
Abstraction layer
Encyclopedia
OSI model
The Open Systems Interconnection model is a product of the Open Systems Interconnection effort at the International Organization for Standardization. It is a prescription of characterizing and standardizing the functions of a communications system in terms of abstraction layers. Similar...
for computer network
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
protocols, the OpenGL
OpenGL
OpenGL is a standard specification defining a cross-language, cross-platform API for writing applications that produce 2D and 3D computer graphics. The interface consists of over 250 different function calls which can be used to draw complex three-dimensional scenes from simple primitives. OpenGL...
graphics drawing library, and the byte stream
Byte stream
In computer science, a byte stream is a bit stream, in which data bits are grouped into units, called bytes.In computer networking the term octet stream is sometimes used to refer to the same thing; it emphasizes the use of bytes having the length of 8 bits, known as octets.Formally, a byte stream...
input/output (I/O) model originated by Unix
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
and adopted by MSDOS, Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
, and most other modern operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
s.
In the Unix operating system, most types of input and output operations are considered to be streams of bytes being read from a device
Computer hardware
Personal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to a computer case to create a personal computer upon which system software is installed including a firmware interface such as a BIOS and an operating system which supports application software that...
or being written to a device. This stream of bytes model is used for file
Computer file
A computer file is a block of arbitrary information, or resource for storing information, which is available to a computer program and is usually based on some kind of durable storage. A file is durable in the sense that it remains available for programs to use after the current program has finished...
I/O, socket
Internet socket
In computer networking, an Internet socket or network socket is an endpoint of a bidirectional inter-process communication flow across an Internet Protocol-based computer network, such as the Internet....
I/O, and terminal I/O in order to provide device independence
Device Independence
Device independence is the process of making a software application be able to function on a wide variety of devices regardless of the local hardware on which the software is used.- Desktop computing :...
. In order to read and write to a device at the application level, the program calls a function to open the device which may be a real device such as a terminal or a virtual device
Virtual device
A virtual device in Unix is a file such as :/dev/null or :/dev/urandom, that is treated as a device, as far as user level software is concerned, but is generated by the kernel without reference to hardware....
such as a network port
Computer port (software)
In computer programming, port has a wide range of meanings.A software port is a virtual/logical data connection that can be used by programs to exchange data directly, instead of going through a file or other temporary storage location...
or a file in a file system
File system
A file system is a means to organize data expected to be retained after a program terminates by providing procedures to store, retrieve and update data, as well as manage the available space on the device which contain it. A file system organizes data in an efficient manner and is tuned to the...
. The device's physical characteristics are mediated by the operating system which in turn presents an abstract
Abstraction (computer science)
In computer science, abstraction is the process by which data and programs are defined with a representation similar to its pictorial meaning as rooted in the more complex realm of human life and language with their higher need of summarization and categorization , while hiding away the...
interface
Interface (computer science)
In the field of computer science, an interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software...
that allows the programmer
Programmer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is someone who writes computer software. The term computer programmer can refer to a specialist in one area of computer programming or to a generalist who writes code for many kinds of software. One who practices or professes a formal approach to...
to read and write byte
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, a byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the basic addressable element in many computer...
s from/to the device. The operating system then performs the actual transformation
Program transformation
A program transformation is any operation that takes a computer program and generates another program. In many cases the transformed program is required to be semantically equivalent to the original, relative to a particular formal semantics and in fewer cases the transformations result in programs...
needed to read and write the stream of bytes to the device.
Most graphics libraries
Library (computer science)
In computer science, a library is a collection of resources used to develop software. These may include pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications....
such as OpenGL provide an abstract graphical device model as an interface. The library is responsible for translating the commands provided by the programmer into the specific device commands needed to draw the graphical elements and objects. The specific device commands for a plotter
Plotter
A plotter is a computer printing device for printing vector graphics. In the past, plotters were widely used in applications such as computer-aided design, though they have generally been replaced with wide-format conventional printers...
are different from the device commands for a CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
monitor
Computer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
but the graphics library hides the implementation and device dependent details by providing an abstract interface which provides a set of primitives that are generally useful for drawing graphical objects.
