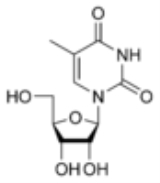
5-Methyluridine
Encyclopedia
The chemical compound
5-methyluridine, also called ribothymidine, is a pyrimidine
nucleoside
. It is the ribonucleoside
counterpart to the deoxyribonucleoside
thymidine
, which lacks a hydroxyl
group at the 2' position. 5-Methyluridine contains a thymine
base joined to a ribose
pentose sugar
.
It exists in solid
form as small white crystals or white crystalline powder
, has a molecular weight of 258.23 u, and has a melting point
of 185 °C. The stability of 5-methyluridine under standard temperature and pressure (STP) is very high.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
5-methyluridine, also called ribothymidine, is a pyrimidine
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound similar to benzene and pyridine, containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 of the six-member ring...
nucleoside
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
. It is the ribonucleoside
Ribonucleoside
A ribonucleoside is a type of nucleoside including ribose as a component.An example is cytidine....
counterpart to the deoxyribonucleoside
Deoxyribonucleoside
A deoxyribonucleoside is a type of nucleoside including deoxyribose as a component.An example is deoxycytidine....
thymidine
Thymidine
Thymidine is a chemical compound, more precisely a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine in double-stranded DNA...
, which lacks a hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
group at the 2' position. 5-Methyluridine contains a thymine
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
base joined to a ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
pentose sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
.
It exists in solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
form as small white crystals or white crystalline powder
Powder (substance)
A powder is a dry,thick bulk solid composed of a large number of very fine particles that may flow freely when shaken or tilted. Powders are a special sub-class of granular materials, although the terms powder and granular are sometimes used to distinguish separate classes of material...
, has a molecular weight of 258.23 u, and has a melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
of 185 °C. The stability of 5-methyluridine under standard temperature and pressure (STP) is very high.

