
AU Microscopii
Encyclopedia
AU Microscopii is a red dwarf star located 10 parsec
s (32 light-year
s) away – about 8 times as far as our closest star after the Sun
. AU Mic is a young star, only 12 million years old, less than 1% of the age of the Sun
. It has only half the mass of the Sun and is only one-tenth as bright. The star was given this name
because it is in the constellation Microscopium
and is a variable star
. AU Microscopii is a member of the β Pictoris moving group
. AU Microscopii may be bound to the binary star AT Microscopii. Like β Pictoris
, AU Microscopii has a circumstellar dust disk known as a debris disk
.
and a mass only 50% of the Sun.
It has an effective temperature
of 3730 K
.
brightness variation was approximately 0.3 magnitude
s in 1971, by 1980 it was merely 0.1 magnitudes.
AU Microscopii has been observed in every part of the electromagnetic spectrum
from radio
to X-ray
and is known to undergo flaring
activity at all these wavelengths. Its flaring behaviour was first identified in 1973.
 AU Microscopii harbors its own disk of dust, first resolved at optical wavelengths in 2003 by Paul Kalas
AU Microscopii harbors its own disk of dust, first resolved at optical wavelengths in 2003 by Paul Kalas
and collaborators using the University of Hawaii 2.2-m telescope
on Mauna Kea
, Hawaii. This large debris disk faces the earth edge-on, and measures at least 200 AU
in radius. At these large distances from the star, the lifetime of dust in the disk exceeds the age of AU Microscopii. The disk has a gas to dust mass ratio of no more than 6:1, much lower than the usually assumed primordial value of 100:1. The debris disk is therefore referred to as "gas-poor". The total amount of dust visible in the disk is estimated to be at least a lunar mass, while the larger planetesimal
s from which the dust is produced are inferred to has at least six lunar masses.
The spectral energy distribution
of AU Microscopii's debris disk at submillimetre
wavelengths indicate the presence of an inner hole in the disk extending to 17 AU, while scattered light images estimate the inner hole to be 12 AU in radius. Combining the spectral energy distribution with the surface brightness profile yields a smaller estimate of the radius of the inner hole, 1 - 10 AU.
The inner part of the disk is asymmetric
and shows structure in the inner 40 AU. The inner structure has been compared with that expected to be seen if the disk is influenced by larger bodies or has undergone recent planet formation.
The presence of the inner hole and asymmetric structure has led a number of astronomers to search for planets orbiting AU Microscopii. By 2007, no searches had led to any detections of planets.
The surface brightness (brightness per area) of the disk as a function of projected distance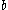 from the star follows a characteristic shape. The inner 15 AU of the disk appear approximately constant in density. Around
from the star follows a characteristic shape. The inner 15 AU of the disk appear approximately constant in density. Around 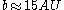 the density begins to decrease: first it decreases slowly as
the density begins to decrease: first it decreases slowly as 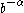 where
where 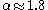 ; then outside
; then outside 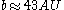 , the brightness drops more steeply, as
, the brightness drops more steeply, as 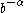 where
where 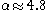 . This "broken power-law" shape is similar to the shape of the profile of β Pic's disk.
. This "broken power-law" shape is similar to the shape of the profile of β Pic's disk.
 AU Mic's disk has been observed at a variety of different wavelength
AU Mic's disk has been observed at a variety of different wavelength
s, giving us different types of information about the system. The light from the disk observed at optical wavelengths is stellar light that has reflected (scattered) off dust particles into our line of sight. Observations at these wavelengths utilize a coronagraphic spot
to block the bright light coming directly from the star. Such observations provide high-resolution images of the disk. Because light having a wavelength longer than the size of a dust grain is scattered only poorly, comparing images at different wavelengths (visible and near-infrared, for example) gives us information about the sizes of the dust grains in the disk.