In computer science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, an abstraction level is a generalization of a model or algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
, away from any specific implementation. These generalizations arise from broad similarities that are best encapsulated by models that express similarities present in various specific implementations. The simplification provided by a good abstraction layer allows for easy reuse by distilling a useful concept or metaphor so that situations where it may be accurately applied can be quickly recognized.
A good abstraction will generalize that which can be made abstract; while allowing specificity where the abstraction breaks down and its successful application requires customization to each unique requirement or problem.
Frequently abstraction layers can be composed into a hierarchy of abstraction levels. The ISO-OSI networking model
OSI model
The Open Systems Interconnection model is a product of the Open Systems Interconnection effort at the International Organization for Standardization. It is a prescription of characterizing and standardizing the functions of a communications system in terms of abstraction layers. Similar...
comprises seven abstraction layers. Each layer of the OSI ISO networking model encapsulates and addresses a different part of the needs of much digital communications, thereby reducing the complexity of the associated engineering solutions.
A famous aphorism
Aphorism
An aphorism is an original thought, spoken or written in a laconic and memorable form.The term was first used in the Aphorisms of Hippocrates...
of David Wheeler goes: All problems in computer science can be solved by another level of indirection;
this is often deliberately mis-quoted with "abstraction" substituted for "indirection". Kevlin Henney
Kevlin Henney
Kevlin Henney is an author who writes on the subject of computer programming in C and C++ for magazines such as the C/C++ Users Journal, Application Development Advisor, JavaSpektrum, C++ Report, Java Report, EXE, and Overload....
's corollary to this is, "...except for the problem of too many layers of indirection."
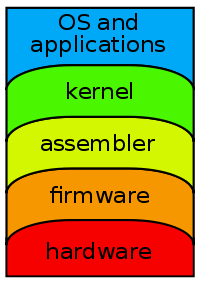
Computer architecture
In computer architectureComputer architecture
In computer science and engineering, computer architecture is the practical art of selecting and interconnecting hardware components to create computers that meet functional, performance and cost goals and the formal modelling of those systems....
, a computer system is usually represented as consisting of five abstraction levels: hardware
Computer hardware
Personal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to a computer case to create a personal computer upon which system software is installed including a firmware interface such as a BIOS and an operating system which supports application software that...
(see hardware abstraction
Hardware abstraction
Hardware abstractions are sets of routines in software that emulate some platform-specific details, giving programs direct access to the hardware resources....
), firmware
Firmware
In electronic systems and computing, firmware is a term often used to denote the fixed, usually rather small, programs and/or data structures that internally control various electronic devices...
, assembler
Assembly language
An assembly language is a low-level programming language for computers, microprocessors, microcontrollers, and other programmable devices. It implements a symbolic representation of the machine codes and other constants needed to program a given CPU architecture...
, operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
and processes
Process (computing)
In computing, a process is an instance of a computer program that is being executed. It contains the program code and its current activity. Depending on the operating system , a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently.A computer program is a...
.
See also
- LayerLayer (object-oriented design)In object-oriented design, a layer is a group of classes that have the same set of link-time module dependencies to other modules. In other words, a layer is a group of reusable components that are reusable in similar circumstances...
for object-oriented meaning - Information hidingInformation hidingIn computer science, information hiding is the principle of segregation of the design decisions in a computer program that are most likely to change, thus protecting other parts of the program from extensive modification if the design decision is changed...
- Abstraction (computer science)Abstraction (computer science)In computer science, abstraction is the process by which data and programs are defined with a representation similar to its pictorial meaning as rooted in the more complex realm of human life and language with their higher need of summarization and categorization , while hiding away the...
- Transparency (computing)Transparency (computing)Any change in a computing system, such as new feature or new component, is transparent if the system after change adheres to previous external interface as much as possible while changing its internal behaviour. The purpose is to shield from change all systems on the other end of the interface...
- Protection ring
- Computer softwareComputer softwareComputer software, or just software, is a collection of computer programs and related data that provide the instructions for telling a computer what to do and how to do it....
- Application programming interfaceApplication programming interfaceAn application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
- Software engineeringSoftware engineeringSoftware Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
- Software
- HardwareHardwareHardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
- DatabaseDatabaseA database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
- NetworkComputer networkA computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....

