizon and shadow so they show at the same point on the horizon vane and sets the sighting vane (C) to align his line of sight with the horizon. The altitude of the sun is the angle between the shadow vane and the sighting vane.
Solar almucantar
The almucantar plane that contains the Sun is used to characterize multiple scatteringScattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
of aerosols. Measurements are carried out rapidly at several angle at both sides of the Sun using a spectroradiometer
Spectroradiometer
Spectroradiometers are designed to measure the spectral power distributions of illuminants. They operate almost like spectrophotometers in the visible region...
or a photometer
Photometer
In its widest sense, a photometer is an instrument for measuring light intensity or optical properties of solutions or surfaces. Photometers are used to measure:*Illuminance*Irradiance*Light absorption*Scattering of light*Reflection of light*Fluorescence...
. There are several models to obtain aerosol properties from the solar almucantar. The most relevant were developed by Oleg Dubovik and used in the NASA AERONET
AERONET
AERONET - the AERONET is a network of ground-based sun photometers which measure atmospheric aerosol properties. The measurement system is a solar-powered CIMEL Electronique 318A spectral radiometer that measures Sun and sky radiances ata number of fixed wavelengths within the visible and...
network and by Teruyuki Nakajima (named SKYRAD.PACK).