Optical observations have been made with the Hubble Space Telescope
and Keck Telescopes. The system has also been observed at infrared
and sub-millimeter wavelengths. This light is emitted directly by dust grains as a result of their internal heat (modified blackbody radiation). The disk cannot be resolved at these wavelengths, so such observations are measurements of the amount of light coming from the entire system. Observations at increasingly longer wavelengths give information about dust particles of larger sizes and at larger distances from the star. These observations have been made with the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope
and Spitzer Space Telescope
.
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s (32 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s) away – about 8 times as far as our closest star after the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. AU Mic is a young star, only 12 million years old, less than 1% of the age of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. It has only half the mass of the Sun and is only one-tenth as bright. The star was given this name
Variable star designation
Variable stars are named using a variation on the Bayer designation format of an identifying label combined with the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in which the star lies...
because it is in the constellation Microscopium
Microscopium
Microscopium is a small constellation in the southern sky, created in the 18th century by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for microscope. Its stars are very faint and hardly visible from most of the non-tropical northern hemisphere.-References:...
and is a variable star
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
. AU Microscopii is a member of the β Pictoris moving group
Beta Pictoris Moving Group
The Beta Pictoris Moving Group is a young moving group of stars located relatively near Earth. A moving group, in astronomy, is a group of stars that share a common motion through space as well as a common origin...
. AU Microscopii may be bound to the binary star AT Microscopii. Like β Pictoris
Beta Pictoris
Beta Pictoris is the second brightest star in the constellation Pictor. It is located 63.4 light years from our solar system, and is 1.75 times as massive and 8.7 times as luminous as the Sun. The Beta Pictoris system is very young, only 8–20 million years old, although it is already in the main...
, AU Microscopii has a circumstellar dust disk known as a debris disk
Debris disk
A debris disk is a circumstellar disk of dust and debris in orbit around a star. Sometimes these disks contain prominent rings, as seen in the image of Fomalhaut on the right. Debris disks have been found around both evolved and young stars, as well as at least one debris disk in orbit around a...
.
Stellar properties
AU Micoscopii is a small M star, with a physical radius of only 60% that of the SunSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and a mass only 50% of the Sun.
It has an effective temperature
Effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation...
of 3730 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
.
Variability
AU Microscopii has a nearly sinusoidal variation in its brightness with a period of 4.865 days. The amplitude of the variation changes slowly with time. The V bandUBV photometric system
UBV photometric system, also called the Johnson system , is a wide band photometric system for classifying stars according to their colors. It is the first known standardized photoelectric photometric system. The letters U, B, and V stand for ultraviolet, blue, and visual magnitudes, which are...
brightness variation was approximately 0.3 magnitude
Absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
s in 1971, by 1980 it was merely 0.1 magnitudes.
AU Microscopii has been observed in every part of the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
from radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
to X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
and is known to undergo flaring
Flare star
A flare star is a variable star that can undergo unpredictable dramatic increases in brightness for a few minutes. It is believed that the flares on flare stars are analogous to solar flares in that they are due to magnetic reconnection in the atmospheres of the stars. The brightness increase is...
activity at all these wavelengths. Its flaring behaviour was first identified in 1973.
Debris disk

Paul Kalas
Paul Kalas is a Greek American astronomer known for his discoveries of debris disks around stars. Kalas led a team of scientists to obtain the first visible-light images of an extrasolar planet with orbital motion around the star Fomalhaut, at a distance of 25 light years from Earth...
and collaborators using the University of Hawaii 2.2-m telescope
UH88
The University of Hawai'i 88-inch telescope called UH88, UH2.2, or simply 88 by members of the local astronomical community is situated at the Mauna Kea Observatory and operated by the University's Institute for Astronomy...
on Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea is a volcano on the island of Hawaii. Standing above sea level, its peak is the highest point in the state of Hawaii. However, much of the mountain is under water; when measured from its oceanic base, Mauna Kea is over tall—significantly taller than Mount Everest...
