
Active rectification
Encyclopedia
Active rectification, or synchronous rectification, is a technique for improving the efficiency of rectification
by replacing diode
s with actively-controlled switches such as transistor
s, usually power MOSFET
s or power BJTs. Historically, motor-driven mechanical commutator
s have also been used for synchronous rectification.
 The constant voltage drop of a standard p-n junction
The constant voltage drop of a standard p-n junction
diode
is typically between 0.7 V and 1.7 V, causing significant power loss in the diode. Electric power
depends on current and voltage: the power loss rises proportional to both current and voltage.
In low voltage converters
(around 10 volt
s and less), the voltage drop of a diode (typically around 0.7 to 1 volt for a silicon diode at its rated current) has an adverse effect on efficiency. One classic solution replaces standard silicon diodes with Schottky diode
s, which exhibit very low voltage drops (as low as 0.3 volts). However, even Schottky rectifiers can be significantly more lossy than the synchronous type, notably at high currents and/or low voltages.
When addressing very low-voltage converters, such as a buck converter
power supply for a computer CPU (with a voltage output around 1 volt, and many ampere
s of output current), Schottky rectification does not provide adequate efficiency. In such applications, active rectification becomes necessary.
governs the voltage drop across the MOSFET, meaning that at high currents, the drop can exceed that of a diode. This limitation is usually dealt with either by placing several transistors in parallel, thereby reducing the current through each individual one, or by using a device with more active area (on FETs, a device-equivalent of parallel).
The control circuitry for active rectification usually uses comparator
s to sense the voltage of the input AC and open the transistors at the correct times to allow current to flow in the correct direction. The timing is very important, as a short circuit across the input power must be avoided and can easily be caused by one transistor turning on before another has turned off. Active rectifiers also clearly still need the smoothing capacitor
s present in passive examples.
Using active rectification to implement AC/DC conversion can allow a design to undergo further improvements (with more complexity) to achieve Active power factor correction, which forces the current waveform of the AC source to follow the voltage waveform, eliminating reactive currents and allowing the total system to achieve greater efficiency.
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
by replacing diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s with actively-controlled switches such as transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s, usually power MOSFET
Power MOSFET
A Power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor designed to handle significant power levels. Compared to the other power semiconductor devices , its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages...
s or power BJTs. Historically, motor-driven mechanical commutator
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
s have also been used for synchronous rectification.
Motivation

P-n junction
A p–n junction is formed at the boundary between a P-type and N-type semiconductor created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy .If two separate pieces of material were used, this would...
diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
is typically between 0.7 V and 1.7 V, causing significant power loss in the diode. Electric power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
depends on current and voltage: the power loss rises proportional to both current and voltage.
In low voltage converters
DC to DC converter
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit which converts a source of direct current from one voltage level to another. It is a class of power converter.- Usage :...
(around 10 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s and less), the voltage drop of a diode (typically around 0.7 to 1 volt for a silicon diode at its rated current) has an adverse effect on efficiency. One classic solution replaces standard silicon diodes with Schottky diode
Schottky diode
The Schottky diode is a semiconductor diode with a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action...
s, which exhibit very low voltage drops (as low as 0.3 volts). However, even Schottky rectifiers can be significantly more lossy than the synchronous type, notably at high currents and/or low voltages.
When addressing very low-voltage converters, such as a buck converter
Buck converter
A buck converter is a step-down DC to DC converter. Its design is similar to the step-up boost converter, and like the boost converter it is a switched-mode power supply that uses two switches , an inductor and a capacitor....
power supply for a computer CPU (with a voltage output around 1 volt, and many ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s of output current), Schottky rectification does not provide adequate efficiency. In such applications, active rectification becomes necessary.
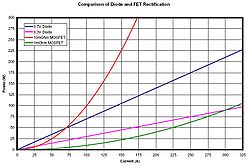
Description
Replacing a diode with an actively controlled switching element such as a MOSFET is the heart of active rectification. MOSFETs have a constant very low resistance when conducting, known as on-resistance (RDS(on)). They can be made with an on-resistance as low as 10 milliohms or even lower. The voltage drop across the transistor is then much lower, meaning a reduction in power loss and a gain in efficiency. However, Ohm's LawOhm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
governs the voltage drop across the MOSFET, meaning that at high currents, the drop can exceed that of a diode. This limitation is usually dealt with either by placing several transistors in parallel, thereby reducing the current through each individual one, or by using a device with more active area (on FETs, a device-equivalent of parallel).
The control circuitry for active rectification usually uses comparator
Comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters .- Input voltage range :...
s to sense the voltage of the input AC and open the transistors at the correct times to allow current to flow in the correct direction. The timing is very important, as a short circuit across the input power must be avoided and can easily be caused by one transistor turning on before another has turned off. Active rectifiers also clearly still need the smoothing capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s present in passive examples.
Using active rectification to implement AC/DC conversion can allow a design to undergo further improvements (with more complexity) to achieve Active power factor correction, which forces the current waveform of the AC source to follow the voltage waveform, eliminating reactive currents and allowing the total system to achieve greater efficiency.
Further reading
- T. Grossen, E. Menzel, J.J.R. Enslin. (1999) Three-phase buck active rectifier with power factor correction and low EMI. IEE Proceedings - Electric Power Applications, Vol. 146, Iss. 6, Nov. 1999, pp. 591–596. Digital Object Identifier:10.1049/ip-epa:19990523.
- W. Santiago, A. Birchenough. (2005). Single Phase Passive Rectification versus Active Rectification Applied to High Power Stirling Engines. AIAA 2005-5687.

