
A-law algorithm
Encyclopedia
An A-law algorithm is a standard companding
algorithm, used in Europe
an digital
communications
systems to optimize, i.e., modify, the dynamic range
of an analog signal
for digitizing.
It is similar to the μ-law algorithm used in North America
and Japan
.
For a given input x, the equation for A-law encoding is as follows,
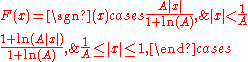
where A is the compression parameter. In Europe,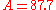 ; the value 87.6 is also used.
; the value 87.6 is also used.
A-law expansion is given by the inverse function,
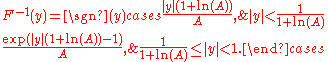
The reason for this encoding is that the wide dynamic range
of speech does not lend itself well to efficient linear digital encoding. A-law encoding effectively reduces the dynamic range of the signal, thereby increasing the coding
efficiency and resulting in a signal-to-distortion
ratio that is superior to that obtained by linear encoding for a given number of bits.
Companding
In telecommunication, signal processing, and thermodynamics, companding is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range...
algorithm, used in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
communications
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
systems to optimize, i.e., modify, the dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
of an analog signal
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
for digitizing.
It is similar to the μ-law algorithm used in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
.
For a given input x, the equation for A-law encoding is as follows,
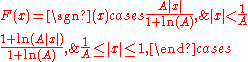
where A is the compression parameter. In Europe,
 ; the value 87.6 is also used.
; the value 87.6 is also used.A-law expansion is given by the inverse function,
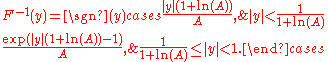
The reason for this encoding is that the wide dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
of speech does not lend itself well to efficient linear digital encoding. A-law encoding effectively reduces the dynamic range of the signal, thereby increasing the coding
Coding
Coding may refer to:* Channel coding in coding theory* Line coding* Computer programming, the process of designing, writing, testing, debugging / troubleshooting, and maintaining the source code of computer programs...
efficiency and resulting in a signal-to-distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
ratio that is superior to that obtained by linear encoding for a given number of bits.
Comparison to μ-law
The μ-law algorithm provides a slightly larger dynamic range than the A-law at the cost of worse proportional distortion for small signals. By convention, A-law is used for an international connection if at least one country uses it.See also
- μ-law algorithm
- Audio level compressionAudio level compressionDynamic range compression, also called DRC or simply compression reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds by narrowing or "compressing" an audio signal's dynamic range...
- Signal compressionSignal compressionIn telecommunication, the term signal compression has the following meanings:In analog systems, reduction of the dynamic range of a signal by controlling it as a function of the inverse relationship of its instantaneous value relative to a specified reference level.Signal compression is usually...
- CompandingCompandingIn telecommunication, signal processing, and thermodynamics, companding is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range...
- G.711G.711G.711 is an ITU-T standard for audio companding. It is primarily used in telephony. The standard was released for usage in 1972. Its formal name is Pulse code modulation of voice frequencies. It is required standard in many technologies, for example in H.320 and H.323 specifications. It can also...
- DS0
External links
- Waveform Coding Techniques - Has details of implementation (but note that the A-law equation is incorrect)
- A-Law and μ-law Companding Implementations Using the TMS320C54x (PDF)
- A-law and μ-law realisation (in C)