, Hawaii. This large debris disk faces the earth edge-on, and measures at least 200 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
in radius. At these large distances from the star, the lifetime of dust in the disk exceeds the age of AU Microscopii. The disk has a gas to dust mass ratio of no more than 6:1, much lower than the usually assumed primordial value of 100:1. The debris disk is therefore referred to as "gas-poor". The total amount of dust visible in the disk is estimated to be at least a lunar mass, while the larger planetesimal
Planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and in debris disks.A widely accepted theory of planet formation, the so-called planetesimal hypothesis of Viktor Safronov, states that planets form out of cosmic dust grains that collide and stick to form larger and larger...
s from which the dust is produced are inferred to has at least six lunar masses.
The spectral energy distribution
Astronomical spectroscopy
Astronomical spectroscopy is the technique of spectroscopy used in astronomy. The object of study is the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other celestial objects...
of AU Microscopii's debris disk at submillimetre
Submillimetre astronomy
Submillimetre astronomy or submillimeter astronomy is the branch of observational astronomy that is conducted at submillimetre wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Astronomers place the submillimetre waveband between the far-infrared and microwave wavebands, typically taken to be between a...
wavelengths indicate the presence of an inner hole in the disk extending to 17 AU, while scattered light images estimate the inner hole to be 12 AU in radius. Combining the spectral energy distribution with the surface brightness profile yields a smaller estimate of the radius of the inner hole, 1 - 10 AU.
The inner part of the disk is asymmetric
Asymmetric
Something which is asymmetric displays asymmetry. Specific uses of the term may include:*Asymmetric relation for information on such relations in mathematics and set theory*Asymmetric warfare for information and theories of modern war...
and shows structure in the inner 40 AU. The inner structure has been compared with that expected to be seen if the disk is influenced by larger bodies or has undergone recent planet formation.
The presence of the inner hole and asymmetric structure has led a number of astronomers to search for planets orbiting AU Microscopii. By 2007, no searches had led to any detections of planets.
The surface brightness (brightness per area) of the disk as a function of projected distance
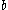 from the star follows a characteristic shape. The inner 15 AU of the disk appear approximately constant in density. Around
from the star follows a characteristic shape. The inner 15 AU of the disk appear approximately constant in density. Around 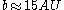 the density begins to decrease: first it decreases slowly as
the density begins to decrease: first it decreases slowly as 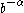 where
where 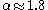 ; then outside
; then outside 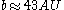 , the brightness drops more steeply, as
, the brightness drops more steeply, as 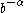 where
where 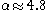 . This "broken power-law" shape is similar to the shape of the profile of β Pic's disk.
. This "broken power-law" shape is similar to the shape of the profile of β Pic's disk.Methods of observation

Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
s, giving us different types of information about the system. The light from the disk observed at optical wavelengths is stellar light that has reflected (scattered) off dust particles into our line of sight. Observations at these wavelengths utilize a coronagraphic spot
Coronagraph
A coronagraph is a telescopic attachment designed to block out the direct light from a star so that nearby objects – which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare – can be resolved...
to block the bright light coming directly from the star. Such observations provide high-resolution images of the disk. Because light having a wavelength longer than the size of a dust grain is scattered only poorly, comparing images at different wavelengths (visible and near-infrared, for example) gives us information about the sizes of the dust grains in the disk.
Optical observations have been made with the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
and Keck Telescopes. The system has also been observed at infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
and sub-millimeter wavelengths. This light is emitted directly by dust grains as a result of their internal heat (modified blackbody radiation). The disk cannot be resolved at these wavelengths, so such observations are measurements of the amount of light coming from the entire system. Observations at increasingly longer wavelengths give information about dust particles of larger sizes and at larger distances from the star. These observations have been made with the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope
James Clerk Maxwell Telescope
The James Clerk Maxwell Telescope is a submillimetre-wavelength telescope at Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii. Its primary mirror is 15 metres across: it is the largest astronomical telescope that operates in submillimetre wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum...
and Spitzer Space Telescope
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope , formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003...
.

