Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase
Encyclopedia
The final step of beta oxidation
is the cleavage of 3-ketoacyl CoA by the thiol
group of another molecule of CoA
. This reaction is catalyzed by Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase (or Β-ketothiolase). The thiol is inserted between C-2 and C-3, which yields an acetyl CoA molecule and an acyl CoA molecule, which is two carbons shorter.
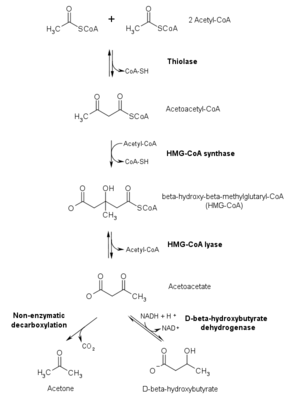
Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase belongs to the thiolase
family of enzymes.
Beta oxidation
Beta oxidation is the process by which fatty acids, in the form of Acyl-CoA molecules, are broken down in mitochondria and/or in peroxisomes to generate Acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the Citric Acid cycle....
is the cleavage of 3-ketoacyl CoA by the thiol
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
group of another molecule of CoA
COA
COA can refer to:*Codename Amscray*Cash on Arrival*Cause of action*CedarOpenAccounts*Center of Attention*Certificate of Appealability*Certificate of Approval for marriage or civil partnership in the United Kingdom*Certificate of Authenticity...
. This reaction is catalyzed by Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase (or Β-ketothiolase). The thiol is inserted between C-2 and C-3, which yields an acetyl CoA molecule and an acyl CoA molecule, which is two carbons shorter.
Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase belongs to the thiolase
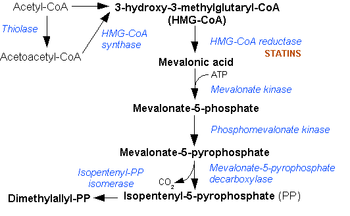
Thiolase
Thiolases also known as acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferases are enzymes which converts two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate pathway....
family of enzymes.
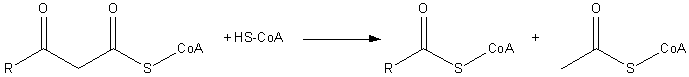 |
 |
 |

