
Adverse pressure gradient
Encyclopedia
An adverse pressure
gradient occurs when the static pressure
increases in the direction of the flow. Mathematically this is expressed as:
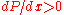 .
.
This is important for boundary layer
s, since increasing the fluid pressure is akin to increasing the potential energy
of the fluid, leading to a reduced kinetic energy
and a deceleration of the fluid
. Since the fluid in the inner part of the boundary layer is relatively slower, it is more greatly affected by the increasing pressure gradient. For a large enough pressure increase, this fluid may slow to zero velocity or even become reversed. When flow reversal occurs, the flow is said to be separated from the surface. This has very significant consequences in aerodynamics
since flow separation
significantly modifies the pressure distribution along the surface and hence the lift
and drag
characteristics.
Turbulent boundary layers tend to be able to sustain an adverse pressure gradient better than an equivalent laminar boundary layer. The more efficient mixing which occurs in a turbulent boundary layer transports kinetic energy from the edge of the boundary layer to the low momentum
flow at the solid surface, often preventing the separation which would occur for a laminar boundary layer under the same conditions. This physical fact has led to a variety of schemes to actually produce turbulent boundary layers when boundary layer separation is dominant at high Reynolds numbers. The dimples on a golf
ball, the fuzz on a tennis
ball, or the seams on a baseball
are good examples. Aeroplane wing
s are often engineered with vortex generator
s on the upper surface to produce a turbulent boundary layer.
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
gradient occurs when the static pressure
Static pressure
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure has several uses:* In the design and operation of aircraft, static pressure is the air pressure in the aircraft’s static pressure system....
increases in the direction of the flow. Mathematically this is expressed as:
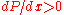 .
.This is important for boundary layer
Boundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is that layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface where effects of viscosity of the fluid are considered in detail. In the Earth's atmosphere, the planetary boundary layer is the air layer near the ground affected by diurnal...
s, since increasing the fluid pressure is akin to increasing the potential energy
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
of the fluid, leading to a reduced kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
and a deceleration of the fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
. Since the fluid in the inner part of the boundary layer is relatively slower, it is more greatly affected by the increasing pressure gradient. For a large enough pressure increase, this fluid may slow to zero velocity or even become reversed. When flow reversal occurs, the flow is said to be separated from the surface. This has very significant consequences in aerodynamics
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
since flow separation
Flow separation
All solid objects travelling through a fluid acquire a boundary layer of fluid around them where viscous forces occur in the layer of fluid close to the solid surface. Boundary layers can be either laminar or turbulent...
significantly modifies the pressure distribution along the surface and hence the lift
Lift (force)
A fluid flowing past the surface of a body exerts a surface force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the surface force parallel to the flow direction...
and drag
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag refers to forces which act on a solid object in the direction of the relative fluid flow velocity...
characteristics.
Turbulent boundary layers tend to be able to sustain an adverse pressure gradient better than an equivalent laminar boundary layer. The more efficient mixing which occurs in a turbulent boundary layer transports kinetic energy from the edge of the boundary layer to the low momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
flow at the solid surface, often preventing the separation which would occur for a laminar boundary layer under the same conditions. This physical fact has led to a variety of schemes to actually produce turbulent boundary layers when boundary layer separation is dominant at high Reynolds numbers. The dimples on a golf
Golf
Golf is a precision club and ball sport, in which competing players use many types of clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a golf course using the fewest number of strokes....
ball, the fuzz on a tennis
Tennis
Tennis is a sport usually played between two players or between two teams of two players each . Each player uses a racket that is strung to strike a hollow rubber ball covered with felt over a net into the opponent's court. Tennis is an Olympic sport and is played at all levels of society at all...
ball, or the seams on a baseball
Baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each. The aim is to score runs by hitting a thrown ball with a bat and touching a series of four bases arranged at the corners of a ninety-foot diamond...
are good examples. Aeroplane wing
Wing
A wing is an appendage with a surface that produces lift for flight or propulsion through the atmosphere, or through another gaseous or liquid fluid...
s are often engineered with vortex generator
Vortex generator
A vortex generator is an aerodynamic surface, consisting of a small vane or bump that creates a vortex. Vortex generators can be found on many devices, but the term is most often used in aircraft design....
s on the upper surface to produce a turbulent boundary layer.

